During pregnancy, the fetus is closely connected with the mother through a special education - the umbilical cord. Through it, he receives everything necessary for life and development - oxygen and nutrients.
Many pregnant women, during an ultrasound scan, find out that the umbilical cord has 3 vessels. They begin to worry and wonder, "Is this normal?" In this article, we will answer it and tell you everything about the umbilical cord, including its possible pathologies. We hope you find this information useful.
What is the umbilical cord? What is its structure?
The umbilical cord (otherwise, the umbilical cord) is a special formation that connects the fetus and the child's place and allows fetoplacental circulation. Outwardly, it resembles a spiral twisted cord or cord and has a bluish-gray color. At the end of the third trimester, the umbilical cord reaches 50-60 cm in length, and its diameter at the umbilical ring is 1-2 cm. Although significant deviations from the average values can be observed in one direction or another. This is what the umbilical cord looks like. The photo shows this.
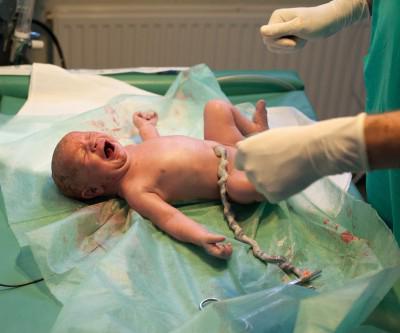
One end of the umbilical cord is attached to the placenta, and the second to the baby in the umbilical ring. He can join the child's place in different places, including in the center, side or from the edge. Rarely, the umbilical cord can attach to the membranes, at some distance from the edge of the placenta. In this case, its vessels reach the child's place, passing between the membranes. Throughout the umbilical cord has bends, depressions and bulges arising due to structural features. Normally, the umbilical cord has 3 vessels, of which two are the umbilical arteries, and one is a thin-walled, wide-open umbilical vein. Along them are nerve fibers. The nerves and vessels of the umbilical cord are surrounded by a special jelly-like connective tissue called jelly warton. It performs a protective function, preventing compression of the arteries. The umbilical cord is covered with an amnion from the outside, which, not reaching 0.5-1 cm to the navel, is transformed into the skin of the fetus.
Arteries and vein of the umbilical cord. What are their functions?
So, we learned that the umbilical cord normally has 3 vessels. Two umbilical arteries originate from the internal iliac arteries.
They transport the blood of a child with carbon dioxide and metabolic products to a child's place. In the placenta, it is saturated with oxygen and essential nutrients to the fetus. Blood is also freed from carbon dioxide and metabolic products. Further along the umbilical cord vein, she returns back to the child. About 80% of all blood is delivered to the baby’s systemic bloodstream through the Arantium duct, which passes along the lower surface of the liver and flows into the
vena cava inferior. The rest of the blood (about 20%) goes into the portal blood flow between the portal and umbilical veins, through the anastomosis. It provides blood supply to the child’s liver.
The umbilical cord in a newborn. What happens to her after the baby is born?
After the birth of the umbilical cord in a newborn is clamped, and then intersects. On the remainder of the umbilical cord adjacent to the umbilical region of the child, impose a ligature or a metal bracket Rogovin. After some time, the bracket is removed, and the remainder of the umbilical cord is removed by clipping, 2-3 cm from the dressing place. A gauze napkin is placed around the umbilical ring.
In the third stage of labor, a woman gives birth to the rest of the umbilical cord along with the placenta and the membranes of the fetus. After the baby is born, the muscles of the arteries contract reflexively, the vessels start and close, and blood circulation in them stops. This wise natural mechanism prevents the possibility of hemorrhage in newborns, in the event that his umbilical cord remains untied. Subsequently, the vessels turn into scar cords.
Research Methods
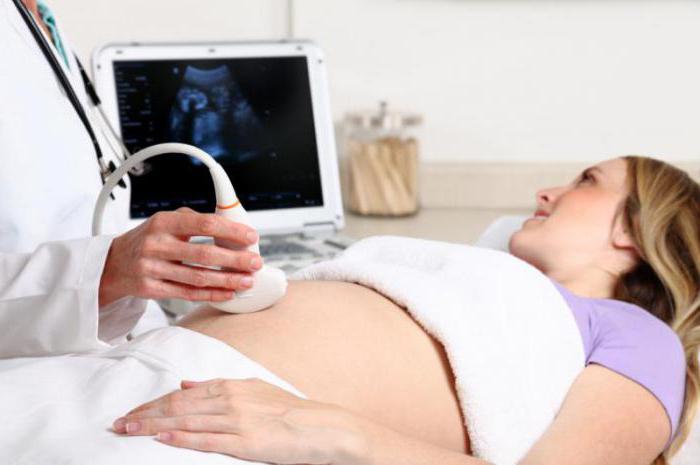
In general, the state of the umbilical cord and its possible pathologies are difficult to detect during pregnancy. As a rule, ultrasound diagnostics are performed, which allows revealing the entanglement of the umbilical cord around the neck, limbs and trunk of the fetus, as well as its presentation. With the help of phonocardiography and auscultation, not only heart defects can be detected, but also the noise of the umbilical cord vessels, which appears in connection with the entanglement of the child’s trunk or neck. Doctors can also use the color mapping method, in which all the umbilical arteries, vein and dopplerometry are clearly visible, allowing you to assess, including the condition of the uteroplacental blood flow. With a vaginal examination, prolapse of the umbilical cord loops is detected. After the birth of the placenta, the placenta and the umbilical cord are examined and, if necessary, the material is sent for histological examination.
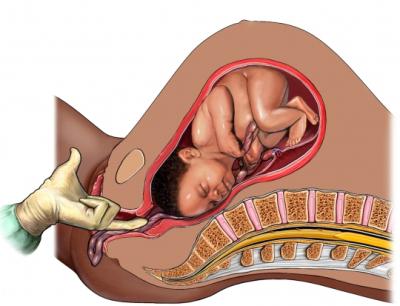
Pathology of the umbilical cord. Entanglement
Most often in clinical practice, there are such pathologies as the entanglement of the umbilical cord around the neck, body and limbs of the fetus and a significant shortening of the umbilical cord. Absolutely short (less than 40 cm) umbilical cord prevents the baby from moving normally, which leads to his incorrect position in the uterus. During childbirth, it is excessively stretched, as a result of which blood flow is disturbed in the umbilical cord vessels. It prevents the fetus from moving through the birth canal, which can lead to its hypoxia. Sometimes a short umbilical cord or its vessels rupture, which can cause the death of the child. The entanglement can occur at any length of the umbilical cord. It can be different - single or multiple, tight or non-tight, isolated or combined. A tight multiple girth of the child’s neck or torso disrupts blood circulation, leads to a lack of oxygen and threatens to prematurely detach the child’s place. In this case, a woman in labor offers a method of delivery using cesarean section.
Anomalies in the structure of the umbilical cord
We know that normally the umbilical cord has 3 vessels. But sometimes there are abnormalities in the number of veins and arteries. 5% of multiple pregnancies and about 1% of single pregnancies are complicated by the pathology of the umbilical cord structure, which has only two blood vessels (one artery and one vein) instead of three. The cause of this anomaly in the structure of the umbilical cord has not yet been identified. The absence of a single umbilical artery impairs fetoplacental circulation. This can lead to various birth defects of the fetus, including heart defects, disruption of the urogenital system and the central nervous system of the baby. Aplasia, that is, a complete absence of the umbilical cord, is extremely rare. In this case, the fetus is directly connected to the placenta and its development is seriously impaired.
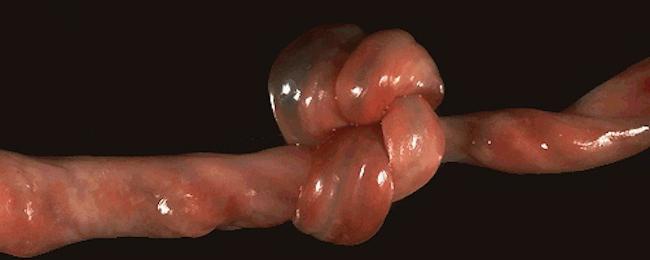
Sometimes in clinical practice there are other pathologies, including umbilical vein aneurysms, embryonic hernia of the umbilical cord, true, false nodes, cysts, etc.
Instead of a conclusion
So, we examined how many vessels the umbilical cord should have. In addition, we learned how her condition is examined during pregnancy and after childbirth and how pathologies of its structure are detected. We hope that now you know that normally the umbilical cord has 3 vessels - two arteries and one vein. They perform an important function of transporting blood to the baby and from him to the placenta.