Modern removable drives in the form of conventional flash drives and memory cards in order to protect confidential user information stored on them from external influences such as virus infection and spontaneous file rewriting allow you to use the protection setup in various ways. However, many of us are faced with situations where write protection (transferring files to the device) turns out to be active by itself, and at the most inopportune moment. And what if the flash drive is write protected? Unfortunately, not every user knows this, therefore, several basic methods will be proposed below that allow you to remove or bypass the device’s lock, as well as restore its functionality if there are software failures. But when choosing the preferred method for eliminating the problem, one should start from the root causes of this phenomenon. To start, let’s dwell on them.
How to unlock a protected flash drive: reasons for the appearance of a lock and methods for its deactivation
To begin with, write protection can have both hardware and software nature. Many models of flash drives and memory cards can be blocked by switches specially installed on them, similar to the way it was done on diskettes that have sunk into oblivion. It’s clear that when you connect the device to a computer and try to copy the necessary files to it, the system writes: “The flash drive is write protected” (not in this version, of course, but with a similar notification). Another thing is software or cryptographic protection installed for a removable drive. You just can’t take it off like that. The situation is even worse when a USB flash drive or card is blocked due to some malfunctions, which most often occur when the device is improperly removed from the corresponding port or card reader, and even when some actions are performed with the drive (formatting, copying, checking for errors, etc.). But the saddest thing is that sometimes even the file system can change. In this case, the drive seems to be recognized by the system, but the unreadable RAW format does not allow either writing information to the device or performing other operations. Finally, one of the reasons can be called a partial failure of the corresponding microcontroller with a “flush” of firmware. Despite the variety of possible situations and failures, eliminating problems with flash drives and memory cards in most cases can be quite simple, using either hardware or software methods.
Note: bypassing cryptographic protection, resetting passwords for removable drives, and issues related to installing or updating drivers for USB controllers will not be considered.
Hardware unlocking on flash drives and memory cards
So, consider the most trivial situation. You insert the device into the port and try to copy or move the necessary information to it, but the system reports that the medium (flash drive) is write-protected. What to do in such a situation? To get started, just inspect the device itself. It may well be that on one of the sides or under the cap you will find the same switch, next to which there may be a designation like Write Protect (by the way, Write protected protection is indicated in English-language system notifications).
On removable memory cards, such locks can also be present, but they are usually indicated as Lock. As already clear, to remove the protection, the lever (switch) simply needs to be moved to the inactive position and copy operations can be repeated.
File System Preference Issues
Now a few words about how to clear a write-protected flash drive. Consider another situation that many have encountered, but are unable to fix it. The point is that sometimes write protection can be set automatically if the file system on the drive does not allow to use the full amount of device memory when copying large files, limited to only four gigabytes. This is due only to the fact that the flash drive is formatted in a file system that simply does not support working with such sizes (FAT32 for drives of this type can sometimes be used by default). Thus, a situation arises when, when trying to copy or move to the drive, the system gives a warning that the USB flash drive is write-protected, although in fact the protection is not active. Simply saving a larger file over the allowable limit on the device is not supported.
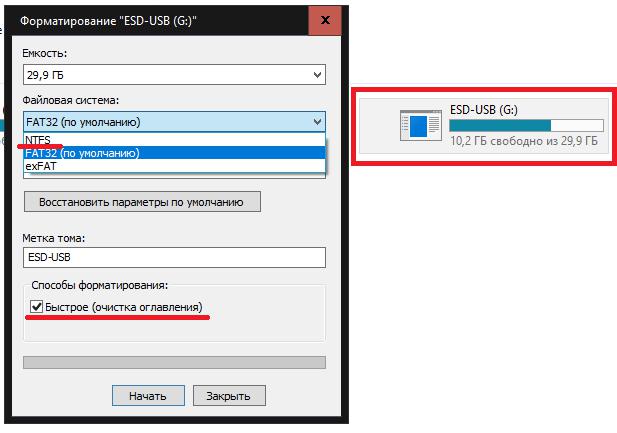
The solution will be the most common quick formatting, but with the choice of the NTFS file system. Such an operation can be performed quite simply using the standard formatting tool, access to which can be obtained in the same “Explorer” through the PCM menu on the selected device (disk). Similarly, the formatting command can be written on the command line or even in the job menu for executing program files, but for the average user the standard option is easier to use.
System registry actions
But what if the flash drive is write-protected, and the previous methods did not give the desired result? Many experts recommend checking the registry settings in which the corresponding setting in the form of a key with a ban can be set. If there is no key, you can create it yourself. This is done quite simply. The registry editor is called through the "Run" console or the file menu with the option to create a new task in the "Task Manager" using the regedit command, but always with administrator rights. In the HKLM branch, through the SYSTEM and CurrentControlSet sections, go to the Control directory and check the presence of the StorageDevicePolicies subfolder in it.
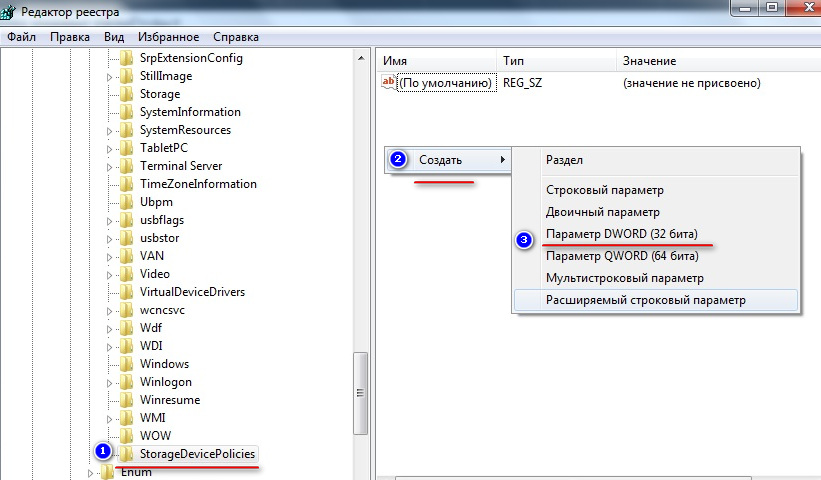
If it is absent, you need to create a section through RMB, assign it the specified name, and then create the DWORD parameter (32 bits) in the window on the right through the RMB menu, assign the name WriteProtect, and then enter the key editing with a double click and set it for it value in the form of zero. After that, you can close the editor, safely remove the USB flash drive from the port and be sure to restart the computer or laptop.
Note: if the corresponding section and key are in the registry, you just need to change the value of the specified parameter (usually it will be set to one).
Group Policy Setting
Now let's see how to remove write protection from a flash drive using the same group policy settings. Why similar? Only because the policy settings completely duplicate the registry keys, only the options installed in the registry have a higher priority (if you change the settings in group policies, you can change them in the registry, on the contrary - nothing).
The call to the Group Policy Editor is most quickly made through the Run console, in which the gpedit.msc command fits.
Using the computer configuration and administrative templates, you need to go to the system section located in the directory tree on the left, and in the right window find the write ban option for removable drives. Having entered editing by double-clicking on a line, then you need to set the disabled state for it. And, if changes are saved automatically in the registry, you need to save them in policies by clicking the corresponding button in the settings window. Upon completion of the installation of the required settings, as in the previous case, a complete restart of the computer system is performed.
How to remove the write protection of the flash drive via the command line?
In Windows-systems there is another quite powerful tool that works, however, only through the command line, which many novice users clearly do not like. Nevertheless, in some cases you can not do without it. You can start the console with the cmd command in the Run menu, but if there is no start item on behalf of the administrator, you can use the task creation in the "Task Manager", as described above, or run cmd.exe from the System32 directory with the appropriate rights.
After starting, the console will use the DISKPART applet toolkit. Its capabilities are quite wide, but in this case we are interested in unlocking and clearing the contents of a protected drive. The essence of removing protection is to remove the Read-Only attribute set for the device.
The sequence of commands looks as shown in the image above. By the way, this technique is also suitable for those cases when the micro-SD flash drive is protected from writing (a removable memory card, and not a regular USB-drive). The main thing here is to choose the right disk from all those that will be presented in the list.
Note: it is impossible to disable the read attribute, as is done for files and folders in the "Explorer", from the drive’s properties section using regular Windows tools.
If we talk about how to clear a write-protected flash drive using the same tool, after removing the read attribute, the operation can be supplemented by creating a primary partition and formatting with or without the type of file system. Some users may object that all the information on the drive will be destroyed. Yes it is. But to restore it after removing the protection can be quite simple, which will be discussed separately.
Specialized microcontroller recovery utilities
Often the error "Flash drive is write-protected" can also occur due to a partial failure of the respective controllers, for the operation of which the original firmware is responsible. Just it and needs to be restored. In principle, on any Internet resource of the device manufacturer you can find the appropriate utilities that allow you to perform such actions (JetFlash Recovery for Transcend devices, USB Flash Drive Recovery for Silicon Power flash drives, USB Flash Drive Online Recovery for Adata drives, Kingston Format Utility, etc. .).
If you don’t know the manufacturer exactly, there is nothing easier than using the small ChipGenius program, using it to identify device identifiers and using them to search for a utility to restore the firmware.
Low Level Formatting Issues
Separately, it is worth saying a few words about how to format a protected USB flash drive (microSD), if for some reason the above methods are not suitable for the user or have not taken the desired action. In this case, you can apply a cardinal method, which consists in performing the so-called low-level formatting. There are a lot of ways to do it, but the average user is best off using the HDD Low Level Format Tool utility, which, incidentally, is perfect for situations where something is wrong with the drive’s file system due to a change to an unreadable RAW format, or even when it is not visible in the operating system.
But it is this program - for formatting protected flash drives and for their intended purpose that works above all praises, and removable devices of any type are recognized, although Windows flatly refuses to identify them. Of all the software, this application is the most powerful and at the same time the simplest.
How to recover information after formatting?
What to do if the flash drive is write-protected, figured out a bit. Now a few words about the complaints regarding the removal of information from the media during formatting. You can restore it, but only with the use of appropriate programs. In most cases, ordinary users on the Internet are advised to use simple utilities like Recuva. But the functionality of such programs is very doubtful. If you really want to recover data on formatted media, you should not use them in any case. To date, nothing better than the R-Studio and R.Saver applications has been created. The second utility is simpler and is designed mainly for use by beginners.
But the first program has a clearly professional level and allows you to restore such old information (and even after full formatting) that users are simply amazed. And for removable memory cards, and for ordinary flash drives, it is simply irreplaceable, however, recovering files and folders on cards of all formats requires more time than performing similar operations with conventional USB-drives.
Troubleshoot viruses
In the end, it remains to add a few words about what to do if the flash drive is write-protected due to the effects of viruses. Unfortunately, such situations are very common. You can scan the media for threats even with a standard scanner installed in the system, or with any portable utility like KVRT, Dr. Web CureIt or AdwCleaner. The latter program is more designed to neutralize adware threats that relate to viruses only partially. You can determine the threat yourself even by the presence of the Autorun.inf file on the USB flash drive, if some portable program or installation distribution is not recorded on the media. The file itself may not be a virus, but it is an autorun component that redirects to an executable virus applet. However, manual removal of it will not be difficult, just use for such manipulations you need not standard deletion, but the command line. Especially when visually detecting a virus, it should be noted that such a file may have a hidden attribute, therefore, if there is access to the drive and the files in the same Explorer are displayed, first you need to enable the display of hidden objects in the view menu.