During the Great Patriotic War , fighter aircraft made a significant contribution to the cause of victory. Despite the fact that the German air force was equipped with such powerful combat vehicles as the Messerschmitt Bf 109G and Focke-Wulf FW 190A, Soviet aircraft dominated the sky. The Wehrmacht air vehicles were significantly inferior to the USSR designers ’product, which was the La-5FN fighter.
What was inferior to German aviation?
When maneuvering vertically and horizontally, the Soviet La-5FN fighter was significantly better than the main German Messerschmitt Bf 109G fighter, because after several turns it could go into the enemy’s tail and make targeted fire. This was possible even with almost the same speed performance that these two competing models possessed.
The La-5FN fighter did not at all leave any chance of victory for the German Fokke-Wulf FW 190A. This model was inferior even in speed. The FW190A-8 fighter that appeared in the Wehrmacht's armed forces had no advantages over the La-5FN, which had high speed characteristics and good maneuverability, which, combined with the pilot's experience, ensured the victory of the Soviet aircraft in air battle. According to the instructions issued by the German command of the flight crew, the Soviet La-5FN fighter was considered the most dangerous enemy, in the battle with which the pilots of the Wehrmacht sides required exceptional attention and composure.
Start of creation
In 1941, the designer S.A. Lavochkin modernized the LaGT-3 aircraft - a fighter, which at that time had already ceased to meet all the requirements. There was an urgent need for a new model that can withstand modern air combat. The basis was taken LaGG-3.
It was decided to use the ASh-82FN rotor-motor group with a power of 1700 hp in the new machine. and synchronous twenty-millimeter cannons of ShVAK. At one time, designers such as A.I. tried to equip their aircraft with this engine. Mikoyan, S.V. Ilyushin, V.M. Petlyakov and A.S. Yakovlev. But best of all, he took root in the aircraft of S.A. Lavochkina.
Initially, the ASh-82FN engine did not fit into the fuselage of the aircraft, since it was developed for the M-105 model. But the designers managed to equip their product with a two-row star-shaped engine, so that in the LaGG-3 glider adopted as the basis, the design, geometry and dimensions remained unchanged.
Thanks to the ASh-82FN engine, the La-5FN fighter received improved maneuverability and speed, which especially affected the quality of the deep turn and vertical maneuvering. The presence of twenty-millimeter ShVAK cannons in Soviet La-5 made it possible for pilots to take an offensive, not defensive, position in air battles with German aircraft.
Application in the design of a new engine
The Shvetsov ASh-82F accelerated engine began to be used in fighters such as La-5F (which was reflected in the abbreviation of the aircraft) and La-5FN. The abbreviation of the latter means that it belongs to forced models with direct fuel injection.
According to legend, equipping this Soviet fighter with a powerful engine was caused by Stalin's discontent with the technical capabilities of the ASH-82 in afterburner mode. They were enough for a few minutes. At the direction of Stalin, one such engine was started in this mode and worked until it failed. The marked time showed a great motor resource - it exceeded 50 hours.
For combat fighters, these are good indicators. In the design of the La-5FN aircraft, this engine produced 1750-1850 hp. and supported afterburner mode for at least ten minutes. With a large supply of fuel, the period of such a regime could be extended.
Testing
The La-5FN fighter is one of the modifications of the La-5 aircraft. In the spring of 1942 in Lyubertsy they passed a comprehensive test, after which their design was approved. Testing was an impromptu air battle between the La-5FN and the captured Bf 109G-2. After the battle, conclusions were drawn: the Soviet fighter is ideal for working at low and medium altitude, which were the main aviation of the Eastern Front.
In April this year, the State Defense Committee gave permission to start mass production, as a result of which several La-5 modifications were released, among which was the La-5FN fighter. The photo below shows the design features of this aircraft.
What flights was intended for?
Air battles at low altitude are considered the main task for which the La-5FN fighter was designed, the device and its controllability made it the best model in Soviet aviation of those times. The effectiveness of the ailerons and climb rate of La-5FN exceeded the performance of the German FW 190A-8, which was significantly heavier and had low acceleration characteristics. But the enemy fighter had the opportunity, during maneuvers with dives at high speeds, to make a combat turn to attack the La-5FN fighter.
The controllability of the Soviet machine provided that by diving at high speeds it dodged attacks and itself went into an attack position in a gentle climb. This was possible, since the La-5FN, in comparison with the FW 190A-8, had better climb rates, which made it possible to overtake a German fighter on a steep slope. Among the recommendations given to pilots by instructors in flight schools in the event of a collision in the sky with the FW 190A-8, there was a ban on prolonged maneuvering and a decrease in speed. In addition, pilots should remember that the aircraft is not designed to perform long-lasting afterburners, since the engine power is designed for less than forty minutes.
Permissible speed
The aircraft could develop speed at cruising power and afterburner. They had various acceptable parameters and differed for the levels of land and sea.
- The La-5FN fighter above sea level in the afterburner could reach speeds of up to 520 km / h.
- At cruising power of this level, the speed was 409 km / h.
- Above ground was allowed afterburner at a kilometer distance. The speed was 540 km / h. It was acceptable for cruising power, but already at an altitude of 2400 meters.
- For a distance of 5 thousand meters, cruising capacity increased to 560 km / h.
The engine design, which was equipped with the La-5FN fighter, was not adapted for afterburning at a distance exceeding two kilometers. This is due to the characteristics of the air channel of the throttle, the passage section of which did not provide maximum motor power.
Fighter La-5 fn. Specifications
The plane was highly appreciated by both Soviet and German, as well as British aviation specialists. La-5FN fighter aircraft was considered the best among all the analogues of the Eastern Front.
- the cockpit was designed for only one pilot;
- the weight of the fighter was 3290 kg;
- dimensions (wing length and size) - 8.67 x 9.8 meters;
- wing area - 17.5 square meters. m;
- the load per wing per square meter was 191 kg;
- the design was equipped with one M-82FN engine with a power of 1750 hp;
- at an altitude of 6250 meters, the car developed a flight speed of up to 634 km / h;
- practical ceiling (maximum height) for the fighter - 10750 meters;
- average rate of climb - 16.6 m / s;
- tanks are designed for 460 liters;
- oil weight - 46 kg;
- two twenty-millimeter ShVAK guns were available in equipment of La-5FN;
- the fighter is capable of withstanding a bomb load of up to 100 kg;
- the aircraft was intended for distances not exceeding 930 km.
Fighter La-5FN. Device
- The design of this aircraft is characterized by direct injection of fuel into the cylinders.
- Instead of exhaust manifolds in the aircraft, individual nozzles were used, of which there were seven pieces on each side.
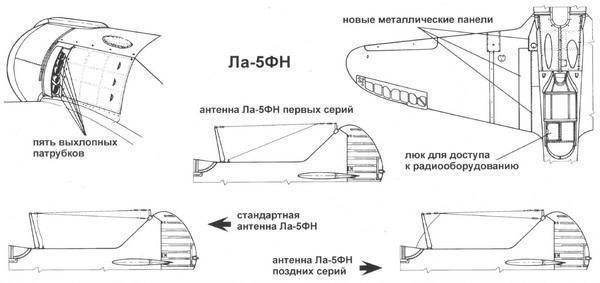
- The upper part of the hood contained a special air intake.
- Gargrot of the fuselage was lowered, the shape of the lantern was also changed (they were designed according to the Yakovlev AS Yak-9 aircraft).
- Using the instrument panel made it possible to carry out flights at night and in bad weather conditions.
- A number of improvements were made that affected the internal sealing and thermal insulation of the La-5FN cab. The fighter received an improvement in general aerodynamics.
- To improve visibility, the aircraft was equipped with a new lantern, which was specially supplemented for the emergency by an easily resettable movable part.
- The design was equipped with a tail wheel. It could be cleaned during the flight, and when taxiing self-orient.
- The two-wing wings had plywood sheathing and contained automatic duralumin slats, which, if necessary, could be deflected by 60 degrees using landing flaps.
- In the production of the fuselage and keel birch veneer was used. It was from several layers that were pasted over with a canvas.
- A welded motor frame made of steel pipes was intended for the installation of a two-row star-shaped engine ASH-82FN. The engine itself was located in a tank, which was built from light-duty duralumin panels. This provided free access to the motor during its repair or maintenance.
What was the plane trimmed with?
Most of the La-5 model warplanes had a solid-wood construction, which was constantly improved. Despite the fact that the tree had fire resistance, the strength of this material was not enough. In the La-5FN model, developers paid special attention to protecting the pilot and engine. The tree was replaced by duralumin and iron, which ensured the uninterrupted and reliable operation of the motor even with shrapnel hits. The fuel tanks were not armored, and this made them very vulnerable in the event of an attack. The wooden wing spar has been replaced by a metal one. For the safety of the pilot and fuel tanks, fighter glass began to use armored glass, the thickness of which for the front of the cockpit was 57 mm. An armored head (68 mm) was made from this material. The armor plate was made of steel 0.7 cm thick.
Arrangement of the cockpit
The upper hemisphere of the cab provided good visibility and all-round visibility. Front visibility was limited. This is due to the low landing of the pilot. The operation of the engine left a large tail of exhaust gases behind the aircraft. The pilot used a high-altitude oxygen system, which was a direct-flow diaphragm economizer (the idea was taken from the German economizer system).
If earlier the propeller pitch, radiators, shutters, trimmers, etc. were controlled by various manual rods - levers, which was a drawback, since during the battle the pilot was distracted by moving rods during acceleration, then everything was automated in La-5FN. The pilot could easily control all the units of the propeller group, firing and control the work of the guns, without breaking away from the battle. Only the power plant was controlled by levers, everything else was done by automation.
How does takeoff take place?
During fighter launch, permissible power fluctuations are observed in its engine. There is a slight distance to take off. When taking off, the tail of the fighter slowly rises. Piloting is currently difficult because the clearance from the machine screw to the ground is small.
Reasons for stalling
Any aircraft has its own characteristics and disadvantages when flying. One of the last is stall. The La-5FN fighter is not without this drawback. The characteristics of stalling by specialists have been analyzed and taken into account when creating the next, more advanced generations of aircraft. The reasons for the stall:
- Speed reduction. When removing the chassis and flap, the slats are issued at a speed of 200-210 km / h. With a decrease in speed, the effectiveness of ailerons decreases. Fighter sliding or braking at 180 km / h causes it to roll over to the wing, since at such a speed it is difficult for the pilot to dampen the roll. Stalling can occur when the landing gear and flaps are released in the event that the pilot continues to pull the lever towards himself, since the fighter reaches the angles that are most achievable for him.
- Performing steep turns. With the rapid deployment of La-5FN, air flows on the wing are disrupted. With an increase in speed, a decrease in the effectiveness of the ailerons is brighter. When the fighter accelerates to 320 km / h and reaches a height of 2400 meters, at which a full turn is performed for 30 seconds, the machine’s design receives a 2.6G overload. If there is a need to perform sharp movements with ailerons, then it is natural that the handle in the cockpit moves in the direction of rotation.
In order to prevent the aircraft from caving in, there are relevant instructions on how long it takes to fully bend at a certain height. So, for 2400 meters, 28 seconds are provided, and at a kilometer height, a turn should be performed in 25 seconds.
Flight stability
The fighter is characterized by high stability at all positions of the landing gear, flaps and during climb. The effort on the handle is negligible. They increase as the aircraft performs a deep turn. The rudder direction is considered satisfactory, but it may decrease due to the low speed at which the La-5FN fighter moves. Manageability of guns in such conditions is simple. When the rudder is deflected, the nose of the aircraft is raised or lowered. These vibrations, which are also called the Dutch step, are corrected by the movements of the steering wheel.
Completion of flight
The value of 200 km / h was considered optimal for the speed at which the La-5FN fighter was reduced. Landing was carried out at three points. Its implementation was simple on a flat surface. Otherwise, it was difficult to keep the car on the run. The reason for the difficulties was the uneven braking of the wheels. Very often, when landing, the fighter pecked its nose, as a result of which the screw could be damaged, since this aircraft had a limited distance between it and the ground. Significantly complicated the retention of the fighter pilot and strong gusts of side wind. In such situations, to cope using only the steering wheel was impossible. Therefore, when landing, they often resorted to wheel braking.
Despite the existing design problems, the La-5FN fighter was one of the best models of Soviet aviation technology, which, among its analogues, provided domestic aircraft with a dominant position in the skies of wartime and made a significant contribution to the victory.