The yield strength is the stress corresponding to the residual elongation after unloading. The determination of this value is necessary for the choice of metals used in production. If you do not take into account the considered parameter, then this can lead to an intensive process of development of deformation in the wrong material. It is very important to consider yield strengths when designing various metal structures.
Physical characteristic
Yield strengths relate to strength indicators. They are macroplastic deformation with a rather small hardening. Physically, this parameter can be represented as a characteristic of the material, namely: stress, which corresponds to the lower value of the yield point in the graph (diagram) of tensile materials. The same can be represented in the form of the formula: σ T = P T / F 0 , where P T means the yield stress and F 0 corresponds to the initial cross-sectional area of the sample in question. PT establishes the so-called boundary between the elastic-plastic and elastic zones of deformation of the material. Even a slight increase in voltage (above the PT) will cause a significant deformation. The yield strengths of metals are usually measured in kg / mm 2 or N / m 2 . The value of this parameter is influenced by various factors, for example, heat treatment mode, sample thickness, the presence of alloying elements and impurities, type, microstructure and defects of the crystal lattice, etc. The yield strength varies significantly with temperature. Consider an example of the practical value of this parameter.
Pipe yield strength
The most obvious is the influence of this value in the construction of pipelines of high pressure systems. In such constructions, special steel should be used, which has sufficiently large yield strengths, as well as minimum break indicators between this parameter and tensile strength. The greater the steel limit, the naturally higher should be the indicator of the permissible value of the operating voltage. This fact has a direct impact on the value of the strength of steel, and accordingly, of the whole structure as a whole. Due to the fact that the parameter of the permissible calculated value of the stress system has a direct effect on the required wall thickness in the pipes used, it is important to accurately calculate the strength characteristics of the steel that will be used in the manufacture of pipes. One of the most authentic methods for determining these parameters is to conduct a study on a discontinuous sample. In all cases, it is required to take into account the difference in the values of the indicator in question, on the one hand, and the permissible stress values, on the other.
In addition, you should know that the yield strength of a metal is always set as a result of detailed reusable measurements. But the system of permissible voltages is overwhelmingly accepted on the basis of standards or generally as a result of the technical conditions, as well as based on the personal experience of the manufacturer. In trunk piping systems, the entire regulatory collection is described in SNiP II-45-75. So, setting the safety factor is a rather complicated and very important practical task. The correct determination of this parameter entirely depends on the accuracy of the calculated values of stress, load, and also the yield strength of the material.
When choosing thermal insulation, piping systems also rely on this indicator. This is due to the fact that these materials directly come into contact with the metal base of the pipe, and, accordingly, can take part in electrochemical processes that adversely affect the state of the pipeline.
Stretching materials
The tensile yield strength determines at what value the stress will remain unchanged or decrease, despite the elongation. That is, this parameter will reach a critical point when a transition from the elastic to plastic region of deformation of the material occurs. It turns out that the yield strength can be determined by testing the rod.
PT calculation
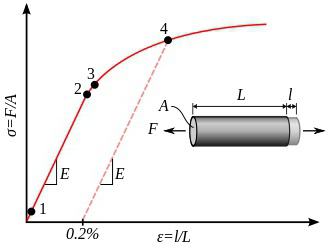
In the resistance of materials, the yield strength is the stress at which plastic deformation begins to develop . Let's look at how this quantity is calculated. In experiments conducted with cylindrical samples, determine the value of the normal stress in the cross section at the time of the occurrence of irreversible deformation. The same method in experiments with the torsion of tubular samples determine the yield strength at shear. For most materials, this indicator is determined by the formula σ T = τ s √3. In some instances, the continuous elongation of a cylindrical specimen in the diagram of normal stress versus elongation leads to the detection of a so-called yield tooth, that is, a sharp decrease in stress before the formation of plastic deformation.
Moreover, a further increase in such distortion to a certain value occurs at a constant voltage, which is called physical PT. If the yield area (horizontal plot of the graph) has a large length, then such a material is called perfectly plastic. If the diagram does not have a pad, then the samples are called hardened. In this case, it is impossible to accurately indicate the value at which plastic deformation will occur.
What is the conditional yield strength?
Let's see what this parameter is. In cases where the stress diagram does not have pronounced areas, it is required to determine the conditional PT. So, this is the stress value at which the relative permanent deformation is 0.2 percent. To calculate it on the stress diagram along the axis of determination of ε, it is necessary to postpone a value equal to 0.2. From this point a straight line is drawn parallel to the initial section. As a result, the point of intersection of the straight line with the line of the diagram determines the value of the conditional yield strength for a particular material. Also, this parameter is called technical PT. In addition, the conditional yield strengths for torsion and bending are separately distinguished.
Melt Flow
This parameter determines the ability of molten metals to fill linear forms. Melt flow for metal alloys and metals has its own term in the metallurgical industry - fluidity. In fact, this is the reciprocal of the dynamic viscosity. The international system of units (SI) expresses fluidity in Pa -1 * s -1 .
Tensile strength
Let's look at how this characteristic of mechanical properties is determined . Strength is the ability of a material, under certain limits and conditions, to perceive various influences without being destroyed. Mechanical properties are usually determined using conditional tensile diagrams. For testing, standard samples should be used. Testing devices are equipped with a device that records a diagram. An increase in excess loads causes a significant plastic deformation in the product. The yield strength and tensile strength correspond to the greatest load preceding the complete destruction of the sample. In ductile materials, deformation focuses on one area where local narrowing of the cross section appears. It is also called the neck. As a result of the development of multiple slides, a high dislocation density is formed in the material, and so-called embryonic discontinuities also arise. Due to their enlargement, pores appear in the sample. Merging together, they form cracks that propagate in the transverse direction to the axis of extension. And at a critical moment, the sample is completely destroyed.
What is PT for rebar?
These products are an integral part of reinforced concrete, intended, as a rule, to resist tensile forces. Steel reinforcement is usually used, but there are exceptions. These products must work together with the mass of concrete at all stages of loading of this structure without exception, have plastic and durable properties. And also meet all the conditions for the industrialization of these types of work. The mechanical properties of steel used in the manufacture of reinforcement are established by the relevant GOST and technical specifications. GOST 5781-61 provides for four classes of these products. The first three are for conventional structures, as well as non-tensioned rods in prestressed systems. The yield strength of reinforcement, depending on the product class, can reach 6000 kg / cm 2 . So, in the first class this parameter is approximately 500 kg / cm 2 , in the second - 3000 kg / cm 2 , in the third 4000 kg / cm 2 , and in the fourth - 6000 kg / cm 2 .
Steel yield strength
For long products in the basic version of GOST 1050-88, the following PT values are provided: grade 20 - 25 kgf / mm 2 , grade 30 - 30 kgf / mm 2 , grade 45 - 36 kgf / mm 2 . However, for the same steels manufactured by prior agreement between the consumer and the manufacturer, the yield strengths may have different values (the same GOST). So, grade 30 steel will have a PT in the amount of 30 to 41 kgf / mm 2 , and grade 45 - in the range of 38-50 kgf / mm 2 .
Conclusion
When designing various steel structures (buildings, bridges, etc.), the yield strength is used as an indicator of the strength standard when calculating the allowable loads according to the specified safety factor. But for vessels under pressure, the allowable load is calculated on the basis of PT, as well as tensile strength, taking into account the specification of operating conditions.