Our article will be devoted to such a biological concept as inflorescences. Types of inflorescences, structural features and their biological significance, examples - consider this and much more.
What are inflorescences
Flowers can be arranged one by one. They are usually large in size and have a brightly colored whisk. But small ones are usually combined in inflorescences. But this is not a bouquet at all. In this structure, all the flowers are located on the same axis in a certain order and are subject to their laws.
Inflorescences: types of inflorescences
There are several types of inflorescences of plants. They are classified according to the principle of branching the axis and the characteristics of the placement of flowers. According to these signs, simple and complex types of inflorescences of plants are distinguished. In the first case, the individual elements are located on the same axis, which is unbranched. An example of it is the lily of the valley brush. But here we have a scheme, the types of inflorescences on which represent another group. They are complex. Please note that in this case the flowers are collected on a common axis.
Inflorescence Types: Examples
Inflorescences are quite unique structures. The number of components in it can be from several to tens of thousands. The record holder is a tropical agave plant. Under natural conditions, its inflorescence appears around 10-15 years of life. Its axis can reach about ten meters. And the number of flowers is approaching 10 thousand. This plant is a real champion. However, this miracle of nature blooms once in a lifetime, after which it dies. And as a result, new young onions of small agaves are formed.
Simple inflorescences
Types of inflorescences of plants that have a single axis are called simple. The most common of these are brush, spike, flap and umbrella. All inflorescences, regardless of their type, have a clear structure. For example, a brush is an axis on which flowers are alternately attached. Its structure is illustrated by the scheme. Types of inflorescences having such a structure are characteristic of lily of the valley, bird cherry, red and black currants, cabbage, lupine.
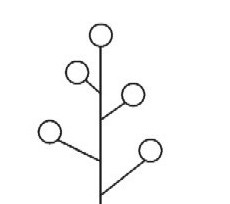
But at the plantain and sedge flowers are also located on the axis of the next. However, they are all sedentary, that is, they do not have pedicels. Such a structure is called an ear. It is characteristic of all cereal plants. An ear whose axis is significantly thickened is called the ear. Examples of this are corn and callas. Flowers located along the main axis form a shield. It can be found in apple trees, plums, quinces. Moreover, the lower pedicels are longer than the upper ones. Therefore, all the flowers are in the shield approximately at the same level.
The next simple inflorescence is an umbrella. It really resembles a rain device. All pedicels converge at one point on the apex of the axis, like the spokes of an umbrella. Cherry, primrose, onion and honesty are the plants for which it is characteristic.
Clover has an inflorescence called the head. Its main axis is thickened and shortened. A basket of cornflower, chamomile and sunflower is formed by sedentary flowers. They are attached to the extended axis, which in appearance resembles a saucer.
Complex inflorescences
The type of flower inflorescence in rye and barley is a complex spike. It is characteristic of many members of the Cereal family. The panicle is arranged differently. It can be a combination of simple brushes, like grapes and lilacs. The second variant of the panicle is a group of spikelets that are located on the side branches. Inflorescences of millet, rice and oats have such a structure.
The regularity of the structure of complex inflorescences is considered to be that they are a combination of simple ones. So the shield of yarrow and tansy is arranged. It consists of simple baskets. And in lilacs and grapes this type of inflorescence consists of simple guards. The complex umbrella of parsley, carrots and dill is additionally surrounded by bracts of leaf.
The biological significance of inflorescences
That's so diverse inflorescences. Inflorescence types, regardless of characteristics, play a very important role in plant life. They make the pollination process more efficient - transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pestle. The result of this process is the formation of fruits and seeds. In other words, generative propagation of angiosperms. The flowers, which are located on the shoot alone, have a fairly large size, bright color and attractive aroma. They are immediately noticed by insects. But if the flowers are small and discreet, bees and butterflies are unlikely to pay attention to them. For this, there are special adaptations in nature. They are the inflorescences. They are more visible to pollinators. However, inflorescences also form in plants in which fertilization occurs with the help of wind. In this form, they better capture pollen that is in the air. In addition, the fact that a larger number of fruits are formed in the inflorescence is also important. This trait increases economic value, contributes to an increase in species diversity, abundance and distribution.
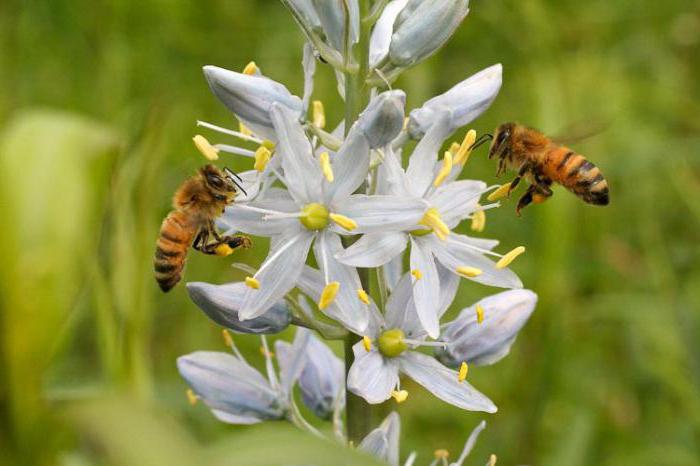

So, we examined what are the inflorescences, types of inflorescences, examples and their biological significance. By structure, these structures are simple and complex. This set of flowers is found in representatives of almost all families of angiosperms, contributing to the efficiency of pollination, and hence their sexual reproduction, species diversity and distribution on the planet.