In the article, we will consider what tooth periodontitis is. Dental diseases are found in people of different ages. Both children and adults have a risk of developing a pathological process in the oral cavity.
Inflammation of the ligaments that hold the tooth in the jaw is called periodontitis. In every third patient, the disease arose after a carious process. Periodontitis in children develops rapidly and has dangerous complications. What is acute periodontitis? This will be discussed later.
Acute periodontitis
Doctors divide this pathology into several types:
- Acute serous periodontitis is the initial stage of the development of inflammation. This stage is characterized by increasing pain. Due to the accumulation of infection in a closed cavity, pressure is generated on the nerve endings. The pain is worse when bitten.
- Purulent acute periodontitis of the tooth is formed if the tooth was not cured in time during the first stage of the disease. A pulsating pain is characteristic, without a clear localization. At this stage, a slight swelling of the gums is possible.
Chronic tooth periodontitis
The chronic form of the disease often occurs after an acute stage. This can happen within 2-10 days. But inflammation is possible not only against the background of untreated acute periodontitis. Probably independent development due to weak immunity. The symptomatology of the disease is practically absent, there are rare bouts of slight pain or discomfort when biting. It is divided into three forms:

- Fibrous - manifests itself in the fact that tissues are replaced with connective fibrous formations over time. There are no special symptoms with periodontitis of the tooth and complaints in patients. An accurate diagnosis can be made after radiography. In the pictures, the doctor will notice noticeable neoplasms on the root of the tooth.
- Granulating - characterized by the appearance of edema in the upper part of the tooth, bright pink or red, with a loose structure. May lead to bone destruction. It is the most dangerous form of the disease. Manifested by aching pain during physical impact on the tooth. In the x-ray, the tissue has blurry shapes.
- Granulomatous. With this form, the attending physician in the picture will notice a bag on the mucous membrane with purulent fluid. At the beginning, the patient will not be bothered by this at all, but over time a constant throbbing, rolling pain will appear.
With an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, pain intensifies, gum swelling may appear, and a slight swelling on the face.
Acute periodontitis of teeth in young children
Most often, cases with chronic and exacerbated forms of periodontitis in temporary teeth are observed, but this does not exclude the development of other acute forms of the disease. A common symptom of acute periodontitis in young patients is the active course of the inflammatory process in periodontium, the rapid transition of a limited process to diffuse. The serous stage of inflammation is usually short-lived and quickly turns into purulent. If the lesions do not touch the roots of the tooth, then pus can exit through the tooth itself or fistula.
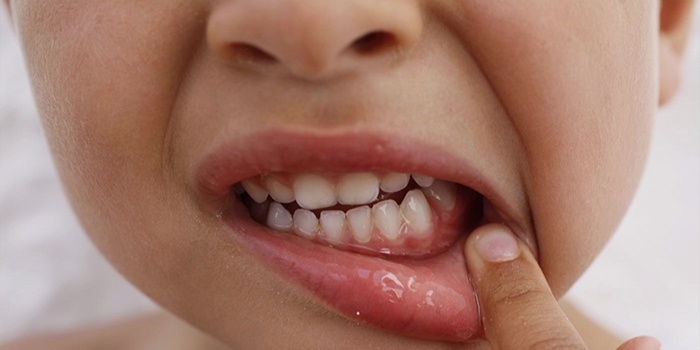
Otherwise, it accumulates, swelling of the gums begins, pain appears and a malfunction occurs in the immune system. With the normal functioning of the immune system, a slowdown of the disease occurs. But with any disease, even acute respiratory viral infections, can provoke a deterioration in the condition of the tooth and lead to infection of neighboring healthy tissue. If the root formation is not completed, then the process leads to the death of the tooth. This complication is manifested by an increase in temperature. Pain during periodontitis should not go unnoticed.
Diagnostics
Clinically, the disease is determined by examination of the oral cavity. In a child, asymmetry of the face is possible due to swelling of the mucous membrane in the mouth, there are cases with an increase in lymph nodes. When examining the tooth itself, the dentist observes gum swelling, mobility, caries, and mechanical injury is also possible.
To make an accurate diagnosis and determine the type of disease, additional diagnostic examinations are used:
- X-ray method;
- computed tomography;
- tooth sounding.
The treatment tactics are chosen by the attending physician. It depends on the degree of damage to the ligaments and root. In the case of a baby tooth, the stage of involvement in the inflammatory process of the primordial embryo will be taken into account. What is the treatment for periodontitis of deciduous teeth? You will learn more about this later.
Therapy of ailment
The main goals of treatment are: elimination of pain, destruction of the focus of inflammation, restoration of the anatomical shape and function of the tooth.
In the absence of the ability to cure inflammation, the question arises of removal. This is necessary, since the damaged area is a source of infection, which can then penetrate into the deep tissues, thereby damaging the permanent dentition. In addition, severe intoxication negatively affects the condition of the child. Treatment of periodontitis of deciduous teeth should be comprehensive and timely.
From another point of view, removal can provoke a delay in the growth and development of teeth in the jaw, leading to malocclusion and other complications.
Home methods
At home, it is impossible to cure the disease. The infection itself is hidden deep in the channels, the action of antibiotics can not cope with it. Drugs can only help with complex treatment.
Everyone knows that toothache calms down if you warm a sore spot with your hand or tie a warming dressing. However, this is not worth it. Any heating is contraindicated. This can provoke even greater suppuration and various complications up to sepsis.
Rinsing your mouth with soda can help get rid of pus. A teaspoon of soda is dissolved in a glass of warm water. With this solution you need to rinse your mouth, then spit it out. And so on, until relief comes. Through the hole in the tooth, if any, the accumulated pus will gradually come out. But this is a temporary measure.
Indications for removal
With periodontitis of a baby’s tooth in a child, before making such a decision, the doctor should carefully examine the x-rays and re-evaluate the condition. If the root has resorbed more than 2/3 of the length, the tooth moves easily and there is a large amount of infected tissue, then this is an obvious indication for removal. Also takes into account the age of the child, how much time is left before the change of primary teeth, the state of immunity.
Therefore, doctors strongly recommend showing their children to a specialist twice a year and monitoring oral hygiene. Since with an early diagnosis a successful treatment of periodontitis is possible, and the tooth can be saved.
Contraindications to therapy
In dental practice, there are a number of contraindications that should be considered when treating periodontitis. Among them are:
- severe inflammation, which is accompanied by a septic reaction;
- detection of neoplasms in the basal region;
- very shaky root;
- atrophy of the alveolar process;
- periodontitis, which is often accompanied by repeated exacerbations;
- upon detection of a curved channel that is not accessible to the doctor’s instrument;
- there is no way to completely seal some area;
- with a perforated wall of the root.
In the presence of at least one situation, it is first recommended to correct these defects, and then proceed to the main treatment.
Conservative methods
If it is possible to save a tooth, the dentist begins a special treatment from the first visit. For children use a more gentle technique than for adults. Treatment is carried out in two to three visits. Therapy is as follows:
- carry out anesthesia of the tooth;
- clean the cavity from caries, remove softened tissue;
- expand the mouth of the canals with the help of medical instruments;
- clean the channels;
- treat the cavity with a special antiseptic;
- if necessary, open the root hole to remove exudate.
The dentist leaves the tooth open for 5-7 days, prescribes rinsing the oral cavity with soda solution up to 7 times a day. Repeated reception depends on the complexity of the situation, it is prescribed by the attending physician. With severe intoxication, antibiotics can be prescribed.
On the second visit:
- carious cavity treatment;
- an antiseptic agent is introduced into the root canal, which fights inflammation;
- a temporary seal is established.
In the third step:
- remove the temporary seal;
- channel obturation with absorbable paste;
- impose an insulating pad;
- establish a permanent seal.
To prevent re-infection from entering the root of the cured tooth, the filling must be installed efficiently and tightly. There are cases when it is not possible to do this on a milk tooth. In this case, it is necessary to install a turundo over the mouth of the canal, impregnated with a special mixture of resorcinol-formalin. Some time after the procedure, the doctor may begin to fill the tooth after treatment for periodontitis.
Physiotherapy
An auxiliary method of treatment is physiotherapy. These are not very expensive and completely painless procedures that are well tolerated by patients:
- Therapeutic electrophoresis. Enhances the antiseptic effect using pulsed current.
- Ultraphonophoresis, in which an antiseptic is administered under the influence of ultrasound.
- Laser therapy, when the laser beam makes the root canals sterile.
Surgery
This method of treatment is used when gentle therapy has not stopped inflammation. Another indication for surgery is obstruction of the root canal or the presence of a purulent sac.
The purpose of the operation is to cut off the root apex. It is carried out in the following order:
- first, the canal is filled with quick-hardening material;
- then cut the gum in the area of the projection of the tooth root;
- a bone section is cut out, and the affected root apex is cut off;
- then remove dead tissue and purulent fluid;
- an antibacterial medicine is poured into the cavity;
- stitches are placed on the wound;
- in difficult cases, put drainage for a day.
This operation is difficult, its time is about 40 minutes, while the patient is under general anesthesia.
Periodontitis in adults
What is a periodontitis tooth permanent? The causes of the disease, in principle, are the same as for deciduous teeth. Only an additional impetus for the development of the inflammatory process can be:
- tooth injury;
- prolonged action of arsenic on the oral cavity;
- sepsis.
Depending on the stage of inflammation, different signs are observed:
- shaky tooth position;
- noticeable swelling on the gums;
- interdental fissures appear;
- bleeding gums, even at night;
- rarely there is an increase in temperature.
At the first signs of the disease, do not postpone the visit to the dentist in order to stop the inflammatory process in time and save the tooth.
The doctor conducts treatment of periodontitis of permanent teeth in two doses. First of all, the root canals are cleaned mechanically from infected tissues, then the cavity is treated with an antiseptic and antibacterial drugs. At the end of the course of treatment, a seal is established. As with milk teeth, the doctor evaluates the patient’s condition after therapy, and in case of repeated inflammation they perform surgery. Perhaps the appointment of a course of physiotherapy and antibacterial drugs.
Complications
The normal body reaction after treatment is a slight aching pain. Ideally, it lasts no more than a day. If the pain increases, a swelling appears, the general condition worsens, you should consult a doctor.
The cause may be individual intolerance to an antiseptic drug. In this case, physiotherapy is recommended.
In this case, a repeated x-ray must be taken to ensure that the seal is installed correctly. It may be necessary to perform repeated mechanical and drug treatment of the canals to neutralize and prevent secondary inflammation.
Possible mistakes
A number of errors in the treatment process can lead to repeated inflammation:
- if a small amount of antiseptic is used, then part of the pathogenic microflora will remain and will cause a new inflammatory process;
- with intensive mechanical cleaning there is a risk of damaging the root or allowing a fracture of the endodontic instrument;
- canal filling error - the seal is not hermetically sealed, and microbes multiply in the formed cavity.
So, we examined what periodontitis is.
Therefore, to avoid problems, follow these guidelines:
- arrange proper nutrition for your child;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- teach your child to clean his teeth from an early age.
These simple recommendations will help to maintain a beautiful and healthy smile for you and your baby.