Cables used to build the infrastructure of computer networks are available in a wide range of varieties. Among the most popular - coaxial, twisted pair, as well as fiber. What is the specificity of each of them? What are the features of mounting the most common - twisted pair?
Cable Types: Coaxial
Among the most historically earliest types of cables used in network connections is coaxial. In thickness, it roughly corresponds to a network power cable for a computer, designed to work with a 220 V outlet.
The structure of the coaxial design is as follows: in the middle is a metal conductor, it is shrouded in thick, most often plastic insulation. On top of it is a braid of copper or aluminum. The outer layer is an insulating shell.
The network cable of the type in question can be connected by:
- BNC connector;
- BNC terminator;
- BNC-T-connector;
- BNC-barrel-connector.
Consider their specifics in more detail.
The BNC connector assumes placement at the ends of the cable; it is used to connect with T- or barrel-connectors. The BNC terminator is used as an insulating barrier to prevent signal movement through the cable. The correct functioning of the network without this element is in some cases impossible. Connection via a coaxial type network cable involves the use of two terminators, one of which requires grounding. The BNC-T connector is used to connect the PC to the main trunk. There are three slots in its structure. The first is connected to the computer’s network card connector, with the help of the other two, the ends of the trunk are connected. Another type of coaxial cable connector is the BNC barrel. It is used to connect the different ends of the highway, or to increase the radius of a computer network.
Among the useful features of coaxial designs - there is no problem solving the question of how to connect two network cables of this type. It is enough to ensure reliable contact of the conductive conductors, of course, subject to the technology of pairing insulation and screen mesh. However, the coaxial cable is quite sensitive to electromagnetic interference. Therefore, in the practice of building computer networks, it is now rarely used. However, it is indispensable in terms of organizing the infrastructure for transmitting television signals - from dishes or cable providers.
Twisted pair
The most likely common computer cables today are called twisted pair cables. Why such a name? The fact is that in the structure of a cable of this type there are pairwise conductors. They are made of copper. The standard cable of this type includes 8 cores (total, thus, 4 pairs), but there are also samples with four conductors. The so-called pinout of a network cable of this type (correlation of each core with a particular function) involves the use of insulation of a certain color on each conductor.
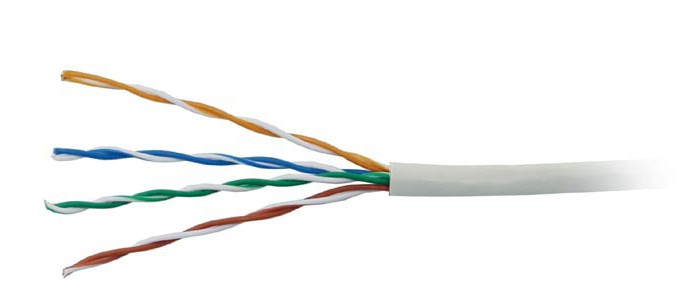
The external insulation of the twisted pair is made of PVC, which provides sufficient protection for the conductive elements from electromagnetic interference. There are shielded cables of this type - FTP and STP. In the first, the foil performing the corresponding function is located on top of all cores, in the second - on each of the conductors. There is an unshielded twisted pair modification - UTP. Generally, foil cables are more expensive. But it makes sense to apply them only if there is a need for high-quality data transmission over a relatively large distance. For home networks, an unshielded version of a twisted pair cable is quite suitable.
There are several classes of the corresponding type of structures, each of which is designated as CAT with a number from 1 to 7. The higher the corresponding indicator, the better the materials that provide signal transmission. Modern network cables for a computer for exchanging data via Ethernet protocol in home networks imply that the elements correspond to CAT5 class. In connections where twisted pair is used, connectors are used that will be correctly classified as 8P8C, but there is also an unofficial name for them - RJ-45. It can be noted that cables corresponding to at least CAT5 and CAT6 classes can transmit data at speeds close to the maximum for the type of structures under consideration - up to 1 Gbit / s.
Optical fiber
Perhaps the most modern and fast network cables for a computer are fiber optic. In their structure there are light-conducting elements made of glass, which are protected by durable plastic insulation. Among the key advantages that these network cables for a computer have are high immunity to interference. It is also possible to transmit data over a distance of about 100 km through optical fiber. The connection of the cables of this type with devices can be carried out through various types of connectors. Among the most common - SC, FC, F-3000.
What does this high-tech network cable for a computer look like? Photo fiber optic design below.
The intensity of the practical use of optical fiber is limited by the rather high cost of the equipment necessary for transmitting data through it. Recently, however, many Russian providers have been actively using this network cable for the Internet. According to IT experts, with the expectation that the appropriate investment will pay off in the future.
The evolution of cable infrastructure
Using the three marked types of cables as an example, we can trace some evolution in the aspect of building the infrastructure of computer networks. So, initially, when transmitting data via the Ethernet standard, it was precisely coaxial designs that were involved. At the same time, the maximum distance to which a signal could be sent from one device to another did not exceed 500 meters. The maximum data transfer rate over the coaxial cable was about 10 Mbit / s. Using twisted pair cable has significantly increased the dynamics of file sharing in computer networks - up to 1 Gbit / s. It was also possible to transmit data in duplex mode (one device could both receive signals and send them). With the advent of optical fiber, the IT industry has been able to transfer files at a speed of 30-40 Gbit / s or more. Largely thanks to this technology, computer networks successfully connect countries and continents.

Of course, when working with a PC, many other types of cables are used when installing computer networks. Theoretically, for such purposes, you can use, for example, a USB cable, although this will not be very effective, in particular, due to the fact that within the USB standard, data can be transmitted over a short distance - about 20 m.
How to connect a twisted pair
Twisted pair, as we noted above, is today the most common type of cable when designing computer networks. However, its practical use is characterized by some nuances. In particular, they reflect such an aspect as the network cable pinout, which we mentioned above. It is important to know how to correctly locate the cores in the area of their contact with the RJ-45 connector. The procedure by which twisted pair is connected to the corresponding element is called crimping, since during its implementation a special tool is involved, which involves the force impact on the structure.
Crimp nuances
During this procedure, the connectors are securely fixed at the ends of the twisted pair. The number of contacts in them corresponds to the number of cores - in both cases there are 8 pieces of such elements. There are several schemes in which twisted pair crimping can be performed.
Further we will consider the corresponding specifics. But first, the person working with the cable, you need to properly take the connectors in hand. They should be held so that the metal contacts are located on top.
The plastic latch should point toward the person who crimps. On the left in this case will be the 1st contact, on the right - the 8th. Numbering is an extremely important nuance of working with twisted pair. So, what crimping schemes are used by network infrastructure specialists?
Firstly, there is a network cable scheme, called the EIA / TIA-568A. It assumes the arrangement of the cores in relation to the metal contacts of the connector in the following order:
- for 1 contact: white-green;
- for the 2nd: green;
- for the 3rd: white-orange;
- for the 4th: blue;
- for the 5th: white-blue;
- for the 6th: orange;
- for the 7th: white-brown;
- for the 8th: brown.
There is another scheme - EIA / TIA-568B. It assumes the arrangement of cores in the following order:
- for 1 contact: white-orange;
- for the 2nd: orange;
- for the 3rd: white-green;
- for the 4th: blue;
- for the 5th: white-blue;
- for the 6th: green;
- for the 7th: white-brown;
- for the 8th: brown.
How to connect the network cable to the connector, you now know. But it is useful to study the specifics relating to the various schemes for connecting twisted pair cables to certain devices.
Crimp and connection type
So, when connecting a PC to a router or switch, you should use the direct connection method. If there is a need to organize file exchange between two computers without using a router, then you can use the cross connection method. The difference between the marked schemes is small. With the direct connection method, the cable must be crimped using the same pinout. At the cross, one end is according to 568A, the other - according to 568B.
High tech savings
Twisted pair is characterized by one interesting feature. With a direct connection scheme, the device can be used not with 4 pairs of conductors, but 2. That is, using one cable it is permissible to connect 2 computers at the same time. Thus, you can save on cable or make a connection if you really need to do this, but there are no extra meters of twisted pair at hand. True, in this case, the maximum data exchange rate will not be 1 Gbit / s, but 10 times less. But for the organization of the home network, this is acceptable in most situations.
How in this case to distribute the veins? According to the contacts on the connectors for connecting the first computer :
- 1 contact: white-orange vein;
- 2nd: orange;
- 3rd: white-green;
- 6th: green.
That is, 4, 5, 7 and 8 cores are not used with this scheme. In turn, on the connectors for connecting a second computer:
- 1 contact: white-brown vein;
- 2nd: brown;
- 3rd: white-blue;
- 6th: blue.
It can be noted that when implementing a cross-wiring diagram, it is always necessary to use all 8 conductors in twisted pair. Also, if the user needs to implement data transfer between devices at a speed of 1 Gbit / s, the pinout will need to be carried out according to a special scheme. Consider its features.
Gigabit cross-connect
The first cable connector should be crimped in accordance with 568B. The second involves the following comparison of cores and contacts on the connector:
- 1 contact: white-green vein;
- 2nd: green;
- 3rd: white-orange;
- 4th: white-brown;
- 5th: brown;
- 6th: orange;
- 7th: blue;
- 8th: white and blue.
The circuit is quite similar to 568A, but the position of the blue and brown pairs of conductors is changed in it.
Compliance with the marked color matching rules for the cores and contacts on the 8P8C connector is the most important factor in ensuring the functionality of the network infrastructure. The person designing it needs to be careful when installing the appropriate elements. It happens that the computer does not see the network cable - this is often due to incorrect crimping of the twisted pair cable.
How to crimp a cable
Let's consider some technical nuances. The main device that is involved in this case is a crimper. It is similar to pincers, but at the same time it is adapted to work with computer cables of the corresponding type.
The design of the crimper involves the presence of special knives designed to trim the structure. Also, sometimes crimpers are equipped with a small device for stripping the insulation of twisted pair. In the central part of the instrument there are special sockets adapted to the thickness of the cable structure.
The optimal algorithm for a person crimping a twisted pair can be as follows.
- First of all, it is necessary to cut a section of cable of suitable length - thus, its accurate measurements will be required.
- After that, remove the outer insulation - approximately at a 3 cm distance at the end of the cable. The main thing at the same time is not to accidentally damage the insulation of the cores.
- Then you need to arrange the conductors in accordance with the above schemes for connecting to the connector. After evenly cut the ends of the cores, so that the length of each of them outside the outer insulation layer is about 12 mm.
- Next, you need to put the connector on the cable so that the wires remain in the order that corresponds to the connection diagram, and each of them is included in the desired channel. The wires should be moved until the resistance of the plastic wall of the connector is felt.
- After the conductors are properly placed inside the connector, the PVC sheath must be located inside the connector housing. If this does not work out, perhaps you should pull out the cores and shorten them a little.
As soon as all the structural elements are located correctly, you can crimp the cable by inserting the connector into a special socket on the crimper and gently pushing the tool handle all the way.