At the time of its release in 2009, AMD Athlon II X2 250 belonged to the middle-class type of processors. The characteristics of this semiconductor product confirmed this once again. Since then, quite a lot of time has passed, and this chip already refers to entry-level products. The specifications, features and relevance of this solution will be further discussed in our review.
The segment of the processor market this semiconductor chip is oriented towards
At the time of the start of sales, AMD Athlon II X2 250 belonged to mid-range processor solutions. The characteristics of the 2009 CPUs distributed them as follows by classes:
- Solutions for office PCs included only 1 computing module, had a cache of the 2nd level in a minimum volume and the lowest clock frequencies.
- Middle-class system units were equipped without fail with 2-core CPUs, had higher clock frequencies. The cache memory structure in this case did not undergo significant changes and was 2-level. But the cache size in this case has been increased. As a result, in this case a higher level of performance was obtained, but such computing systems also cost significantly more. It was to this segment of the computer market that the hero of this material belonged.
- The processor solutions for the most efficient computers were already equipped with four computing modules. Also, some of them had a 3-level cache. But the clock frequency was reduced, but the previously mentioned features ultimately provided the highest possible level of performance at that time.
- Now this distribution has changed dramatically. Entry-level PCs are equipped with chips with two computing units, but single-core CPUs have already left the historical arena. Therefore, to date, the Athlon II X2 has smoothly moved into the segment of entry-level processor devices. Mid-range PCs should be based on a CPU with 4 computing clusters, and the premium segment should be based on 8.

CPU Options
Like most of the current processor devices, this chip was delivered in two versions: simplified TRAY and more advanced BOX. In the first case, in addition to the CPU, the delivery also included installation and configuration instructions, a warranty card and a sticker with the logo of the processor model for the system unit. This configuration option was primarily intended for large companies that specialized in assembling system units of personal computers. As a rule, they bought wholesale specialized CPU cooling systems, which ultimately made it possible to increase the reliability of such computers. The second option was supplied in a black-green box and was supplemented by a standard cooling system and thermal grease.
CPU socket for installing this model of CPU
The AMD Athlon II X2 250 processor was originally aimed at installing in an AM3 socket. The number of contacts in this processor socket was 941 on the side of the system board and 938 on the contact area of the CPU. The key difference between this socket and its predecessors in the face of AM2 and AM2 + was that in this case, only DDR3 slots could be used as RAM, and the earlier AMD computing platforms worked only with the DDR2 standard. But, in turn, the hybrid RAM controller of this processor device allowed it to work with both the first type of memory and the second without any problems. Therefore, this chip could be installed not only in AM3 motherboards, but also AM2 + or AM3 +. The only thing that needed to be done in the case of using the motherboard based on AM2 + was to update the BIOS and thereby get support for new models of central processors.
Silicon Crystal Production Technology
Silicon crystal AMD Athlon II X2 250 was manufactured according to the latest and most advanced technological process. Its characteristics indicated that it corresponded to the technical process standards of 45 nm. Of course, against the background of the current 14 nm, this number looks at least not very impressive, but at that time there was no better. The technology by which pn junctions were sprayed was called SOI (from the English phrase Silicon On Insulator, or, in our opinion, silicon on dielectric). According to the same technique, previous generations of semiconductor chips of this manufacturer were manufactured. As a result, from the standpoint of reliability, there were no significant problems and comments with the AMD Athlon II X2 250. The processor of this model in this regard received all the very best that had been gained before. The area of the silicon crystal in this case was equal to only 117.5 mm 2 .
The cache system of this CPU and its features
As noted earlier, all middle-class CPUs in 2009 were necessarily equipped with a 2-level cache. AMD Athlon II X2 250 was not an exception in this regard either. Its technical characteristics indicate that a total of 256 Kb was on the first level. They were divided into 2 equal parts of 128 kb, which were tied to a specific processor core and could only interact with it. Each of these halves of 128 Kb was also divided into 2 parts. Half of them (i.e. 64 Kb) were used for data storage, and half for instructions of the processed program code. Similarly, cache was also organized at level 2. Its total volume was 2 MB, which were divided in half between the computing resources of the central processor. That is, each core on the second level could use 1 Mb for its needs. Further separation of the storage of instructions and data in this case was not provided.
RAM and its features
As noted earlier, the AMD Athlon II X2 250 processor was equipped with a unified RAM controller. It could successfully function both with RAM modules DDR2 (the dominant standard of RAM at the time the CPU started selling), and with DDR3 (an updated modification of the memory, which at that time was only just beginning to appear on store shelves). According to the specifications, 1066 MHz is the maximum value of the RAM frequency for AMD Athlon TM II X2 250. The processor of this model can also work with lower-speed modules, while the RAM frequency will automatically decrease and the performance level of the computing system will be lower. You can also set more high-speed bars. But their frequency of operation will be limited to 1066 MHz.
Thermal pack. Recommendations for equipping such a CPU with a cooling system
The thermal and temperature parameters of the AMD Athlon TM II X2 250 look quite good even against the background of current processor devices. Its characteristics in this regard were as follows: the thermal package of this silicon product is 65 W, and the maximum allowable temperature is 74 0 C. Such an acceptable value of thermal The package was achieved through significant processing of the architecture of the semiconductor crystal of this CPU, as well as through the use of an advanced technological process at that time. The latter factor also significantly reduced the operating temperature range, which in this case was in the range 35-57 0 . Even after overclocking during the execution of the most complex program code, the maximum value of the chip temperature did not exceed 65 0 . These values are valid for when CPU cooling used a complete cooler. If you replace it with an improved system of active heat removal of third-party production, then the previously mentioned values will decrease by 5-10 0 C.
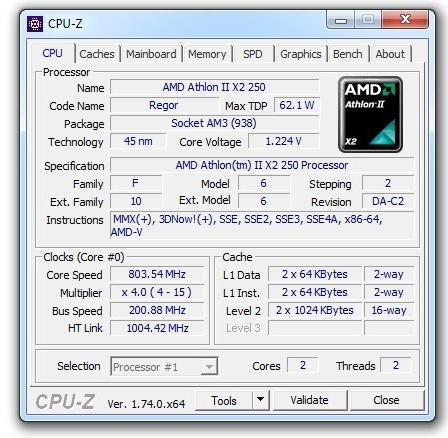
CPU frequency
The nominal clock speed for AMD Athlon II X2 250 is 3.00 GHz. This value is easy to obtain from the specifications of this semiconductor solution. His multiplier is fixed and equal to 15. But the frequency of the system bus in the normal mode is 200 MHz. If we multiply 15 by 200 MHz, we get 3,000 MHz, or 3.0 GHz. There are no technologies for dynamically controlling the frequency of the CPU depending on the degree of its heating, software optimization for single or dual-threaded execution, and the level of complexity of the program code in this case. Therefore, this central processor runs on only one frequency value, which is 3.0 GHz.
Silicon Crystal Architectural Features
In the language of computer professionals, this chip is called DUALCORE. AMD Athlon II X2 250, as you might guess from its name, includes only 2 cores for calculations. Intel-type NT technologies, which would make it possible to obtain twice as many logical code processing flows at the software level, are still not found in AMD processors. Therefore, the operating system in this case will only see what is on the physical level, that is, only 2 threads. The codename for these cores is REGOR. This chip can function both in 32-bit computing mode and in 64-bit mode.
Overclocking
As noted earlier, the clock multiplier is fixed in the AMD Athlon II X2 250. Overclocking it is therefore only possible by increasing the frequency of the system board bus. In normal mode, this parameter is 200 MHz. In combination with a standard cooler, this value can be increased to 235-237 MHz and, as a result, the CPU operating frequency is 3525-3555 MHz. As a percentage, we get an increase of 17.5-18.5%. Given that this is a mid-range processor , and it is not designed for overclocking, these are already excellent indicators. But you can improve the obtained values. To do this, instead of a regular cooler, you need to purchase third-party cooling systems. In this case, you can increase the frequency of the system bus to 247-250 MHz. The chip itself will already operate at frequencies 3705-3750 MHz. In percent, this growth will already be equal to 23.5-25%. The CPU overclocking technique in this case is as follows:
The PC system unit must be specially equipped. This is an improved modification of the motherboard, and the most high-speed RAM, and a more powerful power supply, and a high-quality case with good air circulation.
All software must be updated before overclocking, which is necessary for the stable operation of the AMD Athlon II X2 250. Drivers and application software that monitors the computer system in the first place.
In the future, in BIOS, we omit the frequencies of all components of the personal computer, except for the system bus, which we begin to gradually increase. After each such manipulation, we carry out a stress test of the PC using special programs for stability. As soon as the maximum possible frequency value is reached, increase the voltage to the CPU. Then we increment the frequency again. The maximum allowable voltage value for this processor is 1.425V. It is near this value that the increase in frequency must be stopped. And this is the maximum possible value of this parameter.

Chip cost
Initially, AMD Athlon TM II X2 250 was priced at $ 90. And at that time, such a price of this semiconductor crystal was entirely consistent with its capabilities. But now it's already 2016, and such a CPU in a new state can still be bought from stocks at a very modest price of $ 25 (about 1,500 rubles). And you can buy a used chip for 800-900 rubles. If we consider this processor as the basis for an inexpensive office system unit, then this can be a worthy choice that combines a very affordable price and acceptable performance.
Owner reviews. CPU Operation Features
AMD with the release of a whole successful family of mid-range Athlon chips in 2009 really managed to surprise both its opponents and fans. The most productive solution in this lineup was precisely the AMD Athlon II X2 250 processor. The characteristics of this semiconductor chip at that time were really impressive, but the fact that this central processor has been successfully sold for more than 5 years is an additional confirmation of this. Of course, during this time interval, this chip went down from the niche of middle-class products to the segment of entry-level solutions. The main advantages of this processor from AMD, which its owners draw in reviews, include:
Good performance.
Excellent cache organization, which provides higher performance compared to competing products.
Decent overclocking potential, as for a CPU with a locked multiplier.
Affordable cost.
Excellent degree of energy efficiency.
The only drawback of this processor device is the unsuccessful release time. This CPU appeared on sale in anticipation of the start of sales of the updated computing platform from Intel LGA 1156, against which it no longer looked so confident. The capabilities of this CPU looked significantly better when compared with the LGA775.
Summary
Of course, the AMD Athlon II X2 250 was a successful product in the line of central AM3 processors. At the time of release, its characteristics made it possible to cope with direct competitors based on the LGA775 socket. Moreover, both in terms of productivity and energy efficiency. An additional factor that confirms the success of this processor is that it has been successfully sold to this day. Only now has he moved from the middle-class CPU segment to the niche of entry-level products. If all AMD processors were as successful as the hero of this review, then the market for microprocessor products would probably have a radically different situation today. And so the success of this CPU is rather an accident than a regularity.
Of course, I would like AMD to take into account the success of this processor and apply it within the framework of the new AM4 platform, which should be introduced at the end of 2016. At the same time, the success of this socket can radically change the current situation in the personal computer market. If this happens, then Intel will be forced to adequately respond to such an AMD move (lower prices for existing CPU models, for example). In any case, the buyer should benefit from such healthy competition and get a more efficient computer for less money. But this is all in theory. In practice, the answer to such a wish of most users can give only time. At the same time, the wait was not so long: about six months.