Under the hood of any car is, of course, an engine. This device is designed so that the thermal energy that is supplied to the system through fuel is converted into mechanical energy . Any engine consists of a great many auxiliary and complementary parts and mechanisms that interact with each other, thus putting the car in motion. All this and much more are the constituent elements of science called the “ICE theory”. In order to learn more about it, you must first deal with the details.
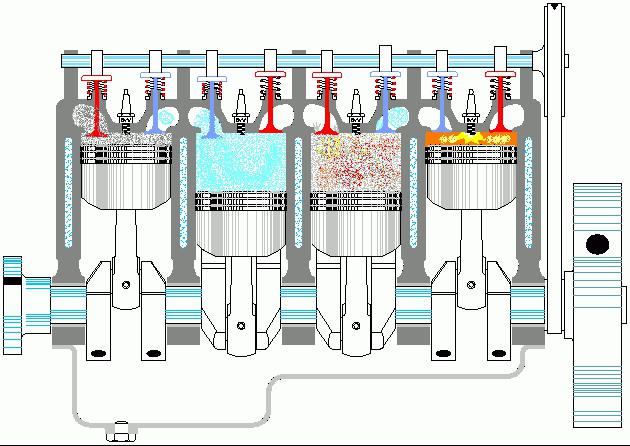
So, the main parts that trigger the mechanism are the cylinders. The theory of internal combustion engines suggests that in cars of a new type, their number can range from 2 to 15 pieces. The movement of the machine, first of all, depends on how the cylinders are located. There are five options. Linear position is the most common (assumes gradual wear and smooth running). The V-shaped position of the cylinders can significantly save space under the hood, however, significantly increases vibration, reducing the level of crankshaft balancing. The opposition position, unlike the previous version, takes up a lot of space, however, with it the car goes smoothly, all the details work smoothly, and the vibration is almost inaudible. Also, cylinders can be arranged by analogy with the letter W, which is characteristic of only a few models. And the fifth, final, type of cylinder placement is a triangular rotor-piston, which is mounted only in racing models.
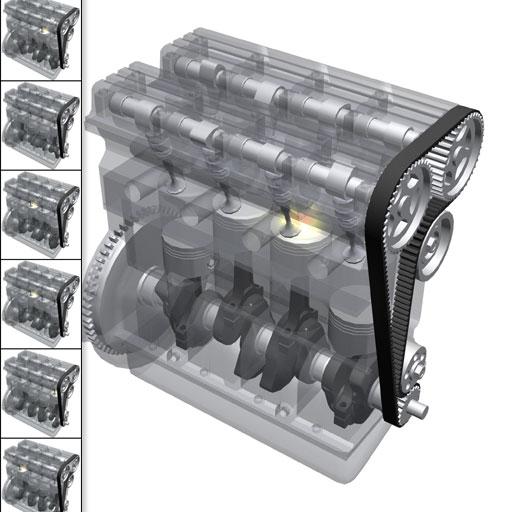

The calculation of internal combustion engines, as a rule, begins with the determination of its volume. This indicator depends on the power of the machine, and it also affects fuel consumption. The higher the displacement, the more gas the car will “eat”.
It is worth noting that the ICE theory divides cars into four categories - subcompact, subcompact, mid displacement and large displacement. If the volume indicator does not exceed 3 liters in the first three types of machines, then in the latter case it can reach any number. As a rule, large-volume cars are SUVs and crossovers, and racing models equipped with a rotor-piston do not require a large amount of fuel, which will wear out very soon.
Often, motorists carry out engine tuning in order to finalize some of the technical characteristics of their car, increase its power and improve ride quality. Most often, this procedure includes an increase in the working volume of the engine, therefore, the torque increases and the machine acquires new technical indicators. Also, tuning can consist in increasing the compression force, due to which the efficiency is increased. In this case, fuel consumption does not increase, but rather decreases.
ICE theory also involves the study of such components as engine power, which is determined in horsepower, fuel supply system, fuel consumption, torque and many others. To work with the machine and, moreover, to make tuning of its internal parts, it is necessary to study in advance all the nuances that you can stumble upon in such a job.