The development of psychiatry and neurology in modern conditions is impossible without in-depth knowledge of the structure and functions of the brain. Without an understanding of the processes occurring in this body, it is impossible to effectively treat diseases and return people to a full life. Violations at any stage of embryogenesis - genetic abnormalities or disorders due to teratogenic effects of external factors - lead to the development of organic pathologies and irreparable consequences.
Important department
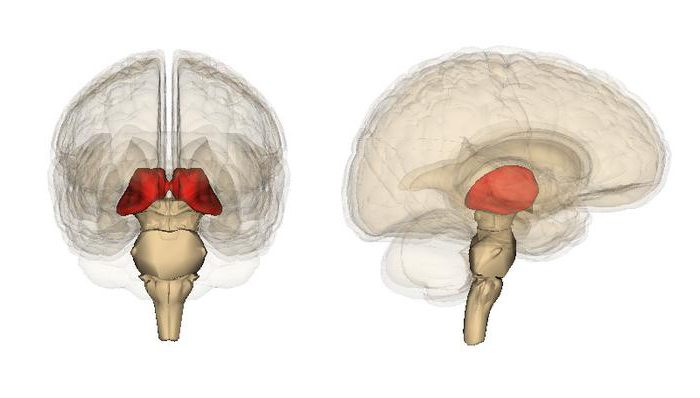
The brain is a complex structure of the body. It includes various elements. One of the most important departments is considered intermediate. It includes several links: the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus and metalamus. The first two are considered the most basic.
Thalamus: Physiology
This element is presented as a median symmetrical formation. It is located between the midbrain and the cortex. The element consists of 2 departments. The thalamus is a formation that is part of the limbic system. He performs various tasks. During the period of embryonic development, this element is considered the largest. It is fixed in the so-called anterior region, near the center of the brain. Nerve fibers depart from it into the cortex in all directions. The medial surface forms the side wall in the third ventricle.
Kernels
The thalamus is part of a complex complex. It is formed of four parts. These include: the hypothalamus, epithalamus, prethalamus, as well as the dorsal thalamus. The last two are derived from the intermediate structure. The epithalamus consists of a pineal cone, a triangle and leashes. In this area are the nuclei involved in the activation of smell. The ontogenetic nature of the epithalamus and peritalamus is different. In this regard, they are considered as separate entities. In general, the structure of the thalamus includes more than 80 nuclei.
Specificity
The thalamus of the brain includes a system of lamellae. It is formed by myelinated fibers and divides different parts of the formation. Other areas are defined by neural groups. For example, intralaminar elements, periventricular nucleus, and so on. The structure of the elements differs significantly from the main thalamic part.
Classification
Each center has its own nucleus. This determines their importance for the human body. The classification of nuclei is carried out depending on their location. The following groups are distinguished:
- Front
- Mediodorsal.
- Midline.
- Dorsolateral.
- Ventrolateral.
- Ventral posteromedial.
- The back.
- Intralaminar.
In addition, the nuclei are divided depending on the orientation of the action of neurons on:
- Visual.
- Carrying out the processing of tactile signals.
- Auditory.
- Regulating balance.
Types of Centers
Relay, nonspecific and associative nuclei are distinguished. The latter include a huge number of median and intralaminar formations. Relay nuclei receive signals that are subsequently projected into different parts of the cortex. These include formations that transmit the primary sensations (ventral-posteromedial, ventral-postlateral, medial and lateral articular), as well as cerebellar impulses involved in the feedback (lateral ventral). Associative nuclei receive most of the impulses from the cortex. They project them back to regulate activity.
Nerve pathways
The thalamus is a formation associated with the hippocampus. Interaction is carried out through a special tract, in which the arch and mastoid bodies are present. The thalamus is connected to the cortex by the thalamocortical rays. There is also a way along which information about itching, touch, temperature is transmitted. It passes in the spinal cord. There are two sections here: ventral and lateral. On the first pass impulses about pain and temperature, on the second - about pressure and touch.
Blood supply
It is carried out from the connecting posterior, lower lateral, lateral and middle choroidal, as well as paramedial thalamic-hypothalamic arterial vessels. Some people have an anatomical anomaly. It is presented in the form of a Percheron artery. In this case, one trunk departs from the posterior cerebral vessel . It provides blood to the entire thalamus. This phenomenon is quite rare.
Functions
What is the thalamus responsible for ? This education performs many tasks. In general, the thalamus is a kind of information concentrator. Through it, relaying between different subcortical areas occurs. For example, each sensitive system, in addition to the olfactory system, uses thalamic nuclei that receive and transmit signals to the corresponding primary regions. For the visual area, incoming pulses from the retina are sent to the lateral departments through a center projecting information onto the corresponding cortical area in the occipital sector. The thalamus plays a special role in the regulation of wakefulness and sleep. Nuclei interacting with the cortex form specific chains that are associated with consciousness. Activity and arousal also regulates the thalamus. Damage to this formation usually leads to coma. The thalamus is associated with the hippocampus, performs certain tasks in organizing memory. It is believed that its areas are connected to some mesio-temporal areas. This ensures the differentiation of familiar and recollective memory. In addition, it is hypothesized that the thalamus is also involved in neural processes necessary for motor regulation.
Pathology
Due to a stroke, thalamic syndrome can develop . It is manifested by one-sided burning (fever), aching sensations. He is often accompanied by mood swings. Bilateral ischemia of the thalamic region can provoke quite serious violations. These include, for example, akinetic mutism, oculomotor disorders. With blockage of the Perheron artery, bilateral heart attack can occur.
Reticular thalamus formation
In the central part of the trunk there is an accumulation of cells. They are intertwined with a huge number of fibers extending in all directions. If you look at this formation under a microscope, then it looks like a network. Therefore, it was called the reticular formation. Neural fibers extend to the cortex and form non-specific pathways. With their help, activity is maintained in all parts of the central nervous system. Under the influence of the formation, reflexes are amplified. In this cluster, information is selected. Overlying areas receive only new and important information. The activity of the formation is always at a high level, since signals from all receptors go through it.
Neurons
They are highly sensitive to pharmacological agents and hormones. Such drugs as Reserpine, Aminazine, Serpazil and others can reduce the activity of the formation. In neurons, upward and downward signals interact. Pulses are in constant circulation in the circuits. Due to this, activity is maintained. It, in turn, is necessary to maintain the tone of the nervous system. In the event of the destruction of the formation, especially its upper sections, deep sleep occurs, although afferent signals continue to enter the cortex through other paths.