What does it mean when they say that the hood on the wisdom tooth has become inflamed? Let's figure it out.
The teeth of wisdom are popularly called chewing teeth (large molars) located on the edge. They appear, as a rule, at the age of 16-36 years. In total, a person may have four wisdom teeth, but dental practice is faced with situations where only 1 or 2 extreme molars erupt. At the same time, the rest continue to grow under the gum, being under a strong slope or in a supine position. In some cases, the beginnings of eights in patients are absent altogether. When wisdom teeth do not erupt until the age of 35, a person should undergo an X-ray examination to exclude likely anomalies.
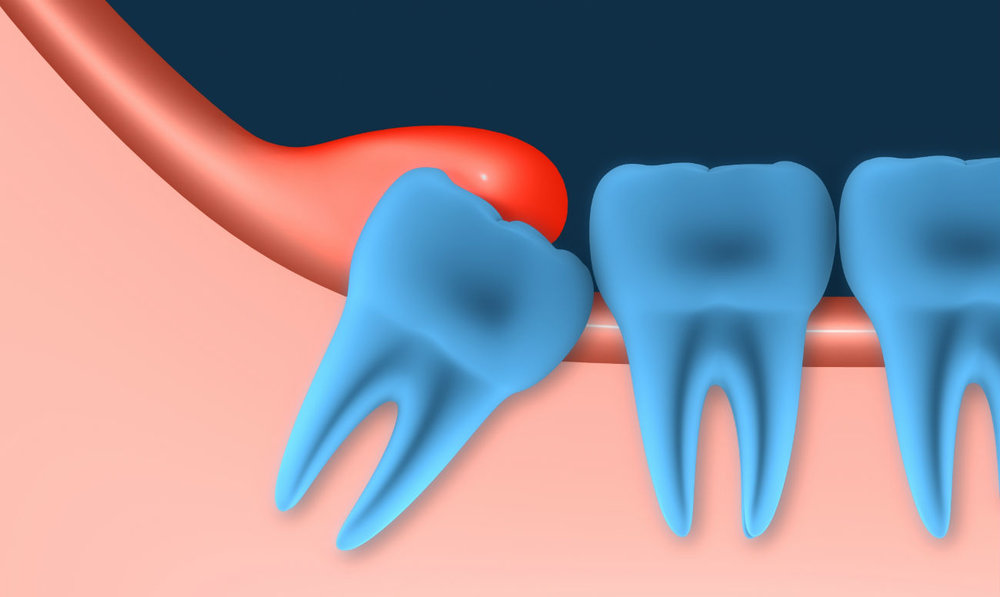
Teething is always a painful process that is accompanied by inflammation of the hood of the wisdom tooth. This is due to the complex interweaving of the root system. With severe inflammation, accompanied by the accumulation of exudative fluid, hyperemia, abscesses, leaving in the deep layers of soft tissues, the patient is diagnosed with pericoronitis. This pathological condition is typical for the process of eruption of eights, but this does not mean that therapy of this condition is not required. The neglected form of pericoronaritis is capable of passing into the inflammation of the deep layers of the mucosa, which has a destructive form.
Possible causes of pericoronaritis
Pericoronaritis is a very painful process, so it is very important to determine the causes of severe inflammation during the eruption of the closing teeth. When the x-ray shows an anatomically incorrect position of the tooth or the presence of interwoven roots, the doctor directs the patient for a consultation with the dentist-surgeon, who determines the need for excision of the gum and subsequent extraction of the tooth before it begins to erupt.
The appearance of extreme molars may be accompanied by the development of complications associated with other reasons. Knowledge of the factors contributing to the occurrence of inflammation of the hood of a wisdom tooth will ensure timely prevention of this pathology.
Gum Thickening
In about a tenth of all patients, tissues located at the site of growth of the wisdom tooth have thickened walls, which prevents teething. In this case, a person has severe pain, often accompanied by a rise in temperature, a headache, and a deterioration in overall well-being. In some patients with thickened gingival walls, hearing loss and soreness in the ears and orbits are noted. If teething does not occur for a long time, the lymph nodes located under the jaw begin to inflame.
For what other reasons is the hood on the wisdom tooth inflamed?
Dense plaque of bacterial origin on the gums
Neglecting hygiene standards and caring for the oral cavity, the likelihood of a patient developing pericoronaritis increases several times. When a teething occurs, the gum is lifted and its subsequent rupture. Microbes and bacteria located on it are able to penetrate into damaged areas and provoke severe inflammation.
A photo of the hood of a wisdom tooth is presented.
This form of pericoronitis is characterized by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- The gum swells and swells in the area of teething wisdom.
- Any load on the site of the lesion causes the appearance of a high intensity pain syndrome. Moreover, the pain affects not only the molar section, but the entire jaw.
- The temperature rises to 38.5 degrees Celsius.
In the absence of timely treatment measures, the pathological process can transform into a purulent-infectious one, which is dangerous because blood infection can occur.
Types of pericoronitis and symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation of the hood of a wisdom tooth depend on its shape. Acute pericoronaritis is characterized by severe pain and high intensity of the main symptomatology, therefore, the diagnosis of the acute course usually does not cause difficulties. Typical symptoms of acute pericoronitis are:
- The appearance of a sharp and unpleasant odor from the oral cavity, which intensifies after eating. Moreover, the use of hygiene products does not allow it to be eliminated.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membranes develops, the temperature in the area of teething rises locally.
- An acute form of pain occurs, which interferes with eating, talking, opening the mouth.
- Pain sensations radiating to the temple area, lower or upper jaw, ear.
- Cervical or submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed.
- Body temperature rises.
If at this stage the patient does not seek the help of a dentist and tries to cure the disease on his own, the process begins to take on a chronic form.
Chronic pericoronitis
Chronic pericoronaritis develops, as a rule, if teething occurs for a long time, as well as in cases where the patient is self-medicating an acute form of pericoronaritis, stopping the pain with analgesics and avoiding a visit to the dentist.
When the hood of the wisdom tooth is inflamed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Unlike acute pericoronitis, chronic is not accompanied by intense pain - the patient can open his mouth almost painlessly, but when eating, the pain increases significantly. Lymph nodes with pericoronitis in chronic form increase slightly, palpation does not cause pain. An exception are cases when the pathology flows into the osteomyelitis of the jaw or periostitis.
Symptoms
The chronic process is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pus is secreted from under the gingival hood.
- The load on adjacent teeth increases, resulting in increased mobility and shakiness.
- Abscesses and abscesses appear at the teething site.
In the absence of adequate therapy, chronic pericoronitis contributes to the development of phlegmon - purulent inflammation in an acute form that does not have certain boundaries.
In addition, the inflammatory process is classified according to the form of its course:
- Pericoronaritis is catarrhal. It is the initial stage of the development of the inflammatory process, the symptoms with this form of pathology are weakly expressed.
- Purulent pericoronitis. It is the most dangerous form of pathology. Inflammation with this form of pericoronitis is accompanied by suppuration of the affected tissues.
- Pericoronaritis ulcerative. A distinctive feature of this form is the presence of a necrotic process in the affected gum.
- Pericoronaritis is postmolar. With this form of pathology, the purulent focus is hidden, as a result of which the normal outflow of exudate is disrupted. Because of this, pus begins to accumulate in the soft tissues, the inflammatory process penetrates deeper, affecting the periosteum and provoking the formation of an abscess.
When the hood over the wisdom tooth has inflamed, the treatment should be comprehensive.
Pericoronitis treatment
Dentists consider surgical intervention to be the only adequate way to treat pericoronaritis in acute or chronic form. Only 2% of uncomplicated pathologies are treatable by the use of anti-inflammatory ointments, gels, and other agents. That is why experts do not recommend spending time and effort trying to cure pathology at home.
Given the anatomical location of the tooth and the severity of the pathology, the doctor chooses one of two surgical treatment methods - extraction of the figure eight and its root system or excision of the gum hood over the wisdom tooth. The first technique is used only in extreme cases, since surgical intervention can provoke various complications, and the recovery period takes up to six months. In some cases, the operation to extract the figure eight from the bone alveoli is carried out under general anesthesia in the maxillofacial surgical hospital, which significantly increases the load on the heart muscle and other important human organs.
Indications for extraction of wisdom tooth
The extraction of a wisdom tooth is carried out only when strict indications are present:
- The patient has a specific anatomical structure of the jaw (for example, the jaw arch is too narrow, and there is no place for dentition in the dentition).
- Pathological disturbances in the formation of tooth rudiments in the embryonic period.
- Abnormal location of the figure eight, its roots, improper tooth growth.
- Lack of effect, relapse of the pathology after the hood was cut off on the wisdom tooth.
- Formation of a new gingival hood (quite rare, only in 5% of cases).
Both surgical methods for excising a hood of a wisdom tooth require careful preparation and effective pain relief. Upon completion of the surgical intervention, the patient is prescribed compliance with a special regime, which involves minimizing the load on the area that has been damaged. The use of various medications aimed at preventing possible complications is also recommended.
Medication after surgery
After the surgical removal of a wisdom tooth or excision of the gingival hood, the patient must be prescribed drug therapy. One of its components is antibacterial drugs. The most commonly used antibiotic drugs with a wide range of effects, which are active against most anaerobic and aerobic pathogens. The most effective drugs are:
- Hemomycin. The patient is prescribed a single use per day of one tablet, the duration of the course is about 5 days.
- Amoxicillin. Three times daily intake of one tablet is indicated. Therapy takes up to 10 days.
- Zinnat. Twice daily use of one tablet is prescribed, therapy takes up to 10 days.
- "Metronidazole." Twice or three times a pill for 10 days.
- Tsiprolet. Twice or three times a day, one tablet for a week.
- "Ciprofloxacin." Three times a day, one tablet. Therapy usually takes 10 days.
Inflammation of the hood of the wisdom tooth
The use of oral preparations should be combined with the use of local exposure. Quite often, dentists recommend rinsing and oral baths using antiseptics such as Miramistin, Hexoral, Chlorhexidine. Sometimes it is prescribed the use of anti-inflammatory gels, which include soothing components, antibacterial substances and antiseptics. In some of them, lidocaine is present, which helps to reduce the intensity of pain after removing the eight.
If the hood over the wisdom tooth becomes inflamed, taking into account the indications, the following gel preparations with the local type of exposure can be prescribed to the patient: Dentinox, Metrogil Dent, Asepta, Kamistad, and Holisal.
It is important to consider that any medications after surgery can be used exclusively on the advice of a dentist, and the combination of local drugs and oral medications is allowed only in some cases. With the uncontrolled use of drugs of the antibacterial group, oral dysbiosis can develop, which reduces the protective functions of the mucous membranes and increases the risk of complications.
Therapy of pericoronaritis with alternative methods
Pericoronaritis is one of the few diseases of the oral cavity that cannot be cured by using alternative recipes. Alternative treatment of this disease has a very low efficiency, for this reason, dentists recommend immediately contacting a medical institution, without waiting for the development of a purulent form of pericoronaritis.
Inflammation of the hood over the wisdom tooth is one of the most dangerous and serious pathologies in dental practice. If there is no treatment, pericoronaritis can lead to serious consequences, among which the greatest danger is systemic blood poisoning. When the eruption of eights is accompanied by the appearance of primary signs of the inflammatory process, the patient should immediately contact a dental clinic. Prevention of the disease involves a periodic visit to the dentist. This will allow to detect the existing deviations at the earliest stages, to predict the further course of the pathology, to take measures to prevent the development of complications, if necessary, to begin treatment immediately.
It is important to remember that only timely diagnosis and therapy will avoid the undesirable consequences of inflammation of the hood of a wisdom tooth.