The internal combustion engine is a brilliant invention of mankind. Thanks to ICE, technological progress began to develop significantly. There are several types of these settings. But the most famous are the connecting rod and piston and rotary piston. The latter was invented by German engineer Wankel in collaboration with Walter Freude. This power unit has a different device and principle of operation, when compared with the classic connecting rod and piston ICE. What is the principle of operation of the Wankel engine and why has this engine not become so popular? All of this we will consider in our article today.
Characteristic
So what is this motor? This is an internal combustion engine that was developed by Felix Wankel in 1957. The function of the piston in this unit was performed by a three-vertex rotor. He made rotational movements inside a cavity of a special shape.
After a series of experimental models of motorcycles and cars that fell on the 70s of the last century, the demand for the Wankel engine significantly decreased. Although today a number of companies are still working on improving this ICE. So, you can meet the Wankel engine on the Mazda PX series. Also, this unit has found its application in modeling.
Wankel engine device
This power unit consists of several components:
- Corps (stator).
- Combustion chambers.
- Inlet and outlet windows.
- Fixed gears.
- Gear wheel.
- Rotor.
- Vala.
- Spark plug.
What is the Wankel engine principle of operation? We will consider this below.
Principle of operation
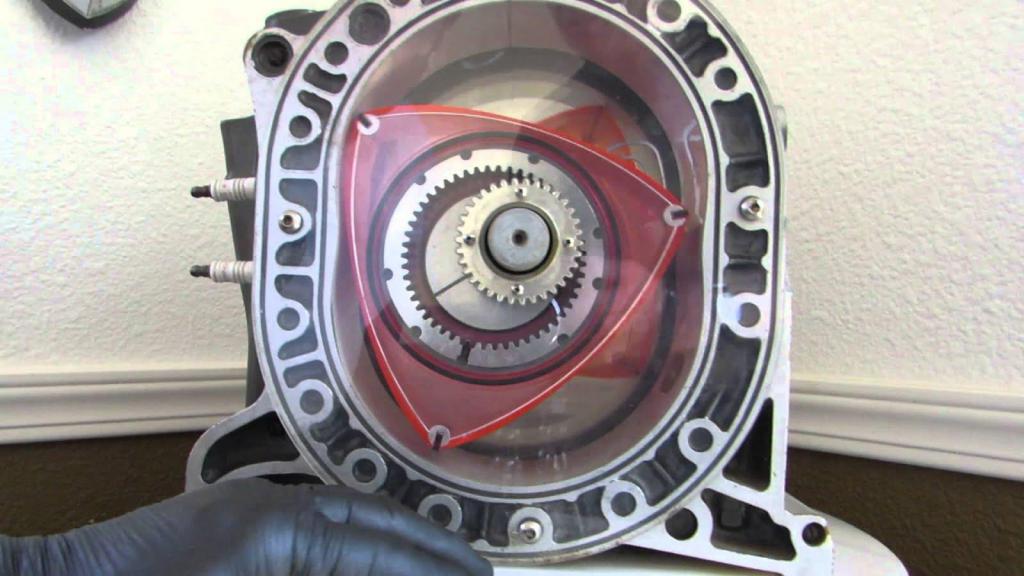
This ICE operates as follows. The rotor, mounted on an eccentric shaft through bearings, is driven by gas pressure, which was formed as a result of combustion of a fuel-air mixture. The rotor of the motor relative to the stator by a pair of gears. One of them (large size) is located on the inner surface of the rotor. The second (supporting) is smaller and tightly attached to the side cover of the engine. Thanks to the interaction of gears, the rotor makes eccentric circular movements. Thus, its faces are in contact with the inner surface of the combustion chamber.
As a result, several insulated chambers of variable volume are formed between the motor housing and the rotor. Their number is always 3. In these chambers, the mixture undergoes compression, combustion, expansion of gases (which subsequently exert pressure on the working surface of the rotor) and their removal. As a result of fuel ignition, the rotor is driven by transmitting torque forces to the eccentric shaft. The latter is mounted on bearings and then transfers power to the transmission units. And only then the moment of Wankel’s engine forces goes to the wheels according to the classical scheme - by means of a cardan drive and half shafts to the hubs. Thus, several mechanical pairs work simultaneously in a rotary motor. The first is responsible for the movement of the rotor and consists of several gears. The second de converts the movement of the rotor into revolutions of the eccentric shaft.

The gear ratio of the stator (housing) and gears is always stable and is 3: 2. Thus, the rotor manages to crank over a full rotation of the shaft by 120 degrees. In turn, a four-cycle cycle of operation of the internal combustion engine in each of the three chambers formed by the faces is performed for a full revolution of the rotor.
Benefits
What are the advantages of this engine? The Wankel rotary piston engine has a simpler design than a piston rod. So, the number of parts in it is 40 percent less than in a four-stroke internal combustion engine piston. But still, creating a Wankel engine with your own hands is not possible without sophisticated equipment. After all, the rotor has a very complex shape. Those who tried to make a self-made Wankel engine with their own hands suffered numerous failures.
But let's continue on the benefits. In the design of the rotor unit there is no crankshaft, gas distribution mechanism. There are also no connecting rods or pistons. The combustible mixture enters the chamber through the inlet window, which opens the face of the rotor. And the exhaust gases at the end of the working cycle are released housing through the exhaust window. Again, the role of the valve here is played by the edge of the rotor itself. Also, the design does not have a camshaft (of which several are now used on connecting rod units). The Wankel rotary piston engine is similar to a two-stroke engine according to the principle of the gas distribution mechanism.
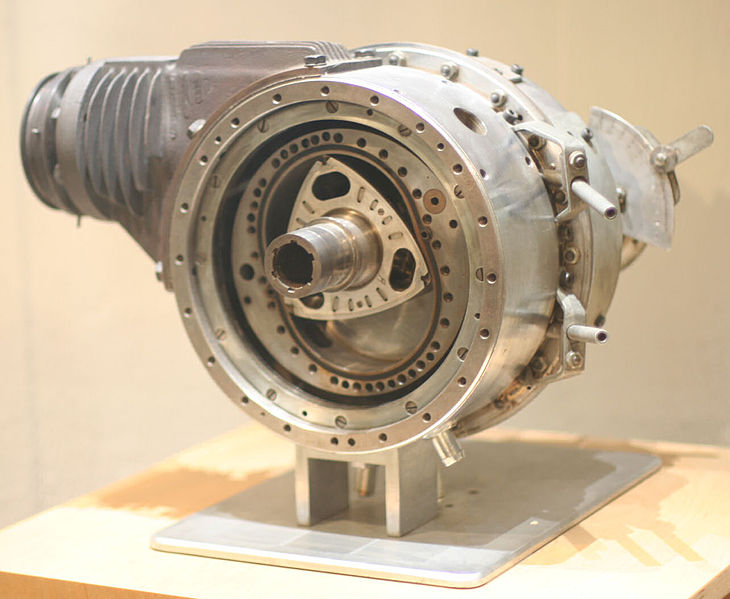
Separately, it is worth mentioning the lubrication system. In fact, it is absent in the Wankel rotary engine. But how then do friction pairs work? It's simple: oil is added to the combustible mixture itself (as in primitive motorcycle engines). Thus, the lubrication of rubbing parts is made by the fuel-air mixture itself. The design lacks the familiar oil pump for everyone, which takes grease from the sump and sprays it under special pressure.
Another advantage of the Wankel engine is its light weight and size. Since almost half of the parts that are mandatory in piston engines are missing here, the rotor unit is more compact and can accommodate in any engine compartment. its compact dimensions make it possible to use the space of the engine compartment more efficiently, as well as provide a more uniform load on the front and rear axles (after all, in cars with conventional engines more than 70 percent of the load falls on the front part). And due to its low weight, high stability is achieved. So, the engine has a minimum level of vibration, which positively affects the comfort of the machine.
The next plus of this unit is its high power density, which is achieved at high shaft speeds. This feature allows you to achieve good technical characteristics. That is why the Wankel engine is used on Mazda sports cars. The motor easily spins up to seven or more thousand revolutions. At the same time, it provides much more torque and power with a small volume. All this positively affects the acceleration dynamics of the car. For example, you can take the car "Mazda RH-8." With a volume of 1.3 liters, the engine produces 210 horsepower.
Design flaws
Considering the device and the principle of operation of the Wankel rotary engine, it is worth noting the main design flaw. This is the low efficiency of the gap seals between the combustion chamber and the rotor. The latter has a rather complex shape, which requires reliable sealing not only along the faces (of which four in total), but also along the side surface (which are in contact with the engine cover). At the same time, they are made in the form of steel spring-loaded strips with particularly precise machining both from the ends and from the working surfaces. All tolerances for expansion during heating, incorporated in the design, worsen these characteristics. Because of this, it is impossible to avoid a breakthrough of gases at the end faces of the sealing plates. In piston engines, however, the labyrinth effect is applied. So, three o-rings with gaps in different directions are used in the design.

But it is worth noting that in recent years, the quality of seals has increased. Designers have made improvements to the Wankel engine using new materials for seals. But still, a gas breakthrough is considered the weakest point in a rotary engine.
Oil consumption
As we said earlier, there is no lubrication system as such in this engine. Due to the fact that the oil comes with a combustible mixture, its consumption increases significantly. And if on connecting rod engines the natural lubrication is excluded or does not exceed 100 grams per 1 thousand kilometers, then on rotary engines this parameter is from 0.4 to 1 liters per thousand kilometers. This is because a complex sealing system requires more efficient surface lubrication. Also, due to the high oil consumption, these motors cannot meet modern environmental standards. The exhaust gases of cars with a Wankel engine contain many substances hazardous to the body and the environment.
In addition, the rotary motor could only work on high-quality and expensive oils. This is due to several factors:
- The tendency of the contacting parts of the engine chamber and rotor to high wear.
- The tendency of friction pairs to overheat.
Other problems
An irregular oil change threatened to decrease the ICE resource, as the old grease particles acted as an abrasive, increasing the gaps and the probability of an exhaust gas breakthrough in the chamber. This unit also wedges during overheating. And when driving in cold weather, cooling could be excessive.
The RPD itself has a higher operating temperature than any piston engine. The combustion chamber is considered the most loaded. it has a small volume. And because of its extended shape, the camera is prone to detonation. In addition to oil, the Wankel engine is demanding on the quality of candles. They are installed in pairs and changed strictly according to technical regulations. Among other points, it is worth noting the lack of elasticity of the rotary motor. So, these ICEs can produce excellent speed and power characteristics only at high rotor speeds - from 6 to 10 or more thousand per minute. This feature forces designers to refine the design of gearboxes, making them multi-stage.
Another disadvantage is the high fuel consumption. For example, if we take the Mazda RX-8 1.3-liter rotary piston engine, according to passport data, it consumes from 14 to 18 liters of fuel. Moreover, only high-octane gasoline is recommended for use.
On the use of RPD in the automotive industry
This engine received the greatest popularity in the late 60s and early 70s of the last century. The patent for the Wankel RPD was acquired by 11 leading automakers. So, in the 67th year, NSU developed the first business-class car with a rotary engine, which was called the NSU RO 80. This model was produced in series for 10 years. In total, more than 37 thousand copies were produced. The car was popular, however, the shortcomings of the rotary motor eventually tarnished the reputation of this car. Compared to other NSU models, the NSU RO 80 sedan was the most unreliable. Mileage to overhaul was only 50 thousand with the declared 100.
Peugeot Citroen Concerns, Mazda Company and VAZ Plant also experimented with rotary motors (we will discuss this case separately below). The greatest success was achieved by the Japanese, releasing a car with a rotary engine in the 63rd year. At the moment, the Japanese are still equipping RPDs on their RX series sports cars. To date, they are spared many of the "childhood diseases" that were inherent in the RPD of that time.
Wankel RPD and motor industry
In the 70s and 80s of the last century, some motorcycle manufacturers experimented with rotary engines. These are Hercules and Suzuki. Now the serial production of rotary motorcycles is established only at Norton. This brand produces NRV588 sportbikes equipped with twin-rotor engines with a total volume of 588 cubic centimeters. The power of the Norton bike is 170 horsepower. with a curb weight of 130 kilograms, this motorcycle has excellent dynamic characteristics. Additionally, these RPDs are equipped with an electronic fuel injection system and a variable intake manifold.
Interesting Facts
These power units are widely used among aircraft models. Since the model ICE does not have requirements for efficiency and reliability, the production of such motors turned out to be inexpensive. In such ICE rotor seals are not at all, or they have the most primitive design. The main advantage of such an aircraft model unit is that it is easy to install in a flying scale model. ICE is lightweight and compact.
Another fact: Felix Wankel, having received a patent for RPD in 1936, became the inventor of not only rotary engines, but also compressors, as well as pumps operating in the same way. Such units can be found in repair shops and in production. By the way, portable electric tire inflation pumps are designed exactly according to this principle.
RPD and VAZ cars
In Soviet times, they also engaged in the creation of a rotary piston engine and its installation in domestic VAZ cars. So, the first RPD in the USSR was the VAZ-311 engine with a capacity of 70 horsepower. It was created on the basis of the Japanese 13B unit. But since the creation of the motor was carried out according to unrealistic plans, the unit turned out to be unreliable after launching into mass production. The first car with this engine was the VAZ-21018.

But the story of installing the Wankel engine on a VAZ does not end there. The second was the power unit VAZ-415, which was used in small batches at the G8 in the 80s. This power unit had better technical specifications. Power with a volume of 1308 cubic centimeters increased to 150 horsepower. Thanks to this, the Soviet VAZ-2108 with a rotary engine accelerated to hundreds in 9 seconds. And the maximum speed was limited to 190 kilometers per hour. But this engine was not without flaws. In particular, it is a small resource. He barely reached 80 thousand kilometers. Also among the minuses it is worth noting the high cost of creating such a car. Oil consumption was 700 grams per thousand kilometers. Fuel consumption - about 20 liters per hundred. Therefore, the rotor unit was used only on special services vehicles, in small batches.
Conclusion
So, we found out what the Wankel engine is. This rotary unit today is used in series only on Mazda vehicles, and only on one model. Despite numerous improvements and attempts by Japanese engineers to improve the design of the RPD, it still has a rather small resource and a high oil consumption. Also, the new 1.3-liter Mazda does not differ in fuel efficiency. All these shortcomings of the rotary motor make it impractical and underutilized in the automotive industry.