Marginal utilities are the acquisitions that a person receives when using an additional unit of good. With pure competition, using this indicator, you can determine the market price of the goods.
Quick reference
We can say that the law of marginal utility describes an increase in the total benefit in terms of consumption of an additional unit of good. This principle was set forth almost simultaneously by three major economists: Leon Walras,
Karl Menger and Stanley Jevons. The latter set forth his own ideas on this issue in a lecture that was published in 1866. Karl Menger talked about this issue in 1871 in The Foundations of Political Economy.
Leon Valras addressed this issue in 1874. At the same time, all three worked on this issue independently. Note that marginal utility is the term coined by Friedrich von Wieser in economics. Consider the basic principle of this phenomenon. In accordance with it, the value of a good of a certain kind is determined in accordance with the utility of the ultimate instance, which satisfies the least urgent need.
Story
“Marginal Utilities” is a concept that modern economists first addressed when they worked on the theory of value. Consider what scientists are investing in this term today. They understand it as the least significant form of benefit brought by a certain good in the field of satisfying the needs of an individual. Suppose, for example, that bread can serve for distillation, livestock feed, sowing and nutrition. The first of the roles can be considered the least important. The ability of bread to satisfy this need can be considered its ultimate utility. Separately, attention should be paid to another important feature of this phenomenon. Even in relation to one need, the good is able to possess various marginal utility. As an example, we can consider the importance of bread for a hungry and well-fed person. The indicator of interest to us decreases with an excess of good and increases with its lack.
The fall
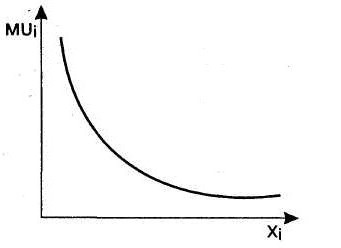
Now we discuss in more detail the law of diminishing marginal utility. He says that due to the increase in the consumption of goods, the general utility increases, but the speed of such a process slows down. Now take a look at the law of diminishing marginal utility from a mathematical point of view. We find out that the first derivative in the function of general utility is positive and depends on the consumption of the good. However, it is decreasing. Moreover, the second derivative is negative. A diminishing marginal utility looks like an increasing function that is convex upward. The indicator of interest to us decreases with increasing consumption. In conditions of maximum general utility, it vanishes. After that, marginal utility becomes negative. The total, in turn, reaches its maximum value and begins to decrease. For example, if we talk about a hungry person, for him the marginal utility of the very first plate of soup is much higher compared to the second. This is true for other types of benefits.
Limited applicability of the law
You can only compare products that include homogeneous units that are consumed by one person. For example, bananas and apples cannot be considered. Even slight differences can affect the final result. For example, red and green apples cannot be considered together. All units of the selected product must have the same quality and weight. For example, apples can be sour and sweet. The second product is able to provide greater customer satisfaction. The buyer is considered with unchanging tastes. No changes are expected in the incomes, preferences, customs and habits of the consumer. Changing one of these factors may affect the usefulness of the product, and the described law will not apply. Also, for the operation of the formula, continuity of consumption is necessary. If this condition is not taken into account, marginal utility may not decline. When there is a pause after consuming the first unit of a product, it is likely that the need for it will resume. Thus, a similar satisfaction will be observed from the next unit of good.
Interesting Facts
Marginal utilities are indicators that prove that lowering the price encourages consumers to increase the number of purchases of a particular product. However, the described law does not always apply. In particular, it may not work if the quantity of goods is small. This case can be illustrated by a medical example. For example, if a person drinks one tablet, he is not completely cured. If there are two, healing is fully possible. But further use of the pills can only harm the body. As a result, marginal utility will turn into negative.