This pathology, which is life-threatening and has serious consequences, is experienced by 10-15% of women. You need to know about the symptoms, signs in the early stages and the treatment of an ectopic pregnancy in order to avoid complications. It is important to understand that the occurrence of such a pathology is quite unpredictable.
Next, we consider in detail the signs, treatment of an ectopic pregnancy, the causes and risk factors, the consequences of this condition for the general health and reproductive function of a woman. It is worth noting that the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy in the future is extremely high if you diagnose and begin treatment of the pathology in time.
Even with one fallopian tube (if the second is removed during an ectopic pregnancy), you can successfully become pregnant and have a healthy baby. Within 18 months after such a pathology and subject to the elimination of the reasons that provoked it, six out of ten women again find themselves in an interesting position. This time the pregnancy develops normally.
What is an ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious pathology that poses a threat to a woman's life. Normally, a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine cavity, but in some cases the egg may not enter the uterus and attach itself to where it is. As a rule, the ovum is attached to the wall of the fallopian tube. The tube has a thickness of one millimeter to one and a half centimeters, cannot stretch like a uterus, so at some point there is not enough space for the development of the fetus.
At about the fourth to sixth week of the development of a pathological pregnancy, the membrane of the embryo grows into the wall of the tube. As a result, the fallopian tube ruptures, bleeding opens into the abdominal cavity. At the same time, the woman feels a sharp and very severe pain in the lower abdomen, signs of early toxicosis, dizziness, she may lose consciousness. In case of damage to a large vessel, there is a risk of heavy bleeding and significant blood loss, which can be deadly for a woman.
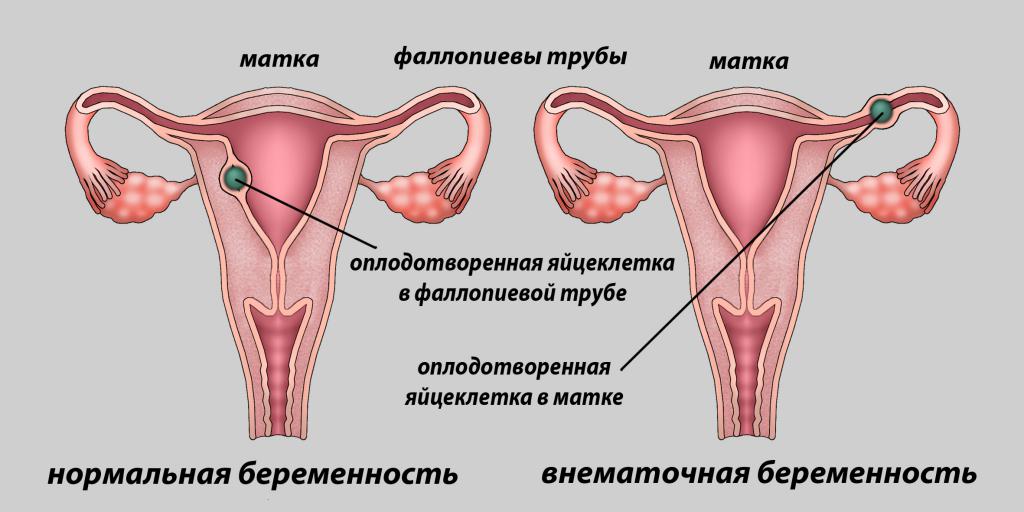
In some cases, an ectopic pregnancy breaks the wall of the fertilized egg, rather than the tube. In this case, the egg is expelled into the abdominal cavity through the end of the tube. In medical practice, this situation is called tubal abortion. The condition is also accompanied by paroxysmal pain in the lower abdomen, which in some cases cannot be tolerated, weakness, dizziness, drowsiness. All symptoms develop more slowly than with a break, so that a woman, when the pain subsides, might think that everything is in order. But bleeding into the abdominal cavity, which continues even after the pain subsides, can lead to the same serious consequences as an ectopic pregnancy, interrupted by a rupture of the tube.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
The treatment of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages is directly dependent on the reasons that provoked it. The risk of such a pathology increases in women after 35 years. It is especially necessary to carefully monitor your condition for those women who have a history of chronic inflammatory diseases caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma or mycoplasma, those who have already undergone therapy for hormonal or tube infertility. At risk are also women with congenital anomalies in the structure and development of the genital organs, endometriosis, and chronic miscarriage. WB can provoke the use of an intrauterine device as a contraceptive.
The main cause of WB is a blockage of the pipe or violation of its contractions. This occurs with congenital problems of the development of the female reproductive system, hormonal disorders and various infectious and inflammatory processes in both acute and chronic course, tumors of a benign or malignant nature, localized in the genital area.
Previously transferred gynecological diseases can cause adhesions and cords to appear in the tubes, which prevent the fetal egg from reaching the uterine cavity in time. As a result, enzymes that soften the mucosa for successful implantation begin to be secreted when the fertilized egg is still in the tube. After inflammation, the transport function of the tubes may also be impaired, problems can occur after surgery on the genitals, with hormonal dysfunction, or if removal of the fallopian tube has previously taken place.
The first signs of an ectopic pregnancy
In the early stages, treatment of VB will help maintain a woman's reproductive health, but in order to start therapy, one must first recognize the pathology. The clinical picture in WB develops over a long period of time. It is characterized by doubtful and probable signs of a normally developing pregnancy, as well as symptoms of spontaneous tubal interruption. In the early stages (four to six weeks), the pathology is almost asymptomatic. For a long time, the manifestations are the same as during normal pregnancy:
- The dubious symptoms of doctors include early toxicosis, drowsiness and weakness, a change in taste and smell, excessive tearfulness, emotionality, and frequent mood changes.
- Probable signs of pregnancy (both physiologically normal and ectopic) are considered to be a delay in menstruation, increased sensitivity and an increase in the mammary glands. With a delay, women who have experienced WB often have bouts of pain in the lower abdomen, which are given to the perineum. Scanty spotting may appear.
With a slight intra-abdominal blood loss, the general condition rarely worsens so much that a woman decides to consult a doctor immediately.
Signs that indicate the eruption of the ovum into the abdominal cavity and bleeding include:
- strong and very intense pains that give to the right hypochondrium, right clavicle and the area between the shoulder blades;
- fainting, vomiting and nausea, severe dizziness, general weakness;
- in laboratory blood tests - an increase in ESR, signs of hypochromic anemia, a decrease in hemoglobin;
- detection of a fertilized egg with an embryo near the body of the uterus is an absolute sign of WB, which can be detected by ultrasound;
- when studying the concentration of hCG in dynamics, the hormone level does not correspond to the gestational age, it grows more slowly than physiological (this may be a sign of complicated normal implantation, so a comprehensive study of the patient's condition is necessary to confirm an ectopic pregnancy).
Symptoms (treatment depends on the severity of the manifestations, in the early stages, as a rule, you can hope for the most favorable outcome of the situation, that is, without removing the fallopian tube) can manifest gradually, often they are mild. But the manifestations are usually enough to suspect something was wrong and consult a doctor. It is important that a home test shows WB in the same way as a normal one, and a dangerous condition can be diagnosed only with the help of a doctor. That is why, after you see two strips on the test, it is advisable to sign up with a gynecologist. The doctor will confirm the normal conception or determine the pathology, which will allow timely treatment of an ectopic pregnancy to begin.
Tubal abortion: clinic and diagnosis
In the case of spontaneous tubal abortion in WB, the clinical picture develops for a long time. Patients feel severe pain in the lower abdomen (as with menstruation, only much more intense), they are usually cramping, in fits. Dark red vaginal discharge is characteristic due to an altered uterine lining due to interruption.
The severity of symptoms depends on the rate of blood loss and the amount of blood that has poured into the abdominal cavity from the fallopian tube. With minor blood loss, the patient may not feel any alarming symptoms, and the pain may be minor. In this case, it is rather difficult to identify the pathology. If more than 0.5 l of blood has entered the abdominal cavity, severe pain appears with nausea, vomiting, fainting, dizziness, general weakness.
Among the methods for diagnosing WB can be listed:
- History and analysis of the nature of the discharge. As a rule, with WB, vaginal discharge is not bright red, but dark brown, reminiscent of the color of coffee grounds.
- Laboratory blood test. Blood levels of hemoglobin (elevated in WB), ESR (also elevated) are determined, a shift to the right of the leukocyte formula and a clinical picture of anemia by hypochromic type are characteristic.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis. With ultrasound with a vaginal probe, abnormal egg localization can be determined already in the sixth week, if a sensor is used that is located on the surface of the abdomen, then the diagnosis can be made in the eighth to tenth week. The doctor examines the results of ultrasound in combination with other research methods.
- Determination of hCG in the blood over time. With the normal location of the fetus, the level of chronic human gonadotropin doubles daily; in the case of abnormal localization of the embryo, such a pattern is not observed. The information content of this method is 96.7%.
- A sample of fluid from the peritoneum. At the same time, a sample of the fluid located in the abdominal cavity is taken through the back wall of the vagina. The material is examined for blood. Puncture results can be either false positive or false negative if the procedure is performed incorrectly.
- Curettage of the uterine cavity and histology of the endometrium. This method is used to diagnose and differentiate an incomplete miscarriage during physiologically localized pregnancy and uterine bleeding caused by organ dysfunction.
- Laparoscopy. This is the most accurate diagnostic method. Inspection through a small incision helps to inspect the fallopian tubes, assess the presence and amount of blood in the peritoneum.
If it is possible to correctly identify the signs of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages, the treatment will be sparing. In this case, it is possible to remove the fetal egg while maintaining the fallopian tube.
Clinic and diagnostics of pipe rupture
In the event of a rupture, the pipe symptoms are bright enough, so that does not create any problems in the diagnosis. Signs of a rupture are due to abdominal bleeding. Among the symptoms of a gap can be listed:
- pain from the side of the tube in which the fetal egg is fixed;
- loose stools, burning, cutting pains in the rectum without excretion of feces;
- pain is given to the right clavicle, rectum;
- severe weakness, fainting, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- cold sweat, shortness of breath;
- sharp pain in the abdomen when palpating;
- symptoms of peritonitis;
- lethargy, inhibition of the reaction in the patient;
- weak pulse, decreased blood pressure;
- bloating, palpable tension in the lower part;
- all other signs of hemorrhagic shock.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor may detect blueness of the vaginal mucosa. Enlarged sizes and excessive uterine mobility, soreness, overhanging of the posterior vaginal fornix, and spotting from the uterus are usually absent. The clinical picture is usually so vivid that there is no need for additional diagnostics.
The clinic of rare forms of WB is usually similar to the manifestations of a pipe rupture. The final diagnosis in this case is established during the treatment of an ectopic pregnancy by surgery.
Progressive Pregnancy
A very important diagnosis of an ongoing ectopic pregnancy. The timing of treatment should not be missed, otherwise there is a risk of death. A progressing pathological pregnancy is complicated by the fact that there are no symptoms of an “acute abdomen”, and the patient's condition repeats the signs of physiologically normal attachment and further development of the fetal egg. Patients have all the signs of a normal pregnancy, but when examined, the size of the uterus does not match the expected period, the presence of soft formations in the area of the appendages, pain on palpation. With a short period of time, the increase in the fallopian tube is not possible to determine due to its small size. For timely diagnosis, the previously listed methods are crucial: ultrasound, blood test, laparoscopy, determination of the amount of hCG in the blood.
Diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy
Three to seven days after the delay (and in any case, regardless of whether the test was positive or negative), it is advisable to visit a gynecologist. The doctor will allow you to establish a pregnancy and determine whether it is developing normally. Women who have a delay of critical days accompanied by spotting with an admixture of blood from the vagina, are shown an ultrasound using a vaginal sensor. If the gynecologist has any suspicions, he will offer the patient to stay in the hospital. In a medical clinic equipped with all necessary modern equipment, you can conduct additional research. This will help determine exactly whether the embryo is correctly localized, so you should not refuse hospitalization.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Therapy consists in stopping intra-abdominal bleeding by surgery, restoring hemodynamic parameters (blood flow velocity), and rehabilitating menstrual and reproductive functions. Let us consider in more detail the treatment after an ectopic pregnancy with removal of the tube, and without it. We will also talk about conservative methods of therapy. In conclusion, we will determine what treatment is necessary to undergo after an ectopic pregnancy for the subsequent successful conception, gestation and the birth of a healthy baby.
Surgical intervention
After determining both spontaneously interrupted and progressive WB, surgery is urgently performed - this implies a standard for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy. An indication for surgery is also hemorrhagic shock. Most often, with WB, the fallopian tube is removed, but in some cases conservative-plastic interventions are performed:
- Squeezing a fertilized egg.
- The section of the tube and the subsequent removal of the fertilized egg (with small egg sizes).
- Pipe segment resection (partial removal).
Treatment after an ectopic pregnancy with removal of the tube is carried out if previously there was a WB, in which a conservative intervention was performed. Also indications are:
- spontaneous pipe rupture;
- large egg sizes (more than 3 cm in diameter);
- unwillingness of pregnancy in the future;
- cicatricial changes in the tube.
When carrying out organ-preserving surgery (that is, when squeezing a fetal egg or removing it through a small incision), the risk of recurring WB increases in the future.
Conservative treatments
If the pathology is detected at an early stage, drug treatment of an ectopic pregnancy is possible. Now among doctors there is no single opinion about conservative therapy for such patients, dosage of drugs, route of administration and duration of treatment, however, such methods are also used in some cases. They are used to treat ectopic pregnancy without methotrexate injection, the administration of which is controlled by transvaginal ultrasound monitoring. This method is often accompanied by complications, as a result it can result in a laparotomy - the need to make a small incision to gain access to the organs in the abdominal cavity.
Drug treatment of ectopic pregnancy is possible with egg sizes of no more than two to three centimeters in diameter, and only under the control of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy allows you to assess the condition of the patient, determine the presence or absence of WB, determine a safe puncture point, and provide the necessary manipulations. Dynamic allows, in addition, to daily monitor the condition of the pipe after the introduction of medicines.
Conducted, as already mentioned, conservative treatment of ectopic pregnancy with Methotrexate. This is a drug that causes the death of the embryo, preventing the further division of its cells. There are several regimens for using the medicine. The exact treatment of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages (duration of the course, dosage of the drug) will be selected by the doctor. But a woman needs to know that this method is not suitable for everyone and not in all cases.
Most doctors agree that conservative methods of treating an ectopic pregnancy can be effective. But still, such therapy requires additional study. The consequences of drug treatment of an ectopic pregnancy are also not completely clear. So now the surgical method of therapy remains the most preferred.
Expectant Tactics
. . , . . :
, , . , , , , .
– ? - , . , .
The embryo, attaching itself in the “wrong” place, that is, in the fallopian tube, and not in the uterus, begins to grow and develop. This happens before a certain date. At some point, the substance ceases to be enough for the embryo, there is little space, and the pipe wall can no longer stretch, resulting in a rupture. If the diagnosis and treatment of an ectopic pregnancy has not been carried out, then the following rupture consequences occur:
- Eruption of a fertilized egg (which has already become an embryo) into the abdominal cavity and spontaneous interruption. Most often this happens in the seventh to eighth week. In general, the largest number of spontaneous abortions (including during normal pregnancy) occurs at 8 weeks.
- The formation of the placental site at the site of implantation. This is the name of the area on which an additional vascular network appears, which is necessary for the delivery of the necessary nutrients to the embryo. With spontaneous abortion, the vessels do not overlap, bleeding occurs. In the event of a spontaneous abortion, the uterus would contract and the bleeding would stop, but if it is attached to the tube, the blood vessels will bleed for a long time. Urgent surgery is required.
- A rupture of a pipe causes a condition that threatens a woman’s life — bleeding, which can be fatal in just a few hours.
- If no measures are used to stop bleeding in the abdominal cavity, this can provoke the development of peritonitis. In the late stage of this inflammation, deeply impaired functions develop that are vital to the body.
What are the consequences of an ectopic pregnancy? Treatment (if it was carried out on time and was adequate, passed without complications) allows in some cases to save the fallopian tube. This is the most favorable situation. However, it is not always possible to remove the fetal egg and perform plastic surgery. In emergency cases, the simplest, fastest and most effective methods are used to save a woman's life.
If an ectopic pregnancy was not diagnosed in a timely manner, profuse bleeding and pain shock are possible. Urgent surgical intervention will save the patient's life, even if both fallopian tubes will be removed. A subsequent healthy pregnancy is possible with one tube, but if both are removed, in vitro fertilization remains.
In any case, during the rehabilitation period, a full examination is carried out, the main purpose of which is to find out the cause of VB. Further treatment after surgery for ectopic pregnancy eliminates these causes.
Ectopic Pregnancy Prevention
Prevention of WB involves the timely treatment of any gynecological diseases and inflammatory processes. When planning pregnancy, you need to undergo a comprehensive medical examination and be treated if necessary. It is advisable that the examination be carried out with the woman also a regular sexual partner. In addition, you need to pay attention to quality contraception, because among the causes of WB, abortion in the past remains one of the main causes.
Pregnancy after an ectopic
After an ectopic, a physiological pregnancy is possible if the tubes have not been removed or only one of them has been dissected. In the event that a woman removed both of them during a surgical procedure, pregnancy is possible only with the help of IVF; Difficulties with conception can also occur if only one tube is removed: a fertilized egg may need to go twice as long (if it leaves from the side where there is no tube).
After the operation, considerable importance should be given to methods of contraception, protection from pregnancy in the near future. It is preferable to use combined contraceptives for oral use. Before the next attempts at conception, the duration of protection should be at least six months, sometimes it is even recommended to refrain from trying to conceive a child for a year. The exact recommendations in this regard will be given by a gynecologist who constantly watches the woman. In some cases, the doctor may allow the couple to attempt to get pregnant as early as 3 months after WB.