Uterine fibroids (a benign tumor) is one of the most studied and common gynecological pathologies. It grows from connective or muscle tissue and is located in the cavity or on the walls of the uterus. Most often, it is diagnosed in women of childbearing age (from 30 to 35 years). After menopause, uterine fibroids are rarely diagnosed. Most often it consists of multiple nodes of smooth muscle fibers, less often represents single formations and does not degenerate into a cancerous tumor, that is, it is always benign. This article will discuss the causes, symptoms and treatment of uterine fibroids.
Disease classification
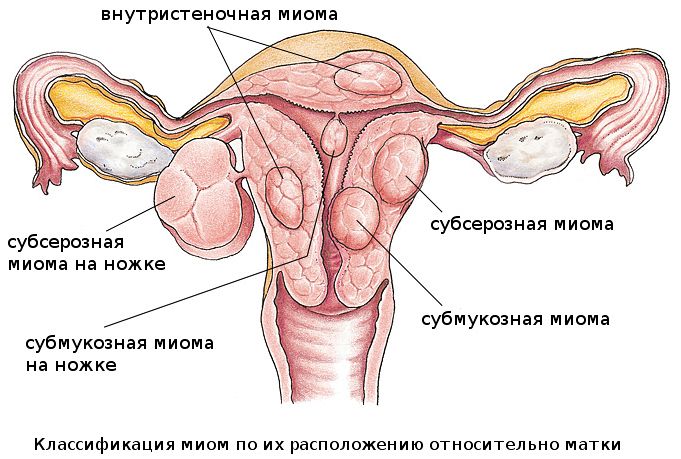
Symptoms and signs of uterine fibroids (a photo of its various types are presented below) depend on various criteria. Specialists adhere to a certain systematization of the disease.
At the location of the tumor:
- Intramural - located in the muscle tissue of the uterus, often changes the contour of the organ, reducing its internal volume. This type of tumor is more common than others.
- Submucous - located in the inner part of the uterus under its mucous layer, is rare.
- Subserous - located under the peritoneum. It is located outside the uterus and, when growing, presses on the peritoneum.
According to the size of the nodes:
- small - up to 2 cm;
- medium - from 4 to 6 cm;
- large - more than 6 cm. In some cases, tumors reach very large sizes.
In shape:
- Nodular - a smooth, rounded neoplasm. May contain one or many nodes of different sizes.
- Diffuse - there is no formed node, it is a vaguely enlarged muscle tissue. Appears as a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process.
Subserous and submucous uterine fibroids has several stages of development:
- 0 - nodes do not grow into the submucosal layer. The subserous node is located on the leg in the abdominal cavity, and the submucous node is in the uterine cavity;
- I - fibroids are half in the tissues of the organ;
- II - most of the nodes are located in the body of the uterus;
- III - there is no muscle tissue between the neoplasm and the mucous membrane.
A large variety of uterine fibroids suggests the need for an individual approach to each patient. Diagnosis of the disease is complicated by the absence of symptoms of uterine fibroids in the early stages of the development of the disease, therefore, an already neglected or complicated form is often found.
Causes of the disease
In medical practice, the exact prerequisites for the development of this benign tumor were not found. However, the dependence of its formation on hormonal coordination in the body was clearly revealed. Failure of ovarian function, which produces excess estrogen (female hormones), leads to the growth of muscle fibers. It is the dependence of uterine fibroids on the amount of sex hormones that often causes hormonal failure. This happens in the following situations:
- abortion - spontaneous and induced abortion;
- menstrual cycle failure - heavy and prolonged bleeding, pain;
- menopause - the restructuring of the body provokes the frequent appearance of a tumor in the late reproductive period or during menopause;
- stressful conditions are the cause of a malfunction of the ovaries.
In addition, the lack of regular sex and relationships without orgasm entail a greater likelihood of developing fibroids. The late onset of the menstrual cycle in girls, the inability to become pregnant and bear a child also indicate hormonal disruptions. As you can see, the symptoms and causes of uterine fibroids are inextricably dependent on each other. Although it is known that myomatous nodes appear in women with normal hormonal indices. In addition, there are other factors that provoke the disease. These include:
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, endometritis;
- injuries of the uterine cavity - when taking samples for diagnosis, surgery, abortion;
- endometriosis - proliferation of cells of the inner layer of the uterine wall;
- application for the protection of intrauterine devices;
- various diseases - diabetes, lack of thyroid hormones, hypertension;
- hereditary predisposition;
- late birth;
- lack of movement and obesity;
- decreased immunity.
Not the last role in the formation of fibroids is nutrition. The use of a large number of meat fatty foods and carbohydrates, as well as a lack of fiber, increase the level of female hormones. The intake of vegetables, fruits, cereals, grains and dairy products reduces the risk of developing a tumor. In addition, there are studies that neoplasms can appear during late first pregnancy, and women who have given birth are less susceptible to the disease.
What to look for
Uterine fibroids in the early stages of symptoms do not. In the future, the following symptoms are possible:
- Heavy menstruation. This is due to the fact that the emerging tumor interferes with the contraction of the muscles of the uterus. In addition, uterine bleeding during the menstrual period is possible. Heavy bleeding leads to anemia, therefore, in these cases, medical attention is needed.
- Pain syndrome. This symptom of uterine fibroids can be of any intensity. More often, pain appears in the lower abdomen and lower back. In case of circulatory disorders in the myomatous node, they occur suddenly. A large tumor that grows slowly during menstrual bleeding causes a symptom of uterine fibroids in the form of pulling pain. Growing in the mucosa, it leads to cramping. In any case, the appearance of pain signals that a certain time has passed since the onset of the pathology.
- Violation of the work of other organs. First of all, the rectum and bladder suffer. With tumor pressure, chronic constipation and polyuria occur on them. Turning to the clinic with such problems, you should visit a gynecologist.
- Infertility. The location of fibroids in the submucous layer of the uterus leads to a violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes, the passage of sperm is difficult.
- Headache, weakness and dizziness. These symptoms of uterine fibroids can occur as a result of a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells due to heavy bleeding.
- Pain in the heart. The development of the tumor tones the heart muscle, therefore, an increase in venous pressure is possible.

Most women with multiple myomas have complicated births. There is statistical evidence that the tumor with the onset of menopause decreases and even completely disappears, which means that the symptoms go away.
Clinic of the disease
Depending on the location and size of the uterine fibroids, symptoms may be as follows:
- Submucous location. The tumor node is located in the submucosa. In this case, various disorders are possible: heavy and prolonged menstruation, uterine bleeding, accompanied by anemia. Intense and cramping pains may appear when the myomatous node falls into the uterine cavity. In other cases, pain is not observed. Often such a myoma provokes infertility and does not make it possible to inform the child until the end of pregnancy.
- Subserous finding. The disease lasts for a long time without any symptoms. With an increase in the node in the lower abdomen, a symptom of uterine fibroids occurs - pulling pain. In case of malnutrition of large fibroids, severe pain appears. In this case, the patient is often mistakenly hospitalized in the surgical department with a diagnosis of acute abdomen. Bleeding with this location of the tumor does not occur.
- Mixed myomatous nodes. They are very difficult to diagnose. When the knot reaches a size of about 30 cm, inexplicable discomfort appears in the lower abdomen. Growing, the tumor begins to put pressure on the rectum, ureters, bladder, inferior vena cava. As a result, problems arise with bowel movements, urination, abdominal pain and shortness of breath begins.
Uterine fibroids has the following specific features:
- This is the most common gynecological disease of late childbearing age and the premenopausal period;
- never goes into a malignant tumor;
- may decrease, grow or disappear without treatment during menopause;
- able to develop rapidly or, conversely, very slowly;
- It has various symptoms or occurs without any signs.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines and instructs the patient using the following methods:
- Examination, palpation and bimanual examination on a gynecological chair.
- Ultrasound - makes it possible to determine the location of the tumor and its size.
- MRI and CT provide information on the location and magnitude of fibroids. However, they are rarely carried out due to the high cost of the study.
- Analyzes: blood - shows the general condition of the patient, urine - is taken to exclude diseases associated with the urinary system, smear - eliminates infections that are sexually transmitted.
- Hysteroscopy. It is performed using a special device equipped with a camera, which allows you to examine the uterine cavity from the inside. In addition, using a hysteroscope, you can take a biopsy and curettage.
Based on the data obtained, a final diagnosis is established and appropriate therapy is prescribed.
Conservative treatment of uterine fibroids
It is carried out with the help of drugs that stop the growth of the tumor, avoid the consequences and reduce the size of the nodes. For conservative therapy, the following indications exist:
- intramural and subserous tumors of the uterus;
- fibroid size up to 12 weeks;
- no acute manifestations;
- premenopausal period;
- contraindications for surgery.
With small sizes of tumors and the course of the disease without symptoms and signs, treatment of uterine fibroids involves the appointment of hormones and progestins.
What medications are prescribed
The doctor selects the hormonal medications that are most suitable for a particular patient after a full examination.
The most commonly used drugs are:
- Oral contraceptives combined action. With minor uterine myomas, the Yarina and Zhanin drugs stop the growth of nodes and reduce their size. The course of treatment lasts up to three months.
- Gestagens. They normalize the endometrium, but have little effect on the tumor. They are often used for mild symptoms of uterine fibroids and for the treatment of a submucous form of the tumor. These are drugs "Dufaston", "Norkolut", "Utrozhestan". Treatment lasts approximately two months.
- Intrauterine device (IUD) Mirena. It contains levonorgestrel, which is secreted daily into the uterus and stops the growth of the neoplasm, but does not affect the general condition of the body. The spiral is set for five years and protects against unplanned pregnancy.
- Antigonadotropins. Suppress the production of female hormones, which prevents the growth of the tumor. They are rarely used, since they have many side effects and a small effect. These include Gestrinon, Danazol.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone analogues. They are used to reduce the production of estrogen, which causes the growth of uterine fibroids. The course of treatment is from three months to six months. Use Zoladex, Buserelin and Diferelin.
Fuzzy ablation of uterine fibroids
This is the effect of ultrasound on the tumor. The procedure is a modern method of treating an ailment, performed in a medical institution for three to six hours. Ultrasound destroys the tissues of the node, disrupting blood flow and nutrition in them. As a result, the tumor stops growing and disappears. For the effectiveness of the procedure, it is necessary to accurately determine the symptoms and signs of uterine fibroids: the size, structure and position of the node. The advantages of the method are as follows:
- no blood loss and injuries;
- no anesthesia is required;
- carried out in an outpatient setting;
- preserves reproductive functions;
- it is applied at large and multiple nodes;
- has no complications and side effects;
- no relapse occurs;
- quick recovery.
Embolization of the uterine arteries with uterine myoma
This method (EMA) is recognized as one of the most advanced in the treatment of tumors, it has a good effect and does not require long-term recovery. When conducting an EMA, doctors use an X-ray chamber to insert a special catheter through a small incision at the site of the inguinal fold. Through the femoral artery, the doctor passes a catheter into the vessels of the uterus and introduces special microcapsules that can block the vessels of the tumor, thereby depriving it of food. After the procedure, the uterus is fully restored, fibroids die. Before surgery, a patient is examined to clarify the symptoms and signs of uterine fibroids, the size, number and location of nodes are evaluated. The procedure is performed in operating x-ray surgery. Staying in a hospital is no more than three days.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention for a benign tumor of the uterus is practiced in the following cases:
- large sizes of fibroids;
- the adherence of the tumor to the inner wall of the uterus (submucous or intramural type);
- the appearance of concomitant diseases;
- a sharp increase in the tumor;
- pregnancy obstruction;
- with necrosis of nodes, circulatory disorders;
- with pronounced symptoms and signs of uterine fibroids, manifested by bleeding and severe pain.
Doctors use several methods of surgical treatment of the disease, choosing the most suitable in each case:
- Laparoscopy - uterine fibroids are removed through holes in the abdominal wall. The device with a video camera is inserted into one, the instruments into the others.
- Hysteroscopy - performed through the vagina. The doctor uses a resectoscope with high-frequency alternating current or a laser beam to cut tissue. The destroyed myoma with a glucose solution is washed out of the uterus.
- Abdominal surgery - produce a horizontal incision about ten centimeters long just above the pubic joint. Subsequently, the incision line is invisible, as it is done in a skin fold. Surgical intervention of such a plan is performed when the symptoms of uterine fibroids are quite clearly expressed (photo of the operation is given above). Although doctors are primarily trying to preserve the organ, especially if the woman is in reproductive age.
- Robotic operation. It is carried out using a robot controlled by a surgeon. Such operations are rarely done in connection with expensive equipment.
Surgeons in the treatment of uterine fibroids prefer laparoscopy and hysteroscopy. Removal of the childbearing organ in a woman is carried out only in the most extreme case, when the symptoms and signs of uterine fibroids are pronounced. After such an operation, a woman will not be able to have children. The postoperative period provides for the restriction of physical activity and abstinence from sexual activity for a month and a half, observation by a doctor in order to notice possible complications in time.
Uterine fibroids: symptoms and treatment with folk remedies
Various phytoreceptions can be used to help conservative treatment to reduce or prevent the growth of uterine fibroids. Before you start using folk remedies, you should find out the type of localization of the nodes and consult with your doctor about the use of herbs. With subserous nodes, plugging with decoctions and oils is more often used, and the submucous location of the tumor involves the use of decoctions inside. Herbs are often used to strengthen the immune system, which have an antibacterial effect and help regulate the production of female hormone. For treatment, apply:
- Celandine. It is indicated for small neoplasms of a benign nature. Use flowers, leaves and roots. Alkaloids and essential oils contained in the plant inhibit fibroids, which leads to its reduction. In addition, celandine has anesthetic and hemostatic effect. Medication for the symptoms of uterine fibroids and alternative drugs helps to stop the development of the disease. A decoction of celandine is taken once a day before meals in half a glass, diluting it with the same volume of water. The course of treatment can be continued for several months. Fresh juice is squeezed from the plant and diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. Used for douching or tamping, which is carried out at night. The tool helps with pain and bleeding.
- Burdock. To prepare the broth, take a teaspoon of crushed dried burdock root and pour 0.5 l of water. Drink several times a day for up to four weeks.
- Calendula. Brew for the night a tablespoon of flowers in a glass of boiling water. In the morning, drink on an empty stomach. With the initial signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids, calendula infusion can stop the development of the tumor.
- Red brush. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and reduces the production of female hormones. Used in the form of a decoction: one and a half tablespoons of dried raw material is poured into 300 ml of water. Take half a glass once a day.
Herbal treatment sometimes gives good results, but do not wait for a miracle. .
:
– . , :
- ( , , );
- ;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- .
. . :
- , ;
- dull and aching by the nature of the pain in the lower abdomen, they give to the lower back or sacrum;
- constipation, pain during bowel movements;
- frequent urination.
Small fibroids in women during menopause, which do not increase and do not give discomfort, do not require treatment. Such a uterine fibroid, the symptoms and signs of which will disappear after the normalization of the hormonal background, will pass by itself. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy.
Prevention of uterine fibroids
To prevent the disease, the following measures should be taken:
- keep calm;
- eat well;
- constant physical activity is shown;
- bad habits should be abandoned;
- annually undergo preventive examinations;
- have regular sexual intercourse;
- plan pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding;
- timely treat gynecological diseases of an inflammatory nature.
In addition, for the preventive purposes of the appearance of uterine fibroids, it is necessary to regularly use dairy products. Scientists, having conducted research, came to the conclusion that, eating more than four servings of various dairy dishes per day, the risk of developing a tumor is reduced by 30%. It is also recommended to take trace elements and vitamins with antioxidant effects. With all the recommendations, the symptoms of uterine fibroids in women will never appear.