Many are accustomed to perceive the soil in the form in which it is presented now. However, nature has been engaged in its formation for millions of years. Initially, the surface was a rock. Over time, it was subjected to erosion, the influence of rain and minerals. The remains of the first and subsequent plants enriched the soil with humus. Thanks to these metamorphoses, the upper layer increased, becoming better in composition and structure. For geological reasons, mechanical and chemical characteristics vary across the surface. Soil - soil, all the variety of rocks, technogenic formations. All this for a long time has been an object of human engineering and economic activity.
Classification
There are several main varieties of soil. These include, in particular:
- Monolithic rock and half-rock with rigid structural bonds.
- Dispersed, separately granular without strong structural joints. Connected - clay, incoherent - coarse.
Soil is used in the construction of buildings, in engineering structures, as well as in road surfaces, embankments and dams. Well suited for the creation of underground channels: tunnels, vaults and more. Soil science is a science whose field of study is soil.
Types of soils and their properties
To build a reliable foundation, it is necessary to take into account the physical qualities of the soil, which is located in the base. The basic information contains a table of soils. Before starting work, the earth resistance must be calculated. In assessing its technical suitability, aspects such as:
- The homogeneity of the composition.
- The coefficient of friction of the soil mass parts against each other should also be taken into account.
- The maximum amount of water absorption, as well as its initial presence.
- The ability of the soil to retain the fluid absorbed by it, despite the efforts made to remove it.
- The erosion and solubility in water, compressibility, loosening, plasticity and the like.
- Grip as well as particle shape and size. In this case, the strength of the bonds that the soil possesses is implied.
Types of soils are divided into two large categories that are different in structure, physical properties and development methods. Intermediate groups of rocky destroyed rocks are also intended. They consist of stones unconnected or interconnected by extraneous impurities. The latter are called conglomerates.
Loose structure
This group consists of sandy soil types that, when dried, do not lose their volume. In pure form, they have an almost insignificant bond between particles. It also includes clay. It is able to increase its volumes when wet and, depending on humidity, may have good connectivity. Sands do not have plasticity. After the use of force, they are instantly compressed, but do not retain their form. But clay is very easy to modify. Under the influence of an external force, it is rather slowly but strongly compressed.
Rock structures
These are rocks cemented and welded together. Externally, these structures are a continuous array or a fractured layer. Saturated with water, they show a high percentage of compressive strength. These structures are readily soluble and softened in water. They are well suited as the basis for the foundation due to their strength, resistance to compression and frost. The undoubted advantage of these structures is also the fact that they do not require additional opening and deepening.
Conglomerates and non-rock structures
Most of them are unfastened crystalline and sedimentary clastic rocks. These structures are able to withstand buildings of several floors. On these soils, laying a strip foundation is carried out, the depth of which is not less than half a meter. On the territory of the Russian Federation there are a lot of varieties of rock structures that have the most diverse physical properties.
Loose structure
It should be said that soil-sand is considered a fairly common structure. What is this category? The composition of the soil includes a loose mixture of grain quartz, as well as other materials that appeared due to the weathering of rock particles of very small size. These structures are divided into several subgroups. These are, in particular, gravel, medium and large, silty rocks. All of these structures are easy to develop, are characterized by high water permeability, are well compacted under pressure. When sand is laid in a uniform layer in density and volume, a good foundation can be laid for subsequent construction. The use of its maximum characteristics will occur if the level of freezing is located above groundwater. It all depends on the characteristics of the region in which the construction takes place. Sand compression occurs in a short time, which means that the sediment of such a structure does not require much time. Its size is directly proportional to the ability to withstand loads. The particle size of dust sand varies from 0.005 to 0.05 mm. It will not be a good basis for construction, because it does not cope with high loads. Sandy soil is able to sag under pressure. Also, it almost does not freeze and easily passes water. If the foundation is based on such soil, then it should be laid at a depth not exceeding 70 cm, but not less than forty centimeters.

Plastic structures. Subcategories
Plastic characteristics of soils allow you to divide them into several subgroups. Consider the main ones. Loose structures containing 5–10% clay are called sandy loam. Some of them, when diluted with water, become fluid, similar to a liquid. Because of this, such a soil is also called a floater. Such structures are unsuitable for foundations. Loams in their composition have from 10 to 30% clay. They are light, medium and heavy. These indicators provide an intermediate position of such soils between clay and sand.
Natural foundation material
The physical characteristics of soils are of great importance in the construction of structures. Not every rock can build a building. Unlike the granular structure, clay has a high compressibility. Moreover, under load, the compaction process is rather slow. Accordingly, the settlement of buildings on such soil will take more time. Combined soil layers - from rock and loose structure - do not have resistance to liquefaction. Because of this, they have a low bearing capacity. The composition of the soil includes the smallest particles, the size of which does not exceed 0.005 mm. This structure also contains a small amount of bulk particles. Clay is easy to compress and wash. Traced for many years, this structure will serve as an excellent basis for laying the foundation of the house. However, there are a number of reservations, because in its natural state, clay is almost impossible to find dry.

The fine structure of the rock contributes to the formation of a capillary effect. It leads to a constant wet state of clay. But the drawback of this kind of structure is not its moisture, but its heterogeneity. She does not pass water well. Because of this, the liquid spreads through various soil impurities. At low temperatures, clay begins to freeze to the building, which leads to its expansion. This helps to raise the foundation. Clay moisture is uneven. In turn, this means that it will rise in every place differently. All this leads to the destruction of the building. In some places it is stronger, in others it is insignificant, but the soil affects the foundation over the entire surface. Types of soil, depending on the properties, affect the foundations in different ways.
Macroporous Structures
This is a separate category that clay soils form. They got their name macroporous due to the presence of large gaps between the particles. Pores are visible even with the naked eye. When considering, you can see that they significantly exceed the skeleton of the soil. Loess rocks belong to this structure. Their composition contains more than 50% of dust particles. These structures are widespread in southern Russia and the Far East. Under the influence of moisture, such a rock softens and loses stability. If the initial stage of clay soils was formed due to structural precipitation in water, in which microbiological processes were present, then it is called silt. They are most often found in marshy and wetlands and in the area of peat mining. If the foundation is being built on the territory where there is a high probability of loess and silty soils, then necessary measures should be taken to strengthen the building.
Determination of consistency on the site
The structure of clay soils is determined visually when developing a shovel. For example, a plastic mixture will stick to the tool. Hard soil will behave completely differently. Types of soils are determined by rolling them into a cord or rubbing them with your palms. So you can evaluate their plasticity. Clay soils are well compressed, eroded and swell when frozen. These structures are one of the most finicky and unfavorable for the construction of the foundation. In such an area, the foundation should be laid to the entire depth of freezing. Assessment of the soil composition on the site is carried out by means of a watering can. Record the time that water has absorbed from the surface. If absorption occurs within a second, the structure is rocky or sandy. It quickly takes water and wet peaty rocks. But on the surface of clay soil, the liquid is retained.
After that, draw a little soaked layer and squeeze it in the palm of your hand. If the structure broke up into grains or seeped through your fingers, then this is rocky or sandy rock. Clay is easily compressible and fixed in the form of a lump. She feels rather slippery. If the soil seems soapy, silky and does not shrink so much, then most likely it is muddy or loamy. The peaty structure is similar to a sponge.
How to determine the structure at home?
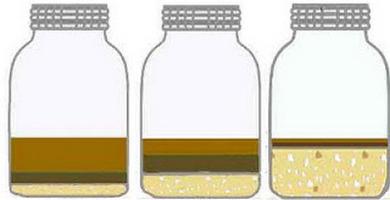
A full tablespoon of soil is placed in a glass of clean water. It must be mixed and left. After a few hours, you can see the result. If the bottom is layered sediment, and the water itself is relatively clean, then you added loamy soil. Sand, stones on the bottom and pure liquid - this is another structure. Most likely, this is a rock formation. In particular, it may be sandy or rocky soil. Grayish water and whitish grains are characters for the limestone structure. Peaty soil will make the water cloudy. Thin and light fragments will float on the surface, and a small precipitate will appear at the bottom. If the water is clayey and silty soil, then it will cloud. In this case, a thin precipitate forms at the bottom.
PH level
Soil can be subdivided depending on the degree of acidity. Thus, in terms of pH, structures are weakly acidic, neutral, or slightly alkaline. In the latter, the level of soil acidity varies from 6.5 to 7.0. It is great for garden plants, including vegetables, contributes to their faster growth and development. Acid soil has indicators from 4.0 to 6.5, but from 7.0 to 9.0 - this is an alkaline structure. In addition to the indicated ones, there are also extreme points of the scale - from 1 to 14, however, they are practically not found in the practice of European gardening. Knowledge of these data is necessary for the correct selection of plants for planting. Soil acidity can be reduced by mixing the structure with lime. Organic conditioners will help to increase the pH level. However, the latter process is quite expensive. In this regard, in areas with alkaline soil, acidophiles can be grown in containers and tubs that are filled with an acidic structure.
Growing plants
When choosing soil for plantations, it is necessary to focus on such moments as:
- The scope of its application. There is soil for flowers, seedlings, as well as garden and universal. There is the possibility of acquiring peat. It all depends on what the soil is needed for, what cultural or decorative plantings it will be grown on.
- Types of plants. If you are going to grow representatives of one category, then the best choice will be special soil for him. But if there are several, universal will do.
- Volume consumed.
To make the soil mixture more loose, use vermiculite. So that the roots do not rot from stagnant water, a drainage layer is laid on the bottom when planting plants. For cacti and a number of other plants, the soil is mixed with a loose structure. If planting occurs in infertile places, then its quality will help to improve peat. Hydrogel helps to improve moisture and air exchange processes. Charcoal is used to reduce pH. It is added to the soil for flowers (for example, for orchids) and other plants.
Beneficial impurities
Plant soil structures are mainly used in landscaping. But the scope of structures with various "useful" impurities is much wider due to the inclusion of stones, clay and other components. What is the percentage of required beneficial ingredients? As a rule, fertile soil is a combination of 50% peat, 30% chernozem and 20% sand. Thus, it contains a high content of organic compounds and minerals. Fertile soil is highly waterproof. This structure provides complete nutrition of cultivated plants, regardless of their stage of growth.
At agro-technical enterprises, farms, as well as in private areas, fertile soil is used quite actively. He copes well with the tasks that are set in the process of growing cultural plantings. Of particular importance is that it helps to improve the structure of the soil, increases productivity. In addition to everything, this mixture does not need additional fertilizer use.
How to improve the structure of the soil?
For poor stony and sandy soils, rotted manure mixed with straw is used. It is better to give preference to horse rather than cow. It helps retain moisture and beneficial components in the root system of plants. But fresh manure cannot be added. For the same purpose, garden compost can be used. A mixture of rotted horse manure, lime and peat is called mushroom compost. If in neutral soils it is necessary to create a slightly alkaline reaction, then such a mixture is perfect. Leaf humus is suitable for plants that require acidic soil, that is, for hygrophilous acidophils. It condition, mulch and acidify the earth. For the same purpose, you can use wood chips and sawdust. Peat is used to oxidize the soil. It decomposes quickly, but contains virtually no nutrients. In winter, you can use bird feathers, which are rich in phosphorus. They are also added to areas where potatoes are supposed to be planted. To improve the permeability and structure of clay soils, crushed wood is used. The bark is also used for mulch, due to the appearance and qualities. It is advisable to use an air conditioner at the same time or instead of applying organic fertilizers. Sites of soil that are only planned to be sown are dug up and mixed with them several months before the start of planting. To fertilize already planted plants, the soil is enriched with a layer of mulch from conditioning organic materials with fertilizers at the very beginning and end of the season.