The last (third) molars, which are called the teeth of wisdom, grow far from all people. Moreover, this is not related to the level of intelligence, but is associated with their late eruption. And their very growth often becomes a cause of trouble for a person, and pulpitis of the wisdom tooth in general becomes a disaster. But not everything is so scary. What is the peculiarity of these teeth, when and how do they grow, whether pulpitis of a wisdom tooth is treated - about this, and at the same time we will talk about the general structure of teeth in this article.
Homo sapiens teeth kit
We will not delve into the importance of teeth for humans. We only recall that in addition to the mechanical processing of food, they play an important role in the formation of speech and are very important in aesthetic terms.
Our biological species is characterized by the change of temporary teeth (milk) to permanent (molars). The first milk tooth - a long-awaited event for parents - appears in a child aged 6 to 9 months. By 2 years of life, 20 teeth appear in the oral cavity, which are practically no different from the molars. But they have less saturation with minerals, they are less and have very shallow roots that go into the gums.
At the age of 5 to 6 years, milk teeth fall out and in place of them molars appear. Most of us no longer have deciduous teeth by the age of 15, although there are such exceptions. Molar teeth in humans are 28 + 4 wisdom teeth. This is the best option.
The dental formula, and this is a description of the number of teeth in one jaw, looks like this: I 2/2 C1 / 1 P2 / 2 M3 / 3, where
- I - incisors. Flat teeth with one root. Grab and bite off food.
- C - fangs. Pointed to the apex, have one root. Their purpose is to tear and hold food.
- P - premolars. Biconvex larger teeth, have two roots. Crush food lumps.
- M - molars. The largest teeth that have three roots. M3 - these are the very same wisdom teeth. The function of the molars is the grinding and grinding of food.
In international dentistry, a single tooth numbering system has been adopted. The reference point is the middle of the jaw to the right and left. Wisdom teeth that are of interest to us are the eights.
General knowledge of tooth structure
Our teeth, like the teeth of all mammals, are bone formations that are motionlessly connected by means of wedging with the jaw of a person. The anatomical structure, both external and internal, on the one hand is quite simple. But the study of the subtleties of the structure of all teeth for dental students takes more than 5 years.
Externally, the tooth consists of 3 parts:
- The crown is the visible part, which is covered with the hardest tissue in our body - enamel.
- The neck - the place where the crown goes to the root, is in the gum. Sometimes the neck is exposed, and then we are talking about cervical caries.
- The root is the part of the tooth located in the alveolar bag of the gum.
The internal structure of the tooth is represented by:
- The outer layer is enamel. It consists of 96% inorganic mineral components, 1% organic substances, 3% is water.
- The basis of the tooth is dentin. The structure is similar to the structure of bones, but more saturated with minerals (72%). Dentin is hidden by enamel and cement.
- The cavity of the tooth is the pulp. Connective tissue of the spongy structure with blood vessels and nerve endings.
- A “house” for a tooth is a periodontium, or gum cavity.
Third molars - structural features
These last two molars in the upper and lower jaw, which dentists call eights, begin to grow from an average of 17 to 27 years, and can grow in their forties. But in many people (8-11%) they never begin to grow, and over time, the rudiment of the tooth in the gum dissolves. For some, growth goes completely unnoticed, and a person learns about them from the dentist when pulpitis of the wisdom tooth has already begun. For others, the growth of the last molars takes place with fever, pain, bleeding and even surgical intervention to dissect the gums or remove an tooth that has not yet grown.
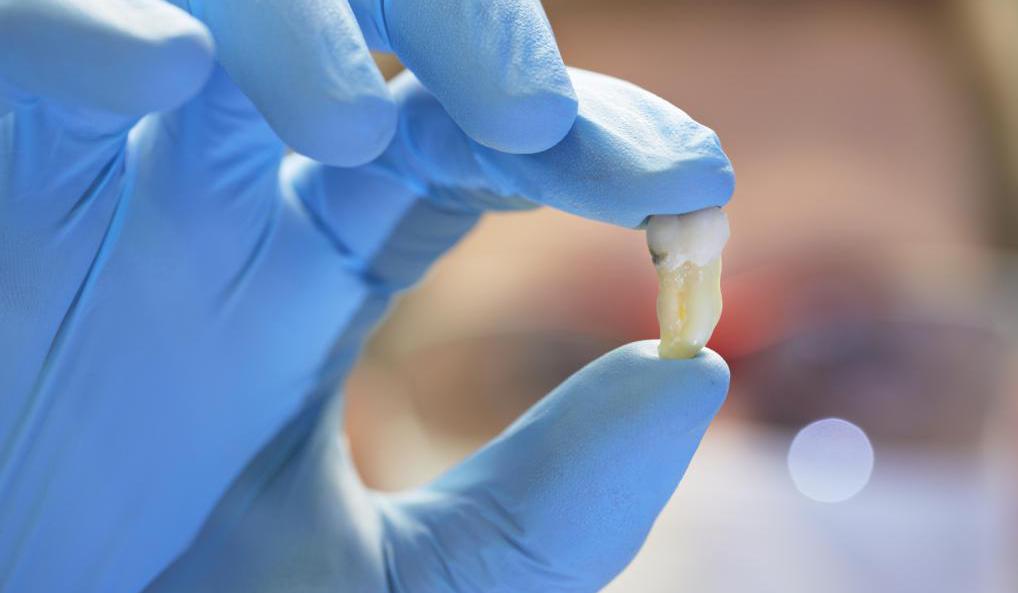
At dentists, it is caries and pulpitis of wisdom teeth that are in the top hits. And all because of their remote location and the difficulty in conducting thorough hygiene. And also because of the many roots or one powerful fused. Often they do not have enough space on the jaw, and they grow crookedly, pressing on adjacent teeth, which inflames the gums and provokes the destruction of enamel, which leads to caries and pulpitis of the wisdom tooth.
Often these teeth, on the contrary, are almost in their infancy and are covered with the soft part of the gums, like a hood. Then bacteria accumulate beneath it, and the wisdom tooth that finally appears, already has a different degree of caries.
There is a theory according to which the teeth of a person’s wisdom are vestigial organs, which we left from our old ancestors, whose jaws were larger and the food was harder. Indeed, these eights do not participate in the mechanical crushing of food. But in the history of dentistry there were lucky people who grew not 4 wisdom teeth, but 6 as many.
Top or bottom - the difference is significant
32 teeth in humans today are a rarity. More often we find 28 or 30 molars in an adult. At the same time, lower wisdom teeth often do not grow in women, and in men - upper ones.
The wisdom teeth on the lower jaw are massive and often have more than 3 roots or one large fused. Often they reach the gingival surface by 20-30%, and this greatly complicates the treatment of pulpitis of the wisdom tooth or its removal. In addition, often they are not located vertically, but partially horizontally. Or their roots can have a horizontal orientation. In this case, is it worth treating a wisdom tooth with pulpitis? Not worth it - it is recommended to remove it.
Third molars in the upper jaw more often have one root, not too deep in the gums. They are easier to cut, quite easily removed.
What is pulpitis
The inflammatory process in the neurovascular bundle (pulp) of the tooth is called pulpitis. Wisdom teeth, like everyone else, may be affected by this process.
The etiology of the development of such inflammation can be:
- Infectious pulpitis. Various bacteria (staphylococci, lactobacilli) penetrate the cavity of the tooth through dentin thinned by caries. This is a direct route of infection. The other way is retrograde: the infection enters the pulp through the roots of the teeth. This happens with enlarged pockets of teeth in the gums with periodontitis and periodontal disease. Also, the infection can get into the pulp during inflammatory processes in the immediate vicinity of the tooth - sinusitis, osteomyelitis. In rare cases, the infection enters the pulp through the lymphatic and blood vessels from other organs.
- Traumatic pulpitis. Various injuries can lead to chipping and cracking of the tooth and the development of inflammation in the pulp.
- Iatrogenic pulpitis. In this case, the mistakes of doctors lead to the development of inflammation - excessive processing of the carious area, overheating, inaccurate turning under the crown.
Pulpitis is different
By the nature of the flow, there are:
- Acute pulpitis is the first stage, which lasts up to 5 days. Inflammation affects only the coronal part.
- Chronic pulpitis - untreated acute pulpitis becomes sluggish inflammation with gradual pulp necrosis.
At the site of inflammation, pulpitis is:
- Root - infection spreads throughout the root canal and can exit through the apical (upper) opening.
- Inflammation under the filling - in this case, secondary caries under the filling leads to inflammation of the pulp.
- Multichannel pulpitis of molars and premolars - the infection spreads in all channels.
Pulpitis is different - the symptoms are the same
The main symptomatology of such inflammation is the appearance of aching pain, often worsening at night. Then the pain occurs several times a day, its attacks become more frequent. Over time, the pain becomes constant and radiating to the ear, temple, chin. With pulpitis of the wisdom tooth, the entire jaw hurts. To distinguish pulpitis from caries is simple. With caries, pain occurs in response to the influence of an external factor - pressure or brushing your teeth. With pulpitis, the pain appears spontaneously. Symptoms of pulpitis of wisdom teeth completely fit into the described picture.
Patience is gold, but not in this case
Most often, inflammatory processes in the pulp proceed in an acute form and are accompanied by severe periodic pain. To treat or remove a wisdom tooth for pulpitis - this largely depends on its type, namely:
- Focal pulpitis - only the upper part of the pulp is affected. Wave-like attacks of pain affect the trigeminal facial nerve.
- The diffuse spread of inflammation affects the crown and root of the pulp.
- Serous pulpitis develops on the 3rd day of inflammation and is accompanied by constant throbbing pain.
- Purulent stage - exudate accumulates in the area of inflammation, the temperature may rise, and health will worsen.
With any course of pulpitis of the wisdom tooth, it is urgent to treat. But there are cases when this does not make sense.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: treat or remove
Unambiguous indications for the removal of pulped "eights" is:
- Tooth retention is a pathology when the tooth is completely or mostly hidden in the jaw.
- Tooth dystopia is a pathologically incorrect location of the molar in the jaw in relation to the rest of the dentition.
With such pathologies, wisdom teeth do not carry any function and are outside the bite zone.
But if you still save?
It is difficult to treat pulpitis of the wisdom tooth for at least two reasons:
- Localization of teeth makes access to them very difficult.
- Wisdom teeth often have curved roots, which makes the process of depulpation jewelry art.
But it is worth agreeing to treatment when only “eights” remain of all the molars and premolars - then it will be possible to install a prosthesis on them. In the initial stages of pulpitis, when the prognosis of treatment is more favorable, do not immediately get rid of wisdom teeth.
Modern methods of treating pulpitis have two directions - to keep the pulp alive (a biological method with temporary filling) or to get rid of inflamed tissues and fill the canals. Both in the first and in the second case, modern medicines are used. All the myths that the treatment of pulpitis of the wisdom tooth in pregnant women can harm the fetus are completely groundless.
Complications and Prevention
It is necessary to treat pulpitis. This is an infection, and it tends to spread. If you neglect measures for its localization, expect troubles, such as:
- Inflammation of the periosteum - flux.
- Osteomyelitis is an inflammatory process with the formation of pus in the bones of the jaw.
- Abscesses - purulent abscesses on the mucous membrane.
- Phlegmon is a dangerous disease in which purulent discharge affects the soft tissues of the face.
And all preventive measures in relation to the development of pulpitis and other dental troubles are simple and easy to do:
- Be sure to carry out preventive examinations at the dentist once or twice a year.
- Observe oral hygiene. Brush your teeth twice a day and use floss.
- Eat right. In the diet, there must be products that contain calcium, potassium, fluoride and vitamin C.
- Timely treat even the smallest caries. And carefully consider the choice of clinic and specialist.
- Take care of your teeth - and the pulp "will not make you nerves."