Improper oral care leads to plaque and stones. As a result of pathological processes, inflammation begins. At first, its symptoms are harmless enough. There is slight bleeding of the gums, swelling, and sometimes soreness. Gradually, tooth mobility increases, purulent secretions may appear. At this stage, they are already talking about advanced periodontitis. For the treatment of this disease, curettage of the periodontal pocket is used. What is this procedure? What other methods are used to combat the disease? You will find answers to these questions in today's article.
Brief Description of the Problem
Against the background of the inflammatory process, bone tissue is gradually destroyed and replaced by granulation. The latter consists mainly of osteoclasts and microbial elements. Day by day they spread to ever new areas, leading to even greater atrophy of the alveolar bone. There is a free area where there is no attachment of the gums to the surface of the tooth root.
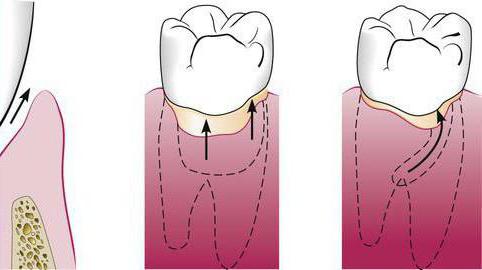
As a result of the described changes, a periodontal pocket is formed. This space is equal in size to the area of the destroyed bone. Its contents are represented by granulation tissue, food debris and purulent secretion. The size of the formed gap judges the degree of tissue deformation. In a healthy person, the depth of periodontal pockets is not more than 3 mm, so that you can freely clear the cavity of food debris. If this value exceeds the specified size, certain difficulties arise when caring for the oral cavity. The likelihood of gum disease increases several times, which leads to the appearance of stone and plaque. Active tissue damage can result in tooth loss.
Diagnosis of the pathology is carried out using an X-ray examination or periodontal probe. The lack of quality treatment over time leads to a deepening of the pocket. The consequence of this process is the movement of the teeth into a fan position.
Causes of Pocket Formation
The main reason for the formation of the periodontal canal is poor quality oral hygiene. Incorrect brushing or lack of teeth leads to the accumulation of bacterial deposits in the crown area. On the entire surface of the tooth enamel, the microbes form a thin invisible film and begin to secrete products of their own vital activity. So there is inflammation of the periodontal pocket.
Risk group
Among the factors that provoke the growth and reproduction of pathogenic flora, it can be noted:
- improper diet, consisting mainly of carbohydrate products;
- poor oral hygiene;
- addictions;
- hormonal disorders;
- immunodeficiency;
- dental diseases;
- malocclusion;
- poor installation of seals.
Symptoms of inflammation
The formation of periodontal pockets for a long time can be asymptomatic. With the development of the inflammatory process, a characteristic clinical picture appears:
- discomfort in the gums;
- bad breath;
- swelling, bleeding and redness of the gums;
- with palpation, purulent secretions may be released;
- expansion of interdental spaces;
- deterioration in general condition.
If these problems occur, you should contact your dentist. The help of a doctor is required even if the inflammatory process has affected only one tooth. Every day the situation will only worsen, which can lead to the progression of the disease.
Treatment methods
Before starting therapy, a diagnosis is made, with the help of which the doctor determines the degree of neglect of the disease. If the periodontal pocket does not exceed 0.15 mm and there are no signs of inflammation, therapeutic methods are used. The following procedures are commonly used:
- Hygienic cleaning with ultrasound. During the removal of stone and plaque, the gums are not damaged.
- Drug treatment. Appointed immediately after ultrasonic cleaning. With a mild degree of the pathological process, aseptic treatment is used (baths, irrigation, rinsing). During the procedures, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin is used. In especially serious cases, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. The following drugs are most effective: Amoxicillin, Linkomycin and Azithromycin.
The listed procedures are ineffective if the pocket depth is more than 2 mm. The doctor will not be able to completely remove the accumulated stone. In addition, the likelihood of additional periodontal trauma increases. As a result of the manipulations, the inflammatory process and tissue destruction begin to progress.
With a complicated course of the disease, surgical intervention is recommended. This method of treatment involves the mechanical impact of dental tools on subgingival areas. Currently, the most effective procedure of this type is the curettage of the periodontal pocket. What it is? There are several types of manipulations: closed, open and patchwork operation. The procedure itself allows you to get rid of all the problems caused by periodontitis. Consider each of its options in more detail.
Open Type Curettage
Such an intervention requires a highly professional doctor. Therefore, such a service is not provided in all medical institutions. The duration of the procedure is about 2.5 hours. It consists of the following steps:
- Brushing teeth from stone and plaque.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Splinting of mobile teeth.
- Dissection of the gingival flap with a scalpel.
- Removing granulations and stones using ultrasound.
- Antiseptic treatment of tooth roots.
- Putting synthetic tissue in a pocket to enhance the growth of natural bone.
- Suturing and closing the damaged area with a gingival dressing.
After about 1.5 weeks, the sutures are removed. A few months later, the final restoration of damaged tissue occurs. Gingival papillae can completely close the gaps between the teeth. In some cases, open curettage of periodontal pockets leads to exposure of the roots. Therefore, for some time it is recommended to abandon the use of hot, sour and cold foods.
Closed curettage
The operation is effective with a pocket depth of 3-5 mm. Intervention is not difficult. It consists of the following steps:
- Inspection of the gums.
- The introduction of local anesthesia.
- Processing periodontal pockets without cutting the gums.
- Polishing tooth roots.
Intervention can affect 2-3 teeth at the same time. Wound healing takes place in one week, but it takes about a month to fully recover. So much time is needed for the formation of connective tissue and attachment of the gums to the tooth. The main disadvantage of the procedure is that the doctor at the time of the manipulation does not see whether all pathological formations are removed.
If the depth of the pocket is more than 5 mm, a closed curettage will only stop the progression of periodontitis. Partial removal of deposits and granulations allows you to get a temporary respite, but in almost all cases the disease resumes its development.
Patchwork operation
This surgery involves cutting the gums to gain access to the periodontal pocket. It is recommended if its dimensions do not exceed 4 mm.
First, the doctor makes two small incisions with a scalpel and exfoliates the mucosal-periosteal flap. Then, standard mechanical cleaning of the pocket and polishing of the tooth surface are carried out. After completion of the treatment of hard surfaces, they proceed to the preparation of soft tissues. Flaps are laid in place. At the end of the procedure, osteogenic medicine is applied to the affected area, and the gum itself is sutured. The entire operation lasts no more than 40 minutes, but involves the use of local anesthesia.
Some patients are additionally prescribed wound healing products for external use (for example, "Furacilin"). They also recommend the use of ointments to stimulate the process of epithelialization of the gums (Actovegin, Solcoseryl).
Vacuum Curettage
In the presence of purulent abscesses and deep pockets (more than 5-7 mm), vacuum curettage is used. Cleaning is carried out using anesthetics. During this procedure, the doctor first scrapes the deposits of stone, and then polishes the tooth tissue. After that, the specialist proceeds to remove granulations and damaged epithelium from the inner walls. The periodontal pocket is cleaned using a vacuum apparatus, which from the bottom of the cavity sucks necrotic masses together with fragments of stone. At the final stage, washing with antiseptic drugs is mandatory.
Vacuum curettage is highly effective. With the help of the procedure, the lymphatic flow in the tissues is restored, the depth of the gingival pockets is reduced and all inflammatory processes are eliminated.
Postoperative period
In order not to open periodontal pockets, within 10 hours after all the manipulations it is recommended to refuse food and drink. To obtain the desired result, you should carefully brush your teeth, while you need to use a brush with a soft pile. The problem area must be bypassed. After a week, you can start rinsing. To do this, use a weak saline solution or Chlorhexidine.
As for nutrition issues, you must first give preference to soft or mashed food. The use of cold or excessively hot drinks is strictly prohibited. During the week after the curettage of periodontal pockets, it is recommended to abandon physical activity, exercise, visit the sauna. In the postoperative period, it is important to monitor the condition of the oral cavity. Hygiene products designed for sensitive teeth can be used. If necessary, consult a dentist. The specialist will select procedures to reduce the sensitivity of the necks of the teeth.
Patient reviews and price of services
The cost of treatment of periodontal pockets in Russia varies slightly. Among the main factors that affect pricing, we can note the anesthesia method and the technological capabilities of the medical institution. Not the last aspect is the status of the clinic. On average, closed curettage of periodontal pockets costs around 5-12 thousand rubles. An open procedure costs a little more (9-18 thousand rubles).
Most patients who have had to survive this pathology prefer surgery. In their opinion, surgery is the only way that can permanently eliminate the problem. It is better to resort to the help of an open type of intervention. This technique allows not only to repair damaged elements, but also restore lost bone over time. The only drawback of the procedure is the long healing period. Closed curettage of the periodontal pocket is characterized by less soreness. Reviews of patients suggest that his help should be resorted to only at the initial stage of the pathological process.
Opinions on therapeutic treatment differ. Most patients do not recommend this method of solving the problem, since it only allows you to temporarily stop the symptoms.
Why is pocket inflammation dangerous?
Periodontal pocket is a serious pathology that requires timely and competent treatment. Lack of therapy can lead to complications. Among them, the most dangerous is an acute abscess, which subsequently acquires a chronic course. It is characterized by an increase in tooth mobility and the appearance of pain. In this state, it becomes difficult for a person to chew food. Neglect of pathology over time leads to the fact that the tooth completely drops out of the alveolar hole. The development of the inflammatory process ends with lymphadenitis and general intoxication of the body.
Prevention of Re-Disease
Do not ignore the inflamed periodontal pocket. Timely treatment increases the chances of a full recovery. However, this does not mean that now you can not visit the dentist. After the course of therapy, you will need to pay a visit to the doctor again, and the specialist himself sets the specific time taking into account the neglect of the disease. On examination, the dentist will be able to determine the success of the treatment, give recommendations for caring for the oral cavity.
High-quality daily dental hygiene allows you to avoid stone formation, to prevent inflammatory processes in the periodontal pocket. It is considered professional to clean the oral cavity once a year at the dental center.