Pulpitis is an inflammation that affects soft tissues, and it is also accompanied by neurovascular formations that affect the tooth cavity. This ailment is characterized by progressive paroxysmal pain, often it spreads to the entire jaw, gives to the ear, temporal region and intensifies at night. Pulpitis does not go away on its own, here you need to urgently consult a dentist. After contacting a specialist, a diagnosis of pulpitis will be prescribed, and then the best treatment method will be selected. If the patient contacted on time, the outcome of the treatment is favorable. If you tighten and wait, what will happen next, then in the end the consequences can be very serious: periodontitis or near-root cyst. Pulpitis can occur in several forms and each is accompanied by its own specific symptoms.
Pulpitis: classification
After the diagnosis of pulpitis is carried out, the doctor can prescribe the correct therapy, which will end with a complete cure of the damaged tooth. Pulpitis, depending on the stage and characteristics of the course of the disease, manifests itself in several forms:
- Acute pulpitis is divided into focal and diffuse. The acute form is the initial stage of the pathology. Inflammation is located in the closest proximity to the carious cavity. Symptoms are manifested in the form of a sharp spontaneous pain, which can last from a couple of minutes to half an hour. After that, she can calm down and not bother for several hours, but at night she will sharply increase. There may also be discomfort in the tooth, which occurs due to exposure to irritants, and it does not go away for a very long time. In this case, the patient can easily indicate which tooth hurts, and then the diagnosis of pulpitis will be facilitated.
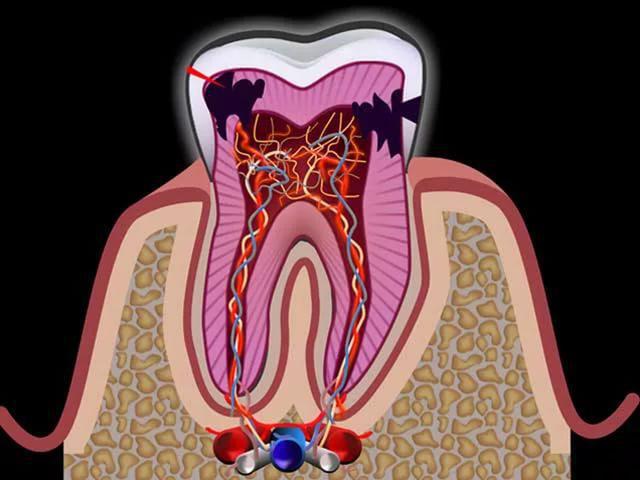
- Acute diffuse pulpitis. During this stage, inflammation spreads to the entire pulp. The patient suffers from bouts of severe pain, relief is rare, and it is short-lived. And after the process from serous to purulent, the pain becomes constant, and there is simply no strength to endure it. It is felt in the temporal part, in the ear and on the half of the jaw on which side the tooth hurts. From the intake of hot food or drinks, the pain intensifies, and from the cold it calms down. This stage can last up to 14 days, and if pulpitis has not been diagnosed during this time, then it goes into the chronic stage.
- Chronic pulpitis can be of several types: fibrous, hypertrophic, gangrenous and retrograde. Chronic fibrous pulpitis appears after the acute form becomes chronic. This period is accompanied by severe aching pain, most often it appears when eating or inhaling cold air. The hypertrophic form occurs at the moment when the carious cavity is connected to the cavity of the tooth. After this, the pulp grows and a process is formed, which is called a polyp, which fills the free space. The patient feels pain when chewing, bleeding appears. The gangrenous form is manifested at the moment when pulpitis was not detected in time, the diagnosis was not carried out in a timely manner, which resulted in a putrefactive infection in the diseased tooth. The patient has a smell from the mouth, tormented by pain. The retrograde type is a chronic form, accompanied by the formation of periodontal pockets, it is in them that the infection is collected. Bacteria passing through the root canals infect soft tissues and cause their inflammation. The bone tissue of the root is absorbed, in this case, it is immediately necessary to conduct therapy and do everything possible to remove pulpitis. Diagnosis and treatment by experienced specialists will help preserve nearby teeth. It is important to seek help on time.

Only modern techniques will help to easily identify pulpitis in the early stages. The clinic, the differential diagnosis in which can be performed, is located in any city. They will help to make a diagnosis with accuracy.
In our modern time, when technology does not stand still, it will not be difficult to identify the disease in the early stages of any kind. Using innovative methods and equipment, pulpitis can be easily diagnosed. Diagnostics in modern medicine can be of several types, and each of them is quite effective. So, where does the process begin after the patient has asked for help:
- Detailed survey. The doctor writes down all the patient's complaints, finds out the reason for the treatment, the nature of the pain and the area of its manifestation. Such a survey helps to make a more accurate diagnosis.
- Inspection of the oral cavity. It is carried out using special tools, the doctor examines all the teeth where the fillings were placed earlier, checks the gums for inflammatory processes.
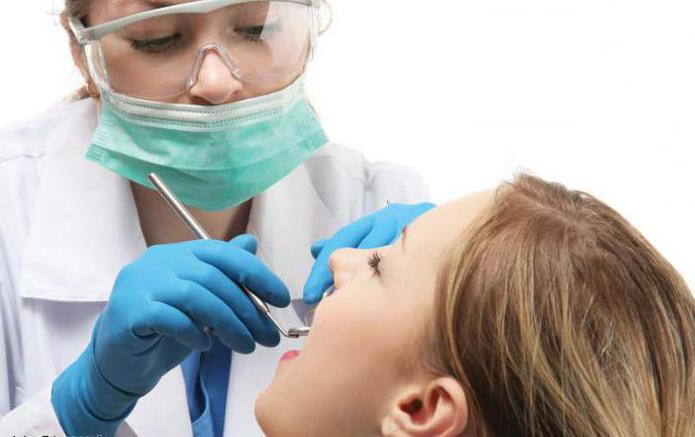

- Sounding. The dentist examines the oral cavity with a probe. This procedure allows you to determine with maximum accuracy the degree of development of the disease. When probing, it is possible to establish the state of dentin at the bottom and walls of the cavity, what is its depth, and also to examine the pulp from the outside. But the main thing in this procedure is to establish the connection of the cavity with the pulp chamber.
- Temperature tests. This diagnosis of acute pulpitis or any other form involves exposure to high and low temperatures on the pulp of the tooth. This method helps to supplement the picture and learn about the state of soft tissues.
- Electroodontodiagnosis. This method is based on testing the reaction of the pulp to electric current. The higher the manifestations of inflammation, the higher the current strength. This method allows you to determine how deeply the neurovascular bundle is affected, and to identify where the focus of inflammation is located. The deeper its location, the stronger the current strength, and if the pulp has completely disappeared, the patient will feel a jolt.
- X-ray With it, you can find out the features of the structure of the tooth, determine how much the disease has developed, and see the results of therapy that was previously performed.
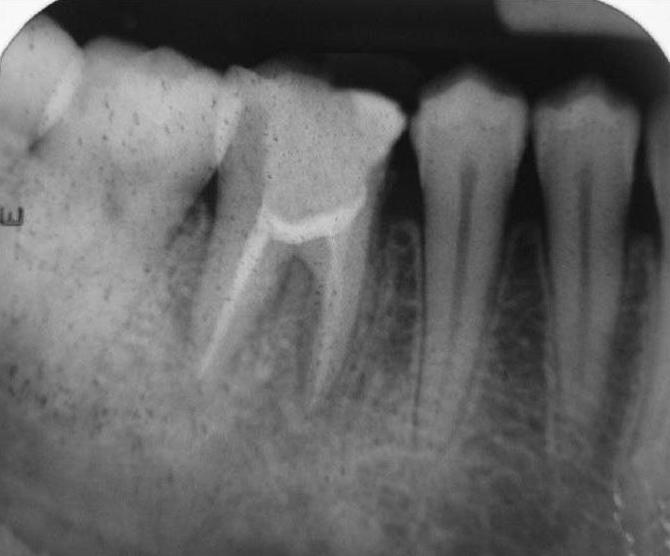
But there is another special method that allows you to determine chronic fibrous pulpitis - differential diagnosis. But what is she like?
Differential diagnosis of pulpitis
This diagnostic method is ideal in cases where it is necessary to distinguish deep caries from chronic pulpitis, because both of these ailments require a special approach to treatment. With pulpitis, the pain that occurs from exposure to irritants does not pass for more than 20 minutes, and with caries it subsides as soon as the irritant is removed.
But to distinguish pulpitis from exacerbated chronic periodontitis, it will be quite enough to simply tap on a diseased tooth. If the patient has periodontitis, then a knock will cause discomfort.
Dif diagnostics of pulpitis of a hypertrophic form will allow you to identify tooth bleeding during mechanical action, this symptom will confirm the diagnosis, the pain in this case is not very pronounced.
If the patient has fibrous pulpitis, then the diagnosis will allow you to notice under the dentin layer in the carious cavity how the pulp is visible. If you touch the probe in this place, the patient will feel severe pain.
During the diagnosis of the hypertrophic form, it is necessary to exclude another diagnosis - the growth of the gingival papilla. If it is a papilla, then it can be pushed out by a probe.
Differential diagnosis of acute pulpitis and the inflammatory process in the trigeminal nerve helps to identify pain, which increases significantly at night. But if it is neuralgia, then at night it passes.
After the diagnosis of chronic pulpitis or any other form has been carried out and the diagnosis has been made, a specific method of therapy is selected for each specific case, only in this way can a stable positive treatment result be achieved.
How to treat pulpitis?
Features of the treatment of pulpitis depend on the form of pathology, as well as on the stages of the development of the disease, in simple words, then on the neglect of the disease. The sooner the patient seeks help from a specialist, the higher the chances of saving the tooth. After one or another form of the disease is detected, for example, chronic pulpitis (differential diagnosis in the formulation of an accurate diagnosis is very effective), the doctor will select a treatment method that will give a good result. But let's take a closer look at what methods doctors use to treat each form of pulpitis.
Acute pulpitis
This form of the disease is treated in three stages:
- The pulp affected by inflammation is removed, the procedure is performed under anesthesia, and in the future, the patient is recommended drug therapy of the root canals.
- Root canal filling, in this case the doctor uses a special sealant.
- Restoration of the tooth crown, a filling agent will come to the rescue.
Serous pulpitis
This is one of the most common forms; it can be of two types: diffuse or focal. Both of these forms are easily treatable if therapy is started in the early stages. First, the doctor cleans the tooth from dentin affected by caries. Then a seal is placed, but a lining with calcium is needed under it, dressings with an antibiotic are also used to help form dentin again. But antibiotics will only help if the patient does not have a chronic form of the disease.
And if the process has been developing for a long time, then in this case the doctor may recommend the removal of dental pulp and nerve.
Purulent pulpitis
This form is considered one of the most dangerous. After all, pathology can be either focal or diffuse. With a focal variety, the pulp is partially affected, and with diffuse it is completely affected. This form is treated only by a surgical method. The doctor cleans the root canals using the vital or devital method. This treatment is very complicated, therefore it is better to entrust this work to a qualified specialist.
It will not be possible to cure this form in one day, on the first day of the visit, the doctor performs the following manipulations:
- anesthetizes, opens and cleanses the carious cavity from dental tissues affected by caries;
- disinfects the cavity with antiseptics;
- using a probe, opens the pulp horn;
- introduces arsenic paste into the tooth to help kill the nerve;
- puts a temporary seal.
The second visit to the doctor involves the following procedures:
- removal of a temporary seal;
- removal of pulp from the root canals;
- treatment of channels with an antiseptic;
- tooth filling ;
- restoration of the tooth crown.
Traumatic pulpitis
This form can be treated both conservatively and surgically, it all depends on the degree of pulp damage. If it is naked at the neck of the tooth and only a small area of it, and the tooth itself is not affected by caries, then conservative treatment will give good results. And if a piece of tooth breaks off and the pulp is severely affected, then the doctor will remove it so as not to provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
Chronic pulpitis
With this form of pathology, conservative therapy is not effective. The only right solution is to use the surgical method. The complexity of this form is that the patient may not realize for a long time that his tooth is ill. Pathology can only be detected if an x-ray is taken.
Depending on the form of the disease, the doctor will use one of the most effective methods. The combined method is considered the best when the doctor uses several treatment options at once, in order to achieve a complete recovery.
Fibrous pulpitis
If a patient has chronic fibrous pulpitis, then the treatment consists in removing the pulp affected by fibrosis. The procedure consists of several stages and is performed under local anesthesia:
- a carious cavity is opened and cleared of caries;
- antimicrobial treatment is carried out;
- resection of the septum;
- removal of part of the coronal pulp that was affected by fibrosis;
- expansion of channels and removal of pulp with fibrosis;
- antiseptic treatment;
- installation of a temporary seal.
After a few days, a temporary seal is replaced by a permanent one.
Hypertrophic pulpitis
This form is characterized by the growth of granulation of pulp tissue, as a result of which blood circulation is disturbed. Depending on the degree of damage, the doctor can apply one of two methods of treatment:
- partial pulp removal, only affected areas;
- complete removal of the pulp, if it is completely affected.
If the pulp is completely removed, then in this case it is very important to clean the root canals well, and then seal them. If all procedures are carried out correctly, then the inflammatory process will not appear.
Gangrenous pulpitis
This is one of the most serious forms when the entire tooth is affected and the pulp is covered with ulcers. Therapy of this form is considered one of the most difficult. The most optimal method is the complete removal of the pulp, or pulpectomy. The procedure consists of the following steps:
- anesthesia;
- opening the cavity and thoroughly cleaning it;
- removal of the coronal part of the pulp;
- expansion of channels and removal of pulp affected by inflammation;
- cauterization of a nerve by electrocoagulation, thus, bleeding can be prevented;
- drying;
- use of an antiseptic dressing;
- filling channels.
Diagnosis of acute focal pulpitis or any other form will help to accurately establish the diagnosis, as well as determine the affected area. Only in this case, the doctor can accurately select the treatment and conduct it as thoroughly as possible.
Even a slight toothache should make you visit a dentist so as not to start the disease and keep the tooth. Any pathology, and this also concerns teeth, is easier to cure if it is detected in a timely manner at the initial stage of development. The current level of development of medicine is such that a visit to the dental office is not always accompanied by pain, the diagnosis of pulpitis and its treatment can be completely painless.