Non-carious lesions of the teeth are a common occurrence in dental practice. This concept includes a wide range of diseases with different etiologies and clinical manifestations.
General concept
Non-carious lesions of the teeth - an extensive group of diseases and pathologies. These include all damage to the enamel, dental tissue, diseases of a non-bacterial nature. In terms of prevalence, they take second place after caries. Such lesions can have a variety of symptoms and a clinical picture, they have different causes. But they are all congenital or acquired.
They can have different distribution - to affect one or all of the teeth in a row, individual sections in a certain order. Many of these diseases are difficult to diagnose, since the signs of different pathologies are similar and difficult to distinguish from each other. This may be due to insufficient knowledge of the disease, which complicates its detection and increases the risk of complications. In this situation, only the best dental clinics can help , where they will choose the right treatment option (for example, SM Clinic, which has several branches in Moscow, Diamed or DentaLux-M).
Classification of non-carious lesions
Due to the variety of diseases that relate to the concept of "non-carious lesions of the teeth", their classification does not have one generally accepted standard. If you summarize all the data, you can get a generalized list of types of lesions.
1. Pathology of development during teething:
- Anomaly of shape, size.
- Fluorosis (mottled teeth).
- Enamel hypoplasia (impaired development).
- Pathologies of the structure of teeth of a hereditary nature (odontogenesis, amelodentinogenesis).
- Syphilis (congenital).
- Other developmental pathologies associated with external factors (taking antibiotics, rhesus conflict).
2. Pathological changes in the hard tissues of the tooth:
- Complete tooth loss.
- Erosion.
- Discoloration after teething.
- Hypersensitivity of tissues.
3. Changes in the internal structure of the tooth:
- Fracture of the root.
- Dislocation of the root.
- Fracture of a tooth crown.
- Dissection of the pulp.
In our country, another classification is more often used, proposed in 1968 by V.K. Patrikeev. On it, non-carious lesions of the teeth are divided into two groups.
1. Lesions that occur before teething:
- Anomaly of teething and development.
- Hypoplasia of the teeth.
- Hyperplasia
- Fluorosis
- Hereditary pathology.
2. Lesions that occur after eruption:
- Erosion.
- Wedge-shaped defect.
- Hard tissue necrosis.
- Hyperesthesia of the teeth.
- Erase
- Tooth injury.
- Pigmentation.
Hypoplasia
This is the name of the pathology of the development of dental tissue during its formation, that is, in children before teething. Such a violation is caused by insufficient mineralization of tissues. The main symptom is the complete absence of an organ or its abnormally small development. Hypoplasia of the teeth can be both congenital and develop after the birth of a child. There are several reasons for this:
- the conflict of the Rhesus factors of the mother and child,
- mother-borne infectious disease during pregnancy, infection in the baby after birth,
- severe toxicosis accompanying pregnancy,
- premature birth, trauma during childbirth,
- pathology of the development of the child after birth,
- dystrophy, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- metabolic disease,
- impaired development of brain activity,
- mechanical damage to the jawbone.
There are two types of hypoplasia - systemic and local. The first is characterized by damage to all teeth, a low thickness of enamel or its absence. Yellow spots appear. Local differs in the defeat of one or two organs. Here there is a lack of enamel (partial or complete), structural defects of the teeth - they can be deformed. Such violations cause pain. Severe hypoplasia causes increased tooth abrasion, tissue destruction or complete organ loss, malocclusion. The treatment of hypoplasia includes teeth whitening (at an early stage) or filling and prosthetics (in case of a serious illness). At the same time, enamel is remineralized with medical preparations (for example, calcium gluconate solution). In order to prevent the occurrence of hypoplasia in children, pregnant women are recommended a balanced diet containing vitamins for teeth (D, C, A, B), calcium and fluorine, as well as strict adherence to oral hygiene.
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia - non-carious lesions of the teeth associated with excessive formation of tooth tissue. Their appearance is due to an abnormality in the development of epithelial, enamel and dentin cells. It appears in the form of "drops", which are also called "enamel pearls." They can reach 5 mm in diameter. The main area of localization is the neck of the tooth. Such a drop consists of tooth enamel, inside there may be dentin or soft connective tissue resembling pulp. Five types of such formations are distinguished by their structure:
- true enamel - consist only of enamel,
- enamel-dentin - the enamel shell contains dentin inside,
- enamel-dentin droplets with pulp - inside is connective tissue,
- drops Rodriguez - Ponti - enamel formations in the periodontium between the root and alveoli,
- intradentinal - located in the thickness of the dentin.
Hyperplasia of tooth tissues does not manifest itself clinically, it does not cause pain, inflammation or any discomfort. One can only highlight the aesthetic factor if the anomaly affects the front teeth.
In this case, grinding and surface leveling are carried out. In other cases, if the patient is not worried, treatment is not carried out. Preventive measures are to protect milk teeth from caries, since their destruction can cause disturbances in the development of permanent.
Fluorosis
Fluorosis occurs during the formation of dental tissue due to increased fluoride intake. It changes the correct structure of enamel and causes its external defects - the appearance of spots, stripes, furrows, dark inclusions. In the development of such a pathology, not only an excess of fluorine plays a role, but also a lack of calcium. In the children's body, fluoride accumulates more and faster than in adults, coming from food and water. Such forms of fluorosis are distinguished:
- dashed - is manifested by the appearance of white stripes without a clear contour;
- spotted - characterized by the presence of yellowish spots with a smooth surface;
- Cretaceous-mottled - matte or shiny spots that have white, brown or yellow color (can affect all teeth);
- erosive - multiple erosion of the enamel surface;
- destructive (tooth broke off or completely destroyed) - harmful processes associated with fluorosis.
Treatment methods for fluorosis vary depending on the form of the disease. So, with a spotty form, bleaching and remineralization is carried out, if necessary, grinding of the upper enamel layer. But the erosive form cannot be cured by such methods; here, restoration of teeth with veneers or crowns is necessary. General treatment methods include remineralization, restoration of the shape and color of the organ, local effects on the body, control of fluoride intake.
Erosion
Non-carious lesions of the teeth include enamel damage such as erosion. Its formation leads to discoloration, aesthetic damage to the tooth, as well as increased sensitivity. It is detected by visual inspection. Tooth erosion is characterized by progressive destruction of enamel and dentin, the course of the disease is chronic, it can take a long time. The cause of the pathology may have a mechanical character, for example, when using hard brushes or pastes with abrasive particles. Also, erosion can be caused by a chemical effect on the enamel when eating foods and drinks with high acidity (pickles, marinades, citrus juices and others). Workers associated with the continuous inhalation of harmful substances most often suffer from such tooth damage. The use of certain drugs can contribute to the onset of the disease (for example, a large amount of ascorbic acid adversely affects the enamel).
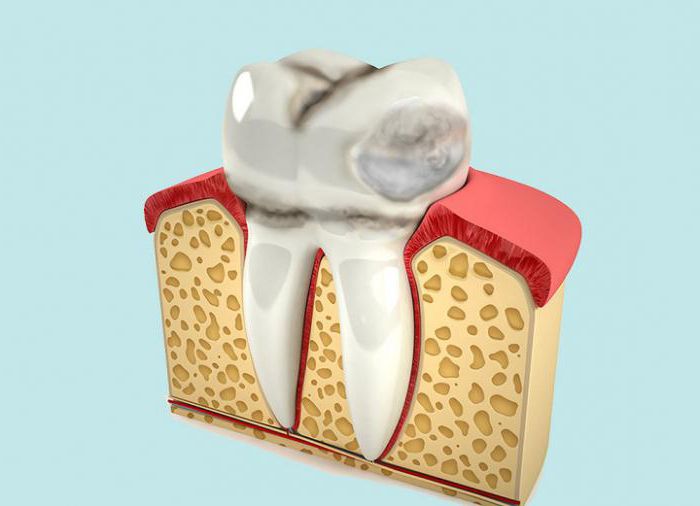
Irregularities in the functioning of the stomach (increased acidity of its environment) or of the thyroid gland can also cause tooth erosion . It is difficult to identify the disease at an early stage, since it manifests itself only by a loss of gloss in a separate small area of the tooth. The further course of the disease leads to a gradual decrease in enamel and dentin. It looks like worn teeth, most often at the base. Treatment is based on stopping the destruction of dental tissue. It includes the use of applications with a fluorine and calcium content of about 20 days, then the affected area is covered with fluoride varnish. It is possible to use veneers or crowns to restore an aesthetic appearance. The complex therapy includes calcium and phosphorus preparations, as well as vitamins for teeth. If erosion is not treated, it can cause tooth hyperesthesia.
Hyperesthesia
Hyperesthesia of the teeth is manifested by increased sensitivity of enamel and in most cases is a concomitant symptom of other non-carious diseases. The prevalence of this pathology is high: about 70% of the population suffer from hyperesthesia, more often women are exposed to it. The manifestation is a sharp, severe pain that lasts no more than thirty seconds and appears when external factors are applied to the enamel. Hyperesthesia is divided into types according to several criteria:
1. Distribution:
- limited form - affects one or more teeth;
- generalized - characterized by the sensitivity of all organs.
2. Origin:
- a form of hyperesthesia associated with loss of dental tissue;
- not associated with loss, due to the general condition of the body.
3. The clinical picture:
- pain arises as a reaction to the temperature of external stimuli (cold water);
- teeth react to chemical irritants (sweet or sour foods);
- reaction to all stimuli, including tactile ones.
The treatment of hyperesthesia is prescribed by a specialist, depending on the cause of its occurrence, the complexity of the problem and the form of the disease. In some cases, surgical intervention is necessary (for example, with pathological lowering of the gums and exposing the cervical region of the tooth), and sometimes therapeutic procedures, such as applying fluorinated applications to damaged areas, can be dispensed with. Orthodontic therapy may be required for hyperesthesia due to increased tooth abrasion. Preventive measures - eating with food all the necessary minerals and vitamins that strengthen dental tissues, regular and proper use of oral hygiene products, as well as an annual examination by a dentist.
Wedge defect
A wedge-shaped defect is a tooth lesion in which its base is destroyed. Externally manifested by damage to the neck of the tooth in the form of a wedge. Most often, fangs are prone to defect. At the initial stage, it is invisible, it is difficult to diagnose. With a prolonged course of the disease, a dark shade appears in the affected area. The main symptom of a wedge-shaped defect is that the teeth react painfully to the influence of high or low temperatures, sweet food, and physical effects (brushing). The cause of the development of the disease may be non-compliance with oral hygiene, improper use of the brush - if after cleaning a bacterial coating remains at the base of the bone formation, it destroys the enamel, leading to a wedge-shaped defect. Gum diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, thyroid dysfunction, increased acidity of the stomach, causing heartburn, can also become a cause. The treatment of a wedge-shaped defect depends on the severity of the damage.
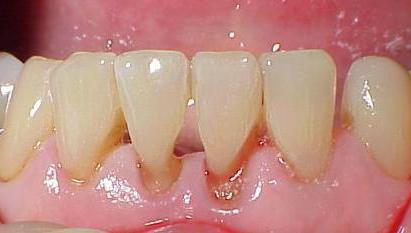
With minor destruction, it is enough to carry out restoration procedures that will replenish calcium and fluoride in tooth enamel and reduce its susceptibility to external factors. With severe damage can not do without installing a seal. Due to the inconvenient location of the defect, such seals often fall out. The best dental clinics are able to solve this problem by drilling holes of a certain shape that holds the seal and using special elasticity material.
Hard tissue necrosis
Necrosis of hard tooth tissues at an early stage is manifested by a loss of enamel gloss, chalky spots appear. In the process of developing the disease, they become dark brown. In the area of the lesion, softening of the tissues occurs, the enamel loses strength, the patient may at the same time complain that his tooth has broken off. Dentin pigmentation occurs. Usually, not one organ is affected, but several. Sensitivity to external stimuli increases. It is localized mainly at the neck of the tooth, as well as a wedge-shaped defect and erosion. But, despite similar symptoms and the affected area, an experienced dentist can easily distinguish these diseases from each other and make the correct diagnosis. Such a pathology occurs against the background of hormonal disorders in the body. Treatment is aimed at strengthening dental tissues, eliminating hypersensitivity (hyperesthesia), and with severe damage, orthopedic therapy is prescribed.
Tooth injuries
The concept of “tooth injury” combines damage to the mechanical nature of the external or internal parts of the tooth. The causes of their occurrence include falls, blows to the jawbone during sports, fights, and accidents. With prolonged exposure to the tooth with foreign objects or solid food, its tissues become thinner and become brittle. In this case, trouble can occur even when chewing food.
Tooth injuries can result from improper dental procedures, such as poor-quality installation of the pin. Some diseases, such as hypoplasia, fluorosis, cervical caries, and a root cyst can also lead to damage. Injuries include fractures of the crown or root, dislocation, contusion of the tooth. Treatment of a bruise is based on the exclusion of physical effects on the diseased organ, the rejection of solid food. In the treatment of dislocation, the tooth returns to the hole for further engraftment. If such an operation does not have prospects, according to the dentist, prosthetics or implantation is performed. A crown fracture needs immediate treatment to restore not only masticatory functions, but also an aesthetic appearance, especially if the front teeth have been damaged. In this case, fixed crowns are installed. In case of a root fracture, a complete tooth extraction is usually performed to establish a pin or implant.