The main disadvantage of most internal combustion engines is the mismatch of the rotational speeds of the wheels and the flywheel. An additional minus is the fact that the maximum torque in power units is achieved only in a small range of revolutions. At maximum speeds of the flywheel, maximum power is gained.
Transmission systems and its various types are used so that the engine can operate in optimal mode under different conditions. Most cars use a manual gearbox, the device and the principle of which is not known to every motorist.
Gearbox operating principle
The design of the gearbox includes gears that enter and go out of gear by the will of the driver, thereby forming gears with different gear ratios.
A manual gearbox in a car functions only with the clutch system, respectively, at the time of gear shifting, the transmission and engine are switched off. At the moment the gear changes, a large torque cannot pass through the transmission. This function is achieved by the gearbox.
Gear wheels and gearbox shafts
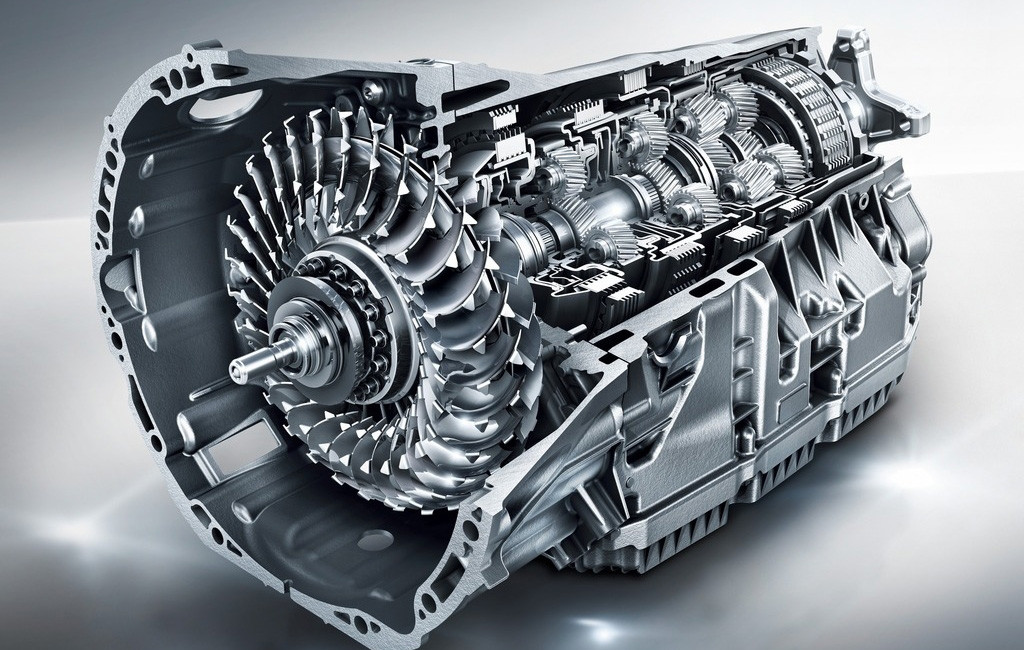
Classic manual transmission consists of a set of shafts assembled in a crankcase or housing. Using bearings, the gearbox shafts rotate. Gears are attached directly to the shafts of the gearbox. The design of the gearbox may vary depending on the number of installed shafts and be two-shaft or three-shaft.
Three Shaft Systems
Rear-wheel drive cars are equipped with similar transmissions. The general arrangement of gearboxes of this type includes special wheels and synchronization devices coupled with a reversing gear designed for reversing.
A mandatory part of the design of the gearbox are shafts: primary, secondary and special located between them.
The main shaft is connected directly to the car engine through a clutch system; secondary, or slave, operates with a universal joint. The energy of rotation from the drive shaft to the driven shaft is transmitted thanks to the intermediate shaft.
Transmission Design Features
In most cases, the primary and secondary shafts in the gearbox are installed one after the other. The support of the driven shaft is made on the basis of the bearing of the drive shaft of the gearbox located in the rear of the drive shaft. A rigid connection between these shafts is not provided for by the design of the gearbox, so that both shafts can function independently of each other.
The intermediate shaft in the transmission design is located between the drive and driven shafts, each of which is equipped with gears. The teeth on such wheels are oblique, which reduces the level of vibration and noise during the operation of the system.
The drive shaft is equipped with only a single gear wheel transmitting torque to the intermediate shaft. The location of the gears of the secondary, or driven, shaft allows them to rotate freely, but they cannot move along the longitudinal axis. To activate the transmission, they are blocked using a special locking device: in this position, they transmit rotational energy from the shaft.
The gears mounted on the intermediate shaft are located opposite each of the wheels of the primary and secondary shafts. They are permanently engaged with other gears of the structure. Torque is always transmitted from the primary shaft to the primary shaft. The principle of operation of the gearbox lies in the inclusion of a specific gear by connecting a specific gear located on the driven shaft.
Transmission Shift
The gearbox does not imply the presence of gears and shafts alone: special clutches are included in the design. Each of them has a design different from gears and is attached to a specific shaft, rotating with it. In this case, their movement along the longitudinal axis is possible.
On the side of the gears of the driven shaft directed to the couplings, special forks are located. Similar parts are located directly on the couplings themselves.
When the driver selects a gear lever with a special drive, the forks moving the clutch are actuated. In this case, the locking system does not allow activating several gears at once, which is quite possible provided that the lever turns on two sliders at once. The locking mechanism stops the sliders in the neutral position at the moment when the third slider begins to move. Similarly, the simultaneous operation of two gears at once is excluded.
The crowns of the clutch and the gear needed for shifting the gear are connected, while the clutch rotates together with the shaft. After connecting to the gear, the latter locks and their subsequent joint rotation, as a result of which the torque is transmitted from the gearbox to the wheel drive.
Synchronizers
In addition to the components listed above, additional parts are included in the gearbox. The principle of operation of the gearbox described above is accompanied by vibrations, loud noises and shocks, coupled with the need for the driver to independently determine the moment of operation of the clutch and gear at the same speed.
Modern gearboxes use special clutches called synchronizers. Their main task is to equalize the speed of rotation of the clutch and gear wheel and to eliminate wheel lock.
Twin-shaft gearboxes
Such transmissions have the same design as the three-shaft gearbox, with one exception: they do not have an intermediate shaft. Such boxes are installed on cars with front-wheel drive. The rotation of the shafts is carried out in parallel axes, while the torque from one of the gears is transmitted to the gear driven by the synchronizers. The principle of operation of the two-shaft system is the same as in the three-shaft system, however, direct transmission is impossible in it.
Transmission device for VAZ cars
Most VAZ cars are equipped with five-speed mechanical transmissions with a two-shaft system equipped with a differential. The input shaft is equipped with gears from 1 to 4 gears, the 5th gear gear is removable. They are interconnected by driven gears.
One of the main advantages is the easy repair of this type of gearbox, since it is a modernized version of the four-stage analogue with standardized parts.
From manual transmission to automatic
Many novice motorists are of the opinion that an automatic transmission is a gearbox and a torque converter.
The torque converter is a system of two blade mechanisms: a turbine and a centrifugal pump. Between them is a guide reactor. The engine crankshaft is rigidly fixed to the pump wheel. A similar connection exists between the turbine wheel and the gearbox shaft. The reactor can rotate or be blocked by an overrunning clutch, depending on the specific mode of the internal combustion engine.
The automatic transmission has a more complex design. Most of the generated energy is directed to pumping oil and operating a pump that creates oil pressure in the channels. Efficiency of automatic transmission is lower than mechanical.
Oil flows transmit rotational energy by pumping them to the turbine. The blades of the pump and turbine have a specific geometry, which improves fluid circulation. Since there is no rigid coupling between the gearbox and the engine , the engine can be stopped even when the gear is engaged.
Planetary gears
The gear ratio changes when some parts rotate and others are rigidly fixed. The torque converter shaft transmits torque and, accordingly, rotation to planetary systems.
The main difference between the machine and the mechanics is that any gear is switched on without interrupting the power flow: when one gear is deactivated, another is activated. Such a transition is carried out without jerking, which can be felt by the driver during the ride.
Transmission Types
Excluding the standard mechanical transmission, there are other types of gearboxes - robotic, CVT and automatic.
- CVT gearbox - continuously variable. The main details of its design are sliding pulleys and a trapezoidal belt connecting them. The main advantage of such a transmission is the maintenance of the optimal operating mode of the car. As additional, it can be noted cost-effectiveness, smoothness of motion and dynamic acceleration. Compared to automatic transmission, the variator design is much simpler, respectively, and repairing a gearbox of this type is easier. Despite its advantages, the CVT is inferior to the mechanical in efficiency and dynamics. In addition, the variator is not compatible with a powerful engine, since its belt is characterized by low durability. Maintenance and repair of such a transmission is an expensive pleasure, and therefore it is easier to replace. In addition, in order to move off and move back, the installation of additional mechanisms is required.
- The gearbox - robot device is practically no different from the mechanical one: torque is transmitted to the transmission from the engine through a single-plate clutch. There is also a nuance: the processes of gear shifting and engaging / disengaging the clutch in a robotic transmission are fully automated. Thanks to this, such a gearbox greatly simplifies the process of driving: the driver does not need to manually shift gears. Additional benefits include light weight and low cost. However, she also has its drawbacks: the lack of smooth operation and the delay in shifting gears. At high speeds, gear changes can be accompanied by jerks and jerks. It will not be possible to correct the situation in manual mode, since the clutch control is fully automated and carried out by electronics. In clarity and accuracy of gear shifting, a robotic gearbox is significantly inferior to an automatic one. In addition, cars equipped with a robotic transmission, at the beginning of the movement, roll back slightly. Taking into account all these shortcomings, robotic boxes are most often installed on budget models of vehicles.
The key to the efficient operation of the transmission is the optimum oil level in the crankcase. Identify it and suggest how to check the gearbox oil, a car service specialist or the information specified in the vehicle’s manual will help.
Main malfunctions and repair of gearbox
Operational repair of the transmission may be required in the diagnosis of the following most frequently encountered malfunctions: spontaneous disengagement and difficult gear shifting, oil leakage, overheating of the box or external noise in operation.
Difficult inclusion of transmission can be triggered by the following factors:
- deformation of the fork or gear lever;
- spherical joint sticks;
- a tight stroke of the stem due to clogged nests, which jam jam blocking crackers.
Transmissions can be switched off spontaneously, and the reasons for this may be different:
- wear of nests or balls of rods;
- wear of synchronizer rings or clutch teeth;
- lowering the elasticity of the retainer springs.
Deterioration of synchronizers, gears or bearings, play of shafts, too dirty oil or its low level can provoke appearance of outside noise during transmission operation.
Many owners note an oil leak from the gearbox, which may be caused by insufficiently fastening of the crankcase cover, wear of gaskets or shaft seals. A low oil level in the box will cause it to overheat, which can cause the transmission to fail completely.
Repair of gearboxes in all of the above cases is carried out either using special repair kits, or by replacing damaged or defective parts.