As you know, the human reproductive system is designed to reproduce offspring. Female and male genitals are significantly different from each other. Next will be considered all the genitals of a person, their purpose.
Female genitals
The reproductive system of a woman performs several important functions. This is the formation of female eggs, which are necessary for reproduction. They are also called mature eggs. After formation, they are transported to the place where fertilization will take place. These are usually fallopian tubes. The next step in fertilizing an egg is to implant it in the uterine wall. This is the beginning of a woman’s pregnancy. If this does not happen, then menstruation begins. Another function of the female reproductive system is the production of sex hormones that support the reproductive cycle.
The structure of the female reproductive system
The system consists of both internal and external parts. Genitals are external organs whose function is to ensure the penetration of sperm into the body, as well as to protect internal organs from infections.
External organs of a woman
The external genital organs of a woman include:
- Large labia. They embrace and protect the labia minora. The structure of the genitals is comparable to the male scrotum, as the large lips are relatively large and fleshy. They contain sweat glands and glands that secrete lubricant. During adolescence, they become covered with hair.
- The labia minora can be really small - only 5 centimeters wide. They surround the entrance to the vagina and are located inside the labia majora.
- The clitoris is a small sensitive organ formed at the convergence of the labia minora. The male reproductive organ is often compared with it. The clitoris is covered with a skin fold, as is the penis. It is also sensitive to touch and erects.
The internal organs of a woman
If the genitals are external organs, then what are the internal organs?
- The vagina is a canal connecting the cervix and the outside of the body. It is also called the birth canal.
- The uterus is an empty organ in which the fetus develops. It is divided into two parts: the neck and the main body. It is easily stretched and adjusted to the size of the developing fetus. The channel that passes through the cervix allows the seed to get inside, and blood during menstruation to go outside.
- The ovaries are small oval glands located on both sides of the uterus. They produce eggs and hormones.
- Fallopian tubes are called narrow tubes attached to the top of the uterus. Mature oocytes into the uterus pass through them. Fertilization occurs in these tubes. The fertilized egg then moves into the uterus, where it is implanted and begins to develop.
Male reproductive system
Unlike the female, most of the male system is located outside the body. This is due to the fact that a man is involved only in conception, and not in the formation of the fetus and its bearing.
Male external organs
The scrotum, penis and testicles belong to the external genitalia.
- The penis is the male organ used during sexual intercourse. It consists of a root attached to the stomach, a rod, as well as a head, which is a cone-shaped part at the end. The head is covered with foreskin, which some remove for various reasons. The urethra and tube transporting the seed and urine are at the end of the organ. The genital organ contains a very large number of nerve endings, which are extremely sensitive. The penis consists of three chambers, which, in turn, consist of spongy tissue. The cavities of this tissue are filled with blood at the time of excitation. This allows intercourse.
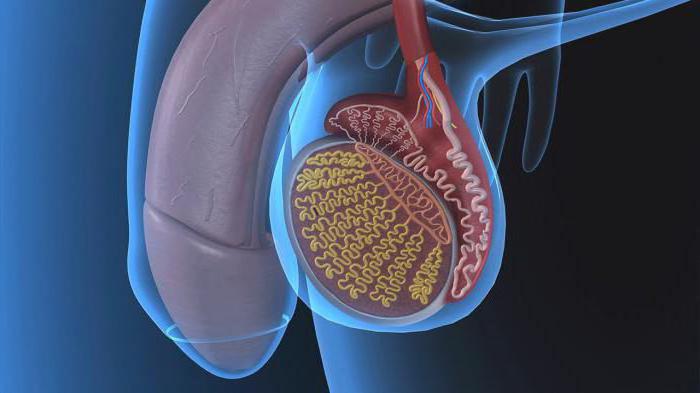
- Male genitals are not only the penis, but also the scrotum. It is a sac containing the testes and many blood vessels and nerves. It regulates the temperature of the testicles, because to produce the seed, it must be slightly lower than the total body temperature.
- The testicles are small oval organs located in the scrotum and attached by a cord. These organs are responsible for the production of male hormone and sperm. Inside them there are a large number of tubules - tubules. They produce sperm.
Male internal organs
The internal organs of the male system, also called the accessory, are:
- The appendage is a long and curved tube on the back of the testicle. She carries sperm and stores sperm. They are also responsible for sperm maturation.
- The vas deferens are a tube that goes from the appendage into the pelvic cavity. In preparation for ejaculation, the ducts transfer mature sperm to the urethra.
- The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the body to the outside. In the male body, it also discards seminal fluid. At this time, the flow of urine is completely blocked.
- Seminal vesicles are pouches attached to the ducts that expel the seed, near the base of the bladder. They produce fructose. It is a liquid that is saturated with sugar. It serves as an energy source for germ cells, which enables them to move. It is the liquid of these vesicles that prevails in the total volume of the seminal fluid of a man, which is also called ejaculate.
- The prostate, or prostate gland, is an organ that is comparable in size to a walnut. It is lower than the bladder. The prostate adds additional sperm feeding elements to the seminal fluid . The urethra, ejecting ejaculate with orgasm, passes just through the middle of the prostate gland.
- Bulburethral glands, also called cooper glands, are a bean-sized structure. They are located below the prostate on the sides of the urethra. These glands form a clear fluid that flows directly into the urethra. It is necessary to lubricate and eliminate any acidity after urination.
Conclusion
So, now it has become clear why the human reproductive system is needed, how it differs in women and men, what genitals are. All this is an integral part of the human body, without which life on the planet would be impossible. It is very important to keep this system healthy in order to produce full-fledged offspring and thereby maintain life in the world.