The command console in Windows systems, despite its DOS-like mode of operation, is one of the most powerful tools that allow you to perform many system configuration operations and fix some problems that are not available for regular Windows tools, even though most the actions performed in the system are duplicated in the console. Most, but not all. How to start the command line using different methods and with different access priorities will be discussed later. But first, let's see what this tool is for, because DOS support on Windows has ended a very long time ago.
What is the command console for?
Yes, indeed, the command console in terms of interface is clearly reminiscent of outdated and without DOS support. Even most of the commands used are borrowed from there. Nevertheless, some of them can be called unique in their own way. So, for example, a disk check (chkdsk with additional attributes) that is run on the command line works much better than a regular system tool called via the properties of a disk or partition. Although, by and large, it seems to be the same thing, nevertheless the difference is enormous.
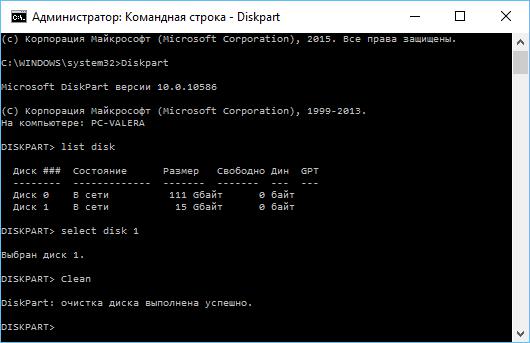
The same applies to the diskpart toolkit, which is indispensable in some cases when the system refuses to boot completely. And there are a lot of such examples. In addition, using the command line, you can revive the operating system when no other tools help (for example, Windows tools do not have an analogue for the sfc / scannow system file checker, and you can use it only from the command line). But let's see how to run the command line to perform a particular task. It should immediately be noted that in order to use some tools, you must have administrator rights and run the console in this mode (this will be discussed separately).
How to run the command line in XP and above in a classic way?
So, the first and easiest way. As you know, the "superuser account" appeared only in Windows 7 and since then it has been present in all subsequent modifications. In version XP, special privileges are not required, therefore, the launch can be done by the classical method, which is also used in systems of rank higher if additional rights are not required to execute a command.
Previously, access to the console could be obtained directly from the Start menu, where the standard program section was selected. To speed up access, the Run menu (Win + R) was used (and is still used), in which the desired cmd abbreviation was written.
In Windows 10, the start menu can be used, but only through RMB. There will be two items in the list for launching the console: normal launch and start on behalf of the administrator.
How to run the command line as administrator in the seventh modification of Windows?
Over time, this way to invoke the console has faded into the background, since Windows 7 and above did not provide sufficient rights to execute certain types of commands. Let's see how to run the command line with administrator rights in the seventh modification of the system.
To do this, use the same Run menu with the same command. However, in some assemblies of this operating system, for launch on behalf of the administrator, a special item was provided in the execution console located just below the field for the commands to be entered, on which it was necessary to check. Over time, Windows developers for some reason decided to get rid of it, and in versions above, starting with the necessary rights in this way became impossible. And how to run the command line on Windows 8 or 10 with the necessary privileges? As it turns out, there are some simple methods available even to a user with limited access rights to system tools.
Launching the console from the Task Manager
In the simplest case, you can use the standard "Task Manager" (taskmgr). How to run the command line as administrator? Elementary!
The creation of a new task is selected in the file menu, the cmd command is entered in the name field and the start item on behalf of the administrator is located below (a complete analogy to what was described for Windows 7).
Start from the "Explorer"
Now let's see how to run the command line using the usual Explorer.
If you open the file menu, it will immediately show the start point of the console. It contains an additional menu, in which, again, two types of start are installed.
Manual execution of executable file
Using the same “Explorer”, you can find the executable file of the program itself (all standard commands for the “Run” menu, used by default, correspond to executable files that are in the System32 directory, and 64-bit systems are also duplicated in the SysWOW64 directory )
How to run the command line from these folders? Yes, just like you open any other program file to start as administrator through RMB on the file. At the same time, it makes absolutely no difference from which directory the launch is made.
Run through search
Finally, let's see how to run the command line using standard search. This method is especially relevant for Windows 10.
Through RMB, on the "Start" button, if there is no link to the command line in the context menu, a search is selected and the phrase "command line" is entered (without quotes). The cmd line will appear in the search results, on which, through RMB, you need to start on behalf of the administrator.
Alternative tool
In principle, if the command line does not start or someone doesn’t like the tool itself, you can use the PowerShell shell that starts using exactly the same methods, but it has much greater capabilities compared to the usual command line. Sometimes even in the "Explorer" the file menu contains a link not to the command line, but to this tool.