The Importance of Genetics
With the discovery of the basics of genetics, science has gained an extensive base of new research on the substrate of evolution - the genetic code. It is in it that information is laid on all past and upcoming changes for the development of the body.
The ratio of heredity and variability allows you to save only the best qualities, and in return for the unsuccessful to acquire new ones, improving the structure and contributing to the victory in natural selection.
Basic concepts of genetics
In modern genetics, the chromosome theory of inheritance is taken as the basis, according to which the main morphological substrate is the chromosome - a structure from a condensed complex of DNA (chromatin), from which information is read during protein synthesis.
Genetics is based on several concepts: a gene (a DNA fragment encoding a specific single character), a genotype and phenotype (a combination of genes and organism traits), gametes (sex cells with a single set of chromosomes) and zygotes (cells with a diploid set).
Genes, in turn, are classified into dominant (A) and recessive (a) depending on the prevalence of one trait over another, allelic (A and a) and non-allelic genes (A and B). Allelic are located on the same chromosome sites and encode one trait. Non-allelic genes are absolutely opposite to them: they are located in different areas and encode different characters. However, despite this, non-allelic genes have the ability to interact with each other, giving rise to the development of completely new traits. According to the qualitative composition of allelic genes, organisms can be divided into homo- and heterozygous: in the first case, the genes are the same (AA, aa), in the other - different (Aa).
The mechanism and patterns of gene interaction
The forms of gene interaction among themselves were studied by the American geneticist T.H. Morgan. He presented the results of his research in the chromosome theory of heredity. According to it, the genes included in the composition of one chromosome are inherited together. Such genes are called linked and form the so-called. clutch groups. In turn, within these groups, recombination of genes also occurs by crossing over - exchange of chromosomes between different regions between themselves. Moreover, it is absolutely logical and proven that the genes located directly one after the other are not subjected to separation during the crossing-over process and are inherited jointly.
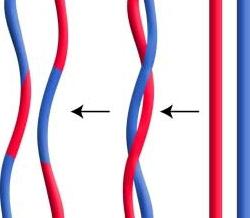
If there is a distance between the genes, then the probability of separation exists - this phenomenon is called "incomplete linkage of genes." If we talk about this in more detail, then the interaction of allelic genes among themselves occurs according to three simple schemes: complete dominance with obtaining a pure dominant trait, incomplete dominance with obtaining an intermediate trait, and coding with inheritance of both traits. Non-allelic genes are more difficult to inherit: according to complementarity schemes, polymers, or epistasis. In this case, both traits will be inherited, but to a different extent.