Intraligamentary anesthesia in medical practice is more commonly known as "intracircular anesthesia." Gradually, this option to eliminate the pain threshold is gaining more and more popularity. It is used in operations, including in dental institutions.
general information
Intraligamental anesthesia is one of the options for local anesthesia. Its principle of action is that a composition is introduced that acts pointwise in periodontal space. Unlike standard anesthesia, here the drug is administered under higher pressure. Under normal pressure, an insignificant percentage of the composition enters the periodontal slit cavity, while the main fluid reaches the intraosseous layers of the alveolar. From here, the medicine will spread to the periapical region, where the analgesic will begin to act inside the bone.
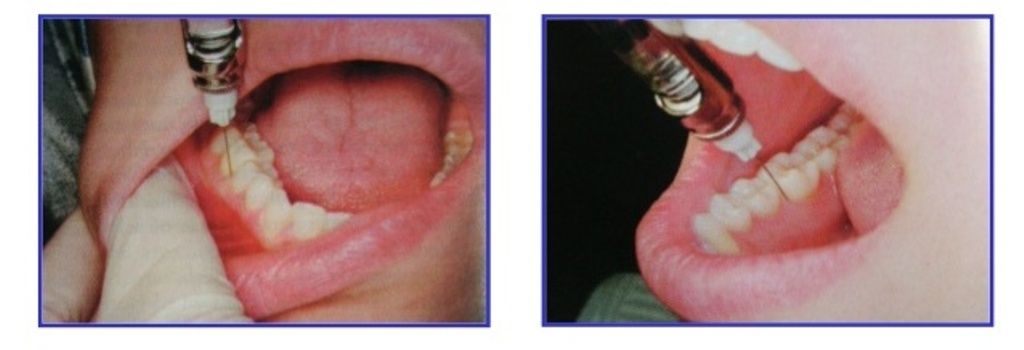
The main task of intraligamentary anesthesia in dentistry is to anesthetize hard tissues of teeth and soft fragments of the oral cavity at the time when surgery is performed. The action of the composition begins 1 minute after it is introduced, and lasts for 30 minutes. Half an hour is enough to carry out standard surgical operations, as well as operations of medium and high complexity. This method of anesthesia is more than justified, especially in relation to children and people whose pain threshold is low. The fact is that with it there is no complete numbness of the jaw and impaired speech function of the patient.
Features and mechanism
A characteristic feature of this method is its almost immediate effect, the uniformity of which remains throughout the entire period of anesthesia.
The process of administering the drug in this way is not associated with causing physical pain. At the time of administration of the drug and throughout its action, soft tissues are not numbed:
Intraligamentary anesthesia does not lead to bruising, involuntary post-surgical chewing of numb parts and oral mucosa. The composition is taken very little, so the effect on the body of the drug itself is minimal. Unlike standard anesthesia, this method of anesthesia is more convenient, easier and faster to eliminate occlusion deficiencies after therapeutic procedures.
Injection is used to inject the drug into the periodontal ligament of the tooth, where it specifically affects a specific unit of the jaw line. At the same time, the working capacity and natural state of the surrounding tissue parts are preserved. There is an effect of intraosseous anesthesia, in which many dental problems can be completely painlessly solved.
Use of injectors
The drug is injected with a syringe syringe - a gun for intraligamentary anesthesia. To do this, press the lever. With each pressure, 0.2-0.6 ml of anesthetic solution is injected onto the piston. For the manufacture of such tools, materials that withstand high temperatures are used. To facilitate the work of the surgeon, they are lightweight. The following systems are considered the best in this regard.
STERINJECT and PERI-PRESS
This type of system comes with a special snap mechanism that is held by four fingers. The difference between this device is a unique cross-shaped. The device allows you to achieve the greatest use of muscle strength. With one mechanical press, approximately 0.2 mm of the composition enters the tissue.
CITOJECT
The design of this device is similar to a simple automatic handle. It’s easy and convenient to work. It has a comb and a special piston mechanism. It is these design features that allow you to enter the fluid extremely accurately and completely painlessly. On average, about 0.3 mm of medication is delivered.
PAROJECT
PAROJECT - a syringe for intraligamentary anesthesia, which has a cylindrical shape, looks like a hollow vessel. Made of high quality metal medical alloy. The main plus is in the increased portion of the supplied drug. 0.6 mm of composition enters the cavity at a time. This is necessary in difficult clinical situations.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of this type of anesthesia include a high threshold for eliminating pain - at least 90%, with the exception of the upper frontal incisors and canines. In these places it is slightly lower. In order to achieve a lasting result, you will need a minimum concentration of the drug. It is also noted that in one visit you can anesthetize several teeth at once.
This method also has disadvantages. During a puncture, as the needle for intraligamentary anesthesia follows, particles of plaque can get into the inner layers of soft tissues. As a result, infection will occur, inflammation will develop. The disadvantages include the possibility of mechanical injury to the dental ligament, leading to discomfort for several days. If the technique of conducting intraligmental anesthesia in dentistry is not followed, then there is a chance of atrophy of the cells of the periodontal ligament.
Indications and contraindications
This technique is recommended for use with:
- lack of effectiveness of other methods of pain relief, such as infiltration and conduction;
- caries treatment;
- inflammation in the pulp;
- extraction;
- crown installation;
- preparation;
- the need for a reduced dose of the drug. This is necessary if the patient is prone to allergic reactions or does not tolerate individual analgesics.
This method of anesthesia is the only one approved for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, because the dose of the drug is very small, and does not pose a threat to the baby.
Often there are situations when this method of pain relief is dangerous, these include:
- acute endocarditis;
- marginal type periodontitis;
- operations on the organs of the heart and blood vessels;
- congenital heart disease.
You can not perform such anesthesia if the formation of the root system of the parts of the jaw row is not completed, and surgical procedures are also performed in the region of the apex of the root. This method is of great danger in the case when medical actions take longer in time than this type of anesthesia proceeds.
Training
Before administering an anesthetic with this method, you need to pass an allergy test. Especially this need arises with a predisposition to intolerance to the components of drugs, as well as with:
- conducting the procedure for the first time;
- even a single diagnosis of anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema;
- atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma.
The test begins with a shallow injection under the skin into the wrist area of the composition with saline. It is bred to an extremely low concentration. The result is evaluated as follows. If an allergic reaction occurs immediately, then it is forbidden to use it, after 15-20 minutes - it should not be used. If the outer side of the wrist remains unchanged, then the sample is considered negative, the composition is allowed to be used.
Technique
The technique of conducting intraligamentary anesthesia begins with a thorough cleansing of the entire external surface of the dentition from plaque and stones. Then the tooth is treated with antiseptic agents. After that, a needle must be inserted strictly parallel to the tooth before the periosteum begins to be felt, but no more than 3 mm. After the required depth is reached, the doctor begins to slowly enter the composition. The number of injections is determined by the number and complexity of the structure of the roots.
For the rapid onset of the effect, the most effective drugs are used, which include:
- Lidocaine
- Ultracain
- "Trimekain."
According to the correctly performed technique of intraligamentary anesthesia, the dose of the administered drug should not exceed 0.6 ml. The tips that are included in the kit must have several angles of inclination. As soon as the composition arrives at the right place, the needle is held in its original position for several seconds, and then pulled out. During this time, the anesthetic will have time to completely absorb.
The nuances of the procedure
Although the number of injections needed is determined by the number of roots, more than 2 injections cannot be carried out simultaneously. It will take the doctor 15 seconds to fully administer the medicine. If this rule is not observed, then there is a greater likelihood of complications and a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug. If for some reason there is no fluid flow, the syringe must be replaced with a new one. Otherwise, the composition will linger in the subcutaneous layer, which will lead to a hematoma.
Possible complications
When performing intraligamentary anesthesia, the occurrence of complications cannot be ruled out. If the angle of inclination is violated with the introduction of the drug, limited necrotic manifestations in the surrounding tissues may be observed. If aseptic is not observed, as well as excessive and rapid administration of anesthetic, complications are expressed in the development of periodontitis.
It is important to contact a competent and experienced dentist who will carry out the procedure correctly, which minimizes the risk of side effects.