The economic status of each constituent entity of the Russian Federation makes it relevant to use a variety of tools to assess economic well-being, financial balance and competition conditions not only in the domestic, but also in the world market. These tools are essential for the implementation of an effective federal policy, which is aimed at eliminating imbalances of the interregional type, and strengthening the integrity of the economy and politics. The independence of the regions leads to the updating of regional policy and to the significance of such an indicator as regional gross product.
Information support using GRP
The prosperity of fiscal federalism becomes the urge to develop regional management decisions with modern approaches to information support and economic feasibility. The optimal basis for analyzing the characteristics of a complex market economy is the system of national accounts, or SNA. At the regional level, the SNA is in the format of the CDS (regional accounts system). The central position in the SNA belongs to gross domestic product, or GDP. The regional equivalent of GDP in the SNA is the regional gross product, or RVP. This indicator shows the level of economic development, is a kind of reflection of the results of economic activity of each of the business entities within the region. GRP is used as the basis for the formation of regional accounts.
Why is GRP calculated?
On the territory of Russia there are about 89 administrative-territorial entities located in different time zones, differing in geographical location and level of economic and social development. GDP reflects only the general situation in the country, not allowing to see clearly how things are in its different corners, which excludes the possibility of making objective decisions. The state is interested in data that can comprehensively characterize the situation in each individual corner of the country.
Differentiated information, the source of which is the regional gross product, allows you to develop a suitable economic policy and evaluate the effectiveness of decisions not at the country level, but at the regional level. With the help of GRP dynamics, in combination with cost and in-kind indicators, it is possible to establish the direction and intensity of economic processes, which can serve as a strong impetus for development at the interregional level. GRP plays a large role in the calculation of macroeconomic indicators and in the reform of interregional relations. The indicator serves as a guideline in the process of allocating funds from the “Fund for the financial support of the regions of the Russian Federation”.
So what is GRP?
The regional gross product is, in fact, a generalized economic indicator characterizing the level of economic development of the region. It reflects and characterizes the process of production of goods and services. The volume of GRP indicates the value of all released goods and services in all economic sectors in a particular region. At the first stages of introducing the indicator into economic analysis, data were published taking into account market prices. GRP assessment in the format of basic prices differs significantly from the market assessment by exactly the amount of net taxes on products. Subsidies are not taken into account. GRP in the dominant workshops reflects the amount of value added at basic prices with a focus on a specific type of economic activity.
GRP structure, or What is included in it
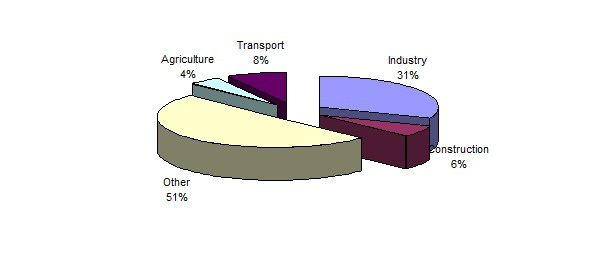
The gross regional product is calculated taking into account the basic price, which is calculated per unit of product or service. Taxes are not taken into account, but subsidies for products are taken into account. Gross value added is calculated in each individual segment of economic activity as the difference between the output of goods or services and their intermediate consumption. For the reporting period, the total price of the release of goods and services within one region is the volume of output. The issue includes goods already sold with services at market value. For calculation, the average value is used. Work in progress is recorded in gross output, but only at cost. Intermediate consumption includes the cost of goods with services that are fully used in production during the reporting period. Fixed capital does not play a role in calculating intermediate consumption. The costs of the final use of GRP include expenses for households, government agencies, and collective services. Estimating the volume of gross regional product and its structure, it is possible to determine the sources of financing of final consumption.
Calculation options
In the modern economy, it is customary to use several options for calculating the GRP. The production method for calculating the indicator is used at the production stage. It is, in fact, the sum of the gross value added, which is formed by each resident institutional unit in the region’s economic territory. The gross regional product, the calculation of which is based on the difference between the output of goods and services and their intermediate consumption, is formed on the basis of prices for goods and services that are fully consumed in production, and is carried out at the level of industries and sectors of the region’s economy. GRP can also be calculated on the basis of current market prices by comparing them.
The difference between GDP and GRP
The gross regional product, which is calculated for each of the regions, has significant differences from GDP. The difference between the indicators is the amount of value added. This may include:
- Non-market collective services of state bodies: defense, management.
- Non-market services financed from the budget, but information about them is not available at the regional level.
- Services of financial institutions, whose activities almost always go beyond the framework of one region.
- Services related to foreign trade, data for which is collected at the Federal level.
Gross Product: Indicator Features
The difference between GDP and GRP is formed by the costs of paying taxes in connection with import and export. This value is very difficult to calculate due to its specificity and uneven integration between individual regions. Gross regional product by region is calculated over a period of 28 months. SAC technique allows you to get a faster result. The government uses many mechanisms to track the dynamics and growth of the indicator. An interesting fact is that, in sum, all GRP indicators do not correspond to GDP, which is determined by the specifics of the calculations and the exclusion of value added.
Based on what data is GRP calculated?
The multifaceted structure of gross regional product determines the simultaneous use of a large number of sources for calculating parameter values. So, in the CIS countries, experts take into account business registers and reports on the production and sale of goods with services, reports on production costs. Sample surveys and special reporting at the regional level are taken into account. The calculation is based on employment reports and on the basis of surveys of each individual segment of the economy, based on a survey of household budgets. Significant sources of information are the data of tax authorities and banking statistics, reports of public organizations and data on the implementation of different types of budgets.
GRP in the practice of Russia
The gross regional product for the regions of Russia fully characterizes the level of development of the region and is compared with macro-level indicators. It plays the role of a territorial factor in the development of social and economic processes. The value calculation uses the methodological principles of the SNA, the development of which was carried out within the framework of the FSGS. The publication of the results after their preliminary approval is also carried out at the level of the FSGS.
Prediction of gross regional product is based on data collected from all residents of the regional economy. These may be corporations, quasi-corporations, and households with a center of economic interest located directly in the region in question. The first calculation and analysis of gross regional product was carried out in 1991 in 21 regions. Since 1993, all regional-territorial authorities took part in the calculations. Since 1995, the assessment and calculation of GRP has been a prerequisite for the implementation of the "Federal Program". Only in 1997, an assessment of the dynamics of the indicator began. It provides the basis for the implementation of the right economic policy in the sphere of production and industry, which in almost all regions account for 60 to 80 percent of the total GRP.