The modern level of development of dentistry allows you to make dreams of a beautiful smile a reality. But it is worthwhile to understand that these are not only snow-white and even teeth, but also healthy gums. No way without it. Unfortunately, everyone comes across gum disease at least once in a lifetime. But not everyone is ready to turn to a specialist with a problem. Many people self-medicate or simply ignore the problem. And this is fundamentally the wrong approach, since at the initial stage, gum inflammation near the tooth can be eliminated without consequences. And in advanced cases, patients often lose their teeth.
Causes of inflammation
In order to prevent inflammation of the gum tissue, it is necessary to understand the causes that cause this disease. These reasons include:
- Microbes. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity cannot be sterile. It always contains a certain number of microorganisms, the regulation of the number of which is carried out by the human immune system. These microbes are not dangerous until a person creates favorable factors for their rapid reproduction.
- Inadequate hygiene. If you brush your teeth irregularly or improperly selected brush and toothpaste, plaque will remain. This is a breeding ground for the development of microbes.
- Tartar. Bacteria secrete substances that convert soft plaque into hard tartar. In turn, tartar injures and lowers the gums, revealing deeper tissues for bacterial growth.
- Unqualified dental care. This cause of gum disease, alas, is quite common. An improperly installed or fitted prosthesis or seal presses on the delicate gum tissue, causing inflammation.
- Smoking. Teeth smokers with experience, in principle, do not look too aesthetically pleasing. They often have an additional plaque that causes inflammation.
- Medical predisposition. Gum disease can occur as a result of vitamin deficiency, endocrine diseases, gastrointestinal tract problems, in violation of the immune system, for hereditary reasons.
Symptoms
For gum disease, treatment is advisable to start as soon as possible. If we consider the process in stages, then it looks like this:
- There is redness and slight swelling. To the touch, the inflamed area becomes softer than the surrounding tissues.
- As a result of the weakness and fragility of the vessels during brushing, there is weak bleeding.
- Bleeding intensifies. Blood is released even when the tongue is carried over the gums.
- The inflamed gum drops, the sensitivity of the teeth increases.
- An increase in sensitivity goes into sharp pain. Teeth react sharply to sour, sweet, hot and cold.
- The surfaces of the gums become heterogeneous, the tissues become loose. The normal contours of the gums are disrupted. Bad breath cannot be removed by brushing your teeth.
A timely visit to a doctor will help to correctly classify the disease that caused the inflammatory process or eliminate the mechanical cause of inflammation. This will allow faster repair of damaged tissue.
International classification
The oral cavity and teeth are the beginning of the digestive system, therefore, in the International Classification (MBK-10) they are referred to as diseases of the digestive system. Further separation brings diseases of the oral cavity, salivary glands and jaw into a separate subgroup (K00-K14 in ICD-10), from which the section on “Gingivitis and periodontal diseases” is considered today. Let us clarify that these diseases differ in the severity of the inflammatory process and the depth of the affected soft tissues. The main diseases of this section are gingivitis and periodontitis.
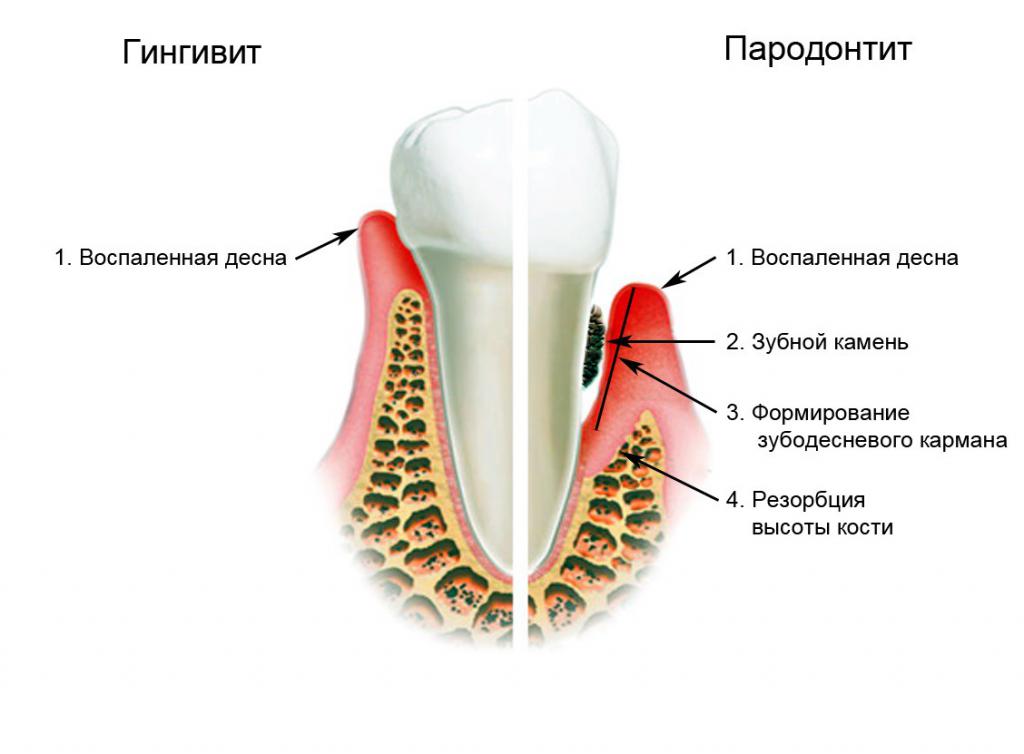
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is called inflammation of the gingival mucosa, which does not affect the gingival attachments. By localization, gingivitis can be generalized, that is, with damage to the soft tissue around all teeth, and localized, which means inflammation of the gums around the tooth. The doctor prescribes treatment in any of the cases after examination and assessment of the situation.
There is an additional division of gingivitis according to the nature of inflammation:
- the simplest is the edematous form, that is, catarrhal gingivitis;
- a more complex, fibrous form, that is, hypertrophic gingivitis;
- the most severe form is ulcerative necrotic gingivitis.
The classification of gum disease in this case was carried out according to the degree of damage in the soft tissues from simple edema to their necrosis. If there are characteristic signs of the disease, you should visit the dentist.
If the patient does not think about how to remove gum disease, does not go to the doctor and does not start treatment, then gingivitis can turn into a more complex disease - periodontitis.
Periodontitis
This disease affects the deeper periodontal tissues, infecting, among other things, the periodontal ligaments of the teeth and the bone edges of the holes. In the process of destruction, the gum exfoliates from the tooth, forming a periodontal periodontal pocket. In the cavities, food debris begins to accumulate and infections develop. Plaque falls under the gum, gradually transforming into tartar. Gradually, due to loss of support, tooth mobility appears, and bacteria under the gums become a hotbed of chronic infection that secrete toxins. The chronic process weakens the body and can go into the acute stage with the appearance of purulent discharge. In difficult cases, tooth loss is possible.
Gingivitis Treatment Methods
If symptoms of gum disease are detected, treatment is prescribed according to the type of disease. In most cases, after examination, the doctor removes plaque and tartar. This is done by professional toothpastes, ultrasonic tools and air-abrasive tips. In cases where the cause of gum inflammation was a defect in prosthetics or demineralization, the doctor eliminates these problems, creating conditions for the restoration of the gums. If the inflammatory process is in the initial stage, then one visit to the doctor with the further implementation of the recommendations received is enough for recovery. With gum inflammation, rinsing with antimicrobials after removing plaque and hard deposits will completely eliminate the problem.
More severe inflammation with ulceration is no longer limited to removing plaque and rinsing. The patient will have to visit the dentist several times. At the first visit, he removes dental deposits with a hand tool and polishing pastes. In the second - the surface of the teeth is finally treated with ultrasonic instruments. Additionally, antimicrobial rinses, anti-inflammatory applications, suitable for the case of paste and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Sanitation of the oral cavity, treatment of caries and pulpitis, replacement of old fillings and bridges (single crowns), all this should be done to eliminate foci of chronic infections. In principle, this work should be considered as a stage in the treatment of gingivitis.
In order to no longer raise the question of how to treat gum disease, the doctor teaches the patient how to clean their teeth and oral cavity, and also selects hygiene products (toothpaste, tooth elixir, and so on).
In the treatment of the hypertrophic form of gingivitis, in addition to the above measures, the doctor must study the list of drugs taken by the patient, and cancel or replace the one that could provoke the growth of gum tissue. If gingivitis does not go away some time after cancellation, then surgical treatment may be recommended.
Methods of treating periodontitis
Periodontitis treatment is more complex, lengthy and financially expensive. They begin it with an initial consultation, during which the depth of the gingival pockets, bleeding spots and plaque are documented in detail. Parameters are entered in the periodontal map. Then, the degree of resorption (resorption) of bone tissue is diagnosed by x-rays. As a result, an individual treatment plan should be drawn up.
The obligatory stage is plaque removal, tartar removal and training in proper hygiene skills. Next, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed: pastes, antiseptic solutions, if necessary, antibiotics. At the same time, caries, pulpitis, periodontitis are treated. And also teeth that cannot be restored are removed, fillings and established dental structures are changed.
Do not be afraid of the appointment of antibiotics. With gum inflammation, which has turned to periodontitis, this may be a necessary stage of treatment. The doctor will choose the optimal form of administration (tablets or injections). In especially difficult cases, an injection is made directly into the affected area of the gum. In the case of antibiotics, you should never self-medicate and arbitrarily prescribe yourself a medicine or replace it with another (an exception is permissible only for drugs from different manufacturers with the same active substance). For reference, we note that most often in the treatment of periodontitis, an antibiotic of the glycosamide group and the fluoroquinol group is used. In the first case, it is "Clindamycin" or "Linkomycin." In the second - “Nomitsin”, “Tavirid” or “Sifloks”.
After completing the first stage of treatment, they conduct a new full examination, the data of which is recorded in the periodontal card. There, an assessment of the results is carried out. When evaluating the results, the doctor takes into account how scrupulously the patient complies with the recommendations on oral hygiene, and the degree of his motivation. If the patient is not ready to fully cooperate, then it is impossible to obtain a favorable result.
If the dynamics are considered positive, the oral cavity is sanitized, and the patient faithfully complies with the recommendations, then the dentist proceeds to the next step of the treatment program. Now you can (if necessary) perform surgical removal of the remaining gingival pockets, and install the tires on the loose teeth to reduce the chewing load. In the same period, prosthetics for missing teeth are performed.
Further on the treatment program, maintenance therapy is usually carried out. Periodontitis is a chronic inflammation of the gums, so the disease can resume.
Prevention of inflammatory processes
Prevention of gum disease is a set of measures consisting of the following items:
- Correct selection of toothbrush and toothpaste. Regular and thorough brushing and gum care.
- Every six months a dental examination. At the first sign of inflammation, an unscheduled visit to the doctor.
- Attentive to health status. Timely treatment for the treatment of systemic diseases.
- The presence in the diet of plant foods. Eating vegetables and fruits raw.
- To give up smoking.
- The use of mouthwashes with antiseptic properties.
What you can use at home
Is it possible to remove the problem by rinsing, and how to rinse the gums during inflammation? Or maybe there are some other means to help yourself on your own? Yes, there are such tools and methods. But the treatment of gum disease at home is possible only when the process is very small. A little discomfort can be eliminated by yourself. For this, both medicines and folk remedies are used.
In pharmacies, they sell anti-inflammatory gels and bottles with sprays, special toothpastes and rinses, ready-made rinses. Of the prepared solutions, you can use "Furacilin", "Malavit", "Chlorophyllipt", "Rotokan" and other means. In addition, gels and balms, such as Holisal, Asepta, Stomatofit, Metrogil Denta, and so on, can be offered to the buyer at the pharmacy. However, one should always remember that self-medication may not work, and the inflammatory process will go into a more complex stage.
Are folk remedies effective
At home, many use herbal decoctions and infusions to treat gum disease. Preference is given to natural antiseptics, such as chamomile, sage, oak bark, calendula, eucalyptus, St. John's wort and so on. It is not possible to completely cure inflammation with decoctions of herbs, but they will perfectly complement the medication prescribed by a specialist. Going to the dentist is the only right way for gum disease, understand this and don't waste time. Do not start the disease so that it does not go into a more complex stage.
What affects the cost of treatment
Of course, the initial degrees of gingivitis are cheaper to treat than the neglected form of the same disease. Well, periodontitis is even more difficult and expensive to cure. For example, ultrasonic cleaning of stones will cost several hundred, and the use of the Vector apparatus will cost several thousand rubles. For opening a periodontal abscess, the doctor will take several hundred, and for a patch operation on several teeth - several thousand rubles. So why avoid extra expenses if you can ask for help right away?
It is better to seek the help of a dentist in a timely manner, then you can avoid the negative consequences that can occur as complications of the inflammatory process.