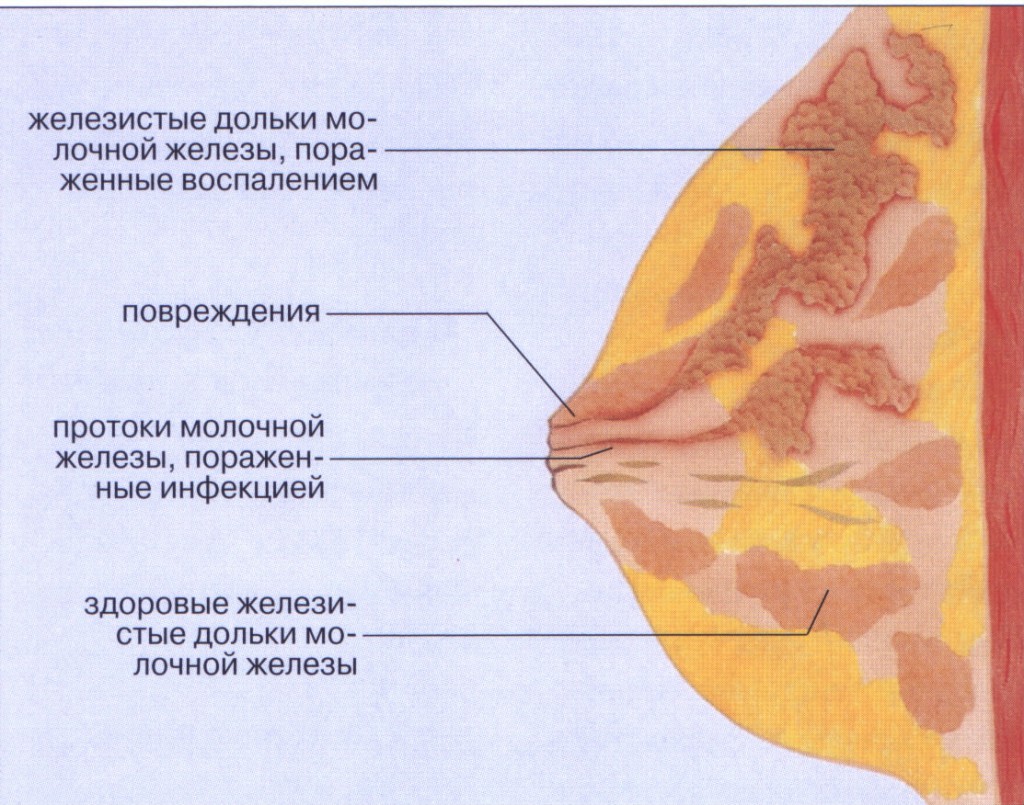
Mastitis is a disease associated with an inflammatory process in the tissues of the mammary gland. Most often, women who breastfeed are exposed to it in the first two weeks after childbirth. Signs of mastitis are: severe pain in the chest area, redness of the skin, thickening, swelling, chills, rapid temperature rise. As a result of the disease, a purulent abscess may occur. The reason is the activity of microbes from the group of staphylococci and streptococci that enter through the damaged nipple. The infection is transmitted from a child or through clothing and household items. The disease sometimes occurs after infection in the postpartum period of the genital organs, i.e. as a secondary infection.
Why does mastitis occur?
The causative agents of mastitis are staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. Infection is possible both inside the hospital and outside it. Bacteria can enter through poorly processed laundry, care items, from hidden bacteria carriers (medical personnel, roommates, relatives). Another source of the disease may be the baby. Sometimes he develops inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, pustular lesions of the dermis. Once on the skin of the breast, bacteria do not cause disease. This requires the presence of certain factors in order for mastitis to develop:
- structural features of the nipples - retracted flat, lobed;
- mastopathy - the growth of glandular tissue associated with hormonal failure;
- the presence of gross scars after surgery;
- abnormal course of pregnancy - premature birth, threatened abortion, toxicosis;
- deviations during childbirth - large blood loss, manual separation of the placenta, large fetus;
- complications after childbirth - exacerbation of chronic diseases, bleeding, fever.
As a result of these phenomena, the resistance of tissues to the harmful effects of bacteria decreases with reduced immunity after childbirth and the presence of hypovitaminosis. There is a favorable soil for the development of the disease.
Causes of mastitis
Any inflammation, including the mammary gland, is caused by the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the body. In a woman, during the period of breastfeeding, this process can occur for the following reasons:
- Lactostasis is the stagnation of milk in one or more areas of the gland. Without urgent measures to eliminate it, uninfected, serous mastitis occurs, which subsequently, with the penetration of microbes from the surface of the dermis, turns into purulent, spreading inside. Stagnant milk is an excellent medium for the development of pathogens.
- Cracks in the nipples. The causative agents of infection penetrate through skin defects. From the wound surface, cracks, bacteria enter the lymph, from which the glands spread through the vessels.
- The presence of chronic diseases. Diseases such as sinusitis, pulpitis, tonsillitis are a constant source of infection. With blood flow, it can enter the mammary gland and cause inflammation.
- Weakened immunity. With the restructuring of the body during pregnancy and the postpartum period, a decrease in the protective functions of the woman’s body and fertile soil for the development of the disease occur.
Diagnostics
For any signs of mastitis, such as pain in the chest, tightness, fever in a nursing mother, you should consult a doctor: mammologist, surgeon or gynecologist. The doctor listens to complaints, conducts an external examination of the organ and, if necessary, prescribes the following studies:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- cytological (white blood cell count) and bacteriological (bacterial content in 1 ml) milk assessment;
- analysis of the secret of the female breast - the acidity of milk with inflammation increases;
- Ultrasound - used to diagnose mastitis of destructive (purulent) forms to determine the exact location of the affected area;
- thermography - shows a picture of the distribution of temperature fields;
- mammography;
- puncture - used with subsequent analysis of purulent discharge.
Based on all the diagnostic tests performed, the patient is prescribed a course of therapy.
Systematization of mastitis
The classification of the disease has several directions and is very confusing. It causes a lot of controversy among medical representatives. Mastitis - inflammation of the mammary gland - is divided into two types:
- infectious;
- non-infectious.
Next comes the classification, depending on the time of its occurrence, depending on the functional activity of the mammary gland, two forms are recognized:
- lactational - after childbirth;
- non-lactational - before childbirth.
With the course of the inflammatory process, it is divided into:
By the nature of inflammation, mastitis happens:
- serous - more common in primiparous women;
- infiltrative;
- purulent - has its own classification;
- abscessed;
- phlegmonous;
- gangrenous.
Symptoms of mastitis in a nursing mother
With the development of inflammation, mastitis passes through the following stages: serous, infiltrative, purulent. After this, three development options are possible:
- abscess - a limited purulent focus;
- phlegmon - the entire mammary gland is inflamed;
- necrosis - the death of tissues.
Signs of the disease depend on the stage of development of mastitis. The inflammatory process begins with a sharp rise in temperature. Weakness appears, chills and profuse sweating begin. An enlargement of the breast occurs. It becomes denser, severe pain occurs, the chest bursts as if. The place where the inflammation is located becomes pinkish on the outside. With lactational mastitis, against the background of milk inflammation, less is produced. The appearance of cracks in the nipples of a woman contributes to the infection entering the gland. The lack of treatment at this stage of the disease leads to a sharp deterioration in the patient's condition.
The high temperature continues to hold, redness of the skin in the inflamed area becomes brighter. On palpation, the affected area can be clearly defined. Phlegmonous stage is characterized by a sharp increase in the volume of the mammary gland. The inflamed dermis becomes cyanotic. Lymph nodes located near the sore chest become inflamed. The process continues further and the gangrenous stage of mastitis sets in. To the existing symptoms of mastitis in a nursing mother, bloody blisters and areas with dying skin are added. Edema begins to capture areas of the body located near the chest. With mastitis, the development of general sepsis, inflammation of the lymph nodes and the formation of fistulas are possible.
Therapy
The treatment of the disease should begin with the appearance of the very first signs - chest fullness, slight swelling or cracking on the nipples. To do this, you should immediately consult a doctor. Depending on the condition of the nursing woman, he will give recommendations, prescribe treatment, and in a more advanced case, he will write out directions for examination. In addition, a general blood test will require a study of breast milk for the content of pathogenic bacteria in it. The issue of continuing breastfeeding is immediately resolved. In the inflammatory process, pathogens may be contained in breast milk.
In order to avoid infection of the baby, doctors recommend transferring the child to artificial feeding until the mother recovers completely, especially since she will be prescribed a course of antibiotics to treat mastitis. Only a doctor can choose the right medicines, after receiving the results of tests on the sensitivity of bacteria to drugs. Drugs are prescribed in the form of droppers, injections or orally. During treatment, mommy needs to constantly express milk so that stagnation does not form again. Sometimes the doctor prescribes hormonal drugs to reduce lactation and facilitate the expression of milk. Treatment of mastitis in the purulent stage is carried out in a hospital. In some cases, the patient is shown only surgical intervention. Supportive therapy is also carried out. A woman is prescribed drugs to increase immunity and reduce general intoxication. After completing the course of treatment, the patient again passes tests for the study of breast milk. If there is no infection in it, the baby can again be breast-fed. After the course of treatment for mastitis, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the mammary glands.
Mastitis surgery
Conservative treatment in some cases does not give a positive result, the disease passes into a purulent stage. In this case, an urgent surgical intervention is indicated, which is carried out in-patient. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. After opening the abscess, purulent-necrotic tissue is removed and the cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution. The incision is closed with a primary suture by installing a drainage-washing system. It allows you to flush the wound with antibacterial agents and allows the outflow of fluid. Washing ends after the localization of the inflammatory process. After the surgical period, antibiotic treatment with antibiotics and supportive therapy are performed.
Antibiotics
When diagnosed with "lactational mastitis" with the manifestation of signs such as a serious condition and high body temperature; the presence of nipple cracks and pain in the mammary glands; milk is expressed, but the condition has not improved, a course of antibiotics should be started, this is done in order to prevent an abscess. The treatment regimen and the drug itself are selected by the attending doctor individually for each patient. On average, antibiotic treatment for mastitis lasts a week.
For this, drugs of the following groups are used:
- Penicillins - drugs with a wide spectrum of action, have rapid absorption. They have side effects: disruptions in the digestive tract, skin reactions. Partially penetrate into mother’s milk, take with caution during breastfeeding.
- Cephalosporins - are characterized by rapid absorption from the stomach, have an effect on the affected tissue. Excreted in urine. May cause an allergic reaction, headache. It enters into mother’s milk in a small amount, the risk for the baby is minimal.
- Macrolides - after taking the drugs by a nursing woman, their high concentration in breast milk is observed. The negative effects of drugs of this group of antibiotics on the baby's body do not have.
- Aminoglycosides - drugs are not used when breastfeeding and pregnant women. Treatment with antibiotics for mastitis from this group is possible if the baby is temporarily transferred to artificial feeding.
- Fluoroquinolones - when taking these drugs, breastfeeding is not recommended. They are absorbed into milk and have a certain toxicity.
Only the doctor selects the necessary antibiotics for treatment of the nursing woman. He will prescribe a specific course of therapy and give advice on breastfeeding.
Another form of mastitis
Non-lactational mastitis refers to it, when inflammation of the mammary gland does not occur during the period of breastfeeding. The reason for its occurrence is usually associated with:
- hormonal changes during puberty in adolescents or in women during menopause;
- weakened state of the immune system: chronic infectious diseases, oncological processes, diabetes mellitus;
- previously performed breast surgery.
The disease proceeds with less pronounced signs of mastitis than in women during lactation. There is pain, a slight swelling of the mammary glands and a slight increase in the lymph nodes in the axillary region. When contacting a doctor during this period, the disease is easily treated. Under certain circumstances, the process can go into a purulent form. In this case, the general condition worsens, the body temperature rises sharply, the pain intensifies, the area of the mammary gland becomes bright pink. Urgent medical attention is needed. Otherwise, a ripened abscess of non-lactational mastitis can open, forming a fistula with the release of pus. The treatment of the disease is carried out depending on the stage of the disease both by conservative methods and with the help of surgical intervention.
Physiotherapy
In the treatment of the initial form of mastitis, physiotherapeutic methods are used that increase lymph and blood flow in the stagnant area, have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and decongestant effects. They do not hurt, and do not cause discomfort. The following procedures are mainly used:
- Ultrasound. It penetrates deep into the tissues and gently massages the tissues of the mammary gland. The duration of the session is 3-5 minutes, the course of treatment is up to 10 sessions, improvement occurs after three procedures.
- Pulse magnetotherapy. Inductors are placed on the affected area on both sides of the mammary gland, the impulses from which affect the seal. Sessions are carried out daily, up to 10 days, for five minutes.
Physiotherapy is carried out in addition to the main course of drug therapy.
Folk remedies
The disease is characterized by the rapid development of inflammation. A woman, having noticed signs of the disease, should immediately consult a doctor. You should not start treatment with alternative methods, although there are a great many of them. In this case, you can simply lose time and aggravate the development of the disease. The treatment of mastitis with folk remedies should not be completely denied, but it should be started after consultation with a doctor, using in conjunction with medications. In the treatment of the disease, the following popular drugs have proven themselves well:
- Dill seeds. Their unique chemical composition contains vitamins and minerals: zinc sulfur, phosphorus, selenium, vitamins B, C, A, which will help recovery. A decoction is prepared from them: a tablespoon of seeds in half a liter of water. Use three times a day in small portions.
- Honey. On the first day of the onset of signs of the disease, apply a honey compress to the chest. It will help relieve pain and facilitate the process of expressing milk.
- Cabbage. It has long been used to treat various diseases. Fight a fresh leaf of cabbage from the inside with a culinary hammer until the juice comes out. Attach it to an inflamed area and loosen tightly. It will relieve fever and anesthetize.
- Burdock root. It contains many vitamins and minerals. It has anti-inflammatory and mild analgesic effects. A decoction is made from it: a tablespoon of crushed raw material is poured with a liter of boiling water. The prepared potion is drunk three times a day in small portions.
- Beet. The raw pulp is wiped on a grater and a compress is made if cracks in the nipple occur. It promotes wound healing, prevents inflammatory processes.
Using natural medicines proven over the years in conjunction with medications and ongoing medical advice, signs of mastitis can be cured quickly.
Breast massage
At the first symptoms of mastitis, massage has a good effect. To conduct it, you need to wash and dry your hands well, while the nails should be cut short. First of all, you need to perform preparatory exercises. To do this, make light movements with the fingertips from the edge of the chest to the center in the form of a spiral. Then find areas for massaging. To do this, they feel the chest, and determine the seals and painful areas. Each seal is massaged separately. Movements are made clockwise from the center to the periphery. Then they proceed to work on the entire mammary gland. Massage with mastitis begins with the axillary region. The duration of the procedure is no more than five minutes. It should be remembered that all movements should be smooth and not cause pain. It is advisable to do the procedure regularly to obtain the desired effect.
Measures to eliminate milk stagnation
Some women, feeling pain associated with stagnation of milk, begin to panic. They are lost and do not know what to do with mastitis, what to do, to whom to turn for help. Inflammation develops very quickly, especially in the evening and at night, so you should immediately consult a doctor. Signs of the disease:
- there was a seal, the mammary gland increased;
- there is a sharp throbbing pain in the place where the inflammatory process occurred;
- severe redness of the skin in the area of inflammation;
- the temperature with mastitis rises sharply to forty degrees;
- general weakness, aches and malaise occurs;
- headache.
The same picture of the patient's condition is also characteristic when lactostasis occurs - a disease preceding mastitis. The only difference is the lack of temperature. Due to the seriousness of the pathology, you should contact the hospital’s emergency room in the evening and at night. ? – , -. , . .
. . :
:
:
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- seek the advice of your doctor.
In order to prevent mastitis, it is necessary to lead an active lifestyle, maintain the immune system, take water procedures twice a day, and eliminate the foci of infection on time. Mastitis is a serious disease that can harm the health of the mother and leave the baby without breastfeeding, which he needs so much in the first days of life. The fight against the disease must be started along with the first signs of its manifestation, and the best thing is to try to prevent it.