Most of the European territory of Russia, as well as some neighboring countries, is located on the continental stretch of the earth's crust, which is called the East European Platform. The shape of the relief here is mostly flat, although there are exceptions, which we will discuss below. This platform is one of the oldest geological formations on earth. Let's take a closer look at what the relief of the East European platform is, what minerals it contains, and how the process of its formation took place.
Geographic location
First of all, we will find out exactly where this geological formation is located.
The East European ancient platform, or, as it is also called, the Russian platform, is located in the geographical regions of Eastern and Northern Europe. It occupies most of the European part of Russia, as well as the territories of the following neighboring states: Ukraine, Belarus, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Moldova, Finland, Sweden, partially Poland, Romania, Kazakhstan and Norway.
In the north-west, the East European ancient platform extends to the formation of Caledonian folding in Norway, in the east it is bordered by the Ural Mountains, in the north - by the Arctic Ocean, and in the south by the Black and Caspian Seas, as well as the foothills of the Carpathians, Crimea and the Caucasus (Scythian plate).
The total area of the platform is about 5500 thousand square meters. km
Formation history
The tectonic landforms of the East European platform are among the oldest geological formations in the world. This is due to the fact that the platform originated in pre-Cambrian times.
Before the formation of a single world continent, Pangea, the territory of the Russian platform was a separate continent - the Baltic. After the collapse of Pangea, the platform became part of Laurasia, and after the separation of the latter, it became part of Eurasia, where it is still located.
Throughout this time, the formation was covered by sedimentary rocks, which thus formed the relief of the East European platform.
Platform Composition
Like all ancient platforms, the foundation of the East European is the crystalline foundation. Over millions of years, a layer of sedimentary rocks was created on top of it. However, in some places the foundation comes to the surface, forming crystalline shields.
There are two such shields in the indicated territory (in the south - the Ukrainian shield, in the north-west - the Baltic shield), which is shown on the tectonic map of the platform.
the East European Plain
What surface does the East European platform have? The shape of the relief here is mostly hilly-flat. It is characterized by alternating low elevations (200-300 m) and lowlands. In this case, the average height above sea level of the plain, which is called the East European, is 170 m.
The East European (or Russian) plain is the largest object of the flat type in Europe and one of the largest in the world. Its area occupies most of the territory of the Russian platform and is about 4000 thousand square meters. km It extends from the Baltic Sea and Finland, inclusively in the west, to the Ural Mountains in the east for 2500 km, and from the seas of the Arctic Ocean in the north (Barents and White) to the Black, Caspian and Azov Seas in the south for 2700 km. At the same time, it is part of an even larger-scale object, which is commonly called the Great European Plain, stretching from the coast of the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees Mountains in France to the Ural Mountains. As mentioned above, the average height of the Russian Plain is 170 meters, but its highest point reaches 479 m above sea level. It is located in the Russian Federation on the Bugulminsko-Belebeyevskaya Upland, in the foothills of the Ural Mountains.
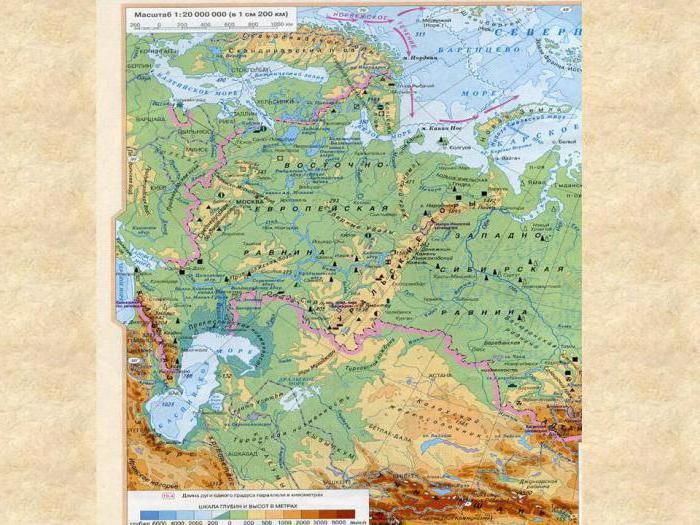
In addition, on the territory of the Ukrainian Shield, which is also located on the Russian Plain, there are uplifts, which are the form of the crystalline rocks of the platform base coming out. These include, for example, the Azov Upland, the highest point of which (Belmak-Tomb) is 324 meters above sea level.
The basis of the Russian Plain is the East European Platform, whose tectonic structures are very ancient. This is due to the flat nature of the area.
Other terrain features
But the Russian Plain is not the only geographical object that contains the East European Platform. The relief form here takes on other forms. This is especially characteristic at the borders of the platform.
For example, in the extreme northwest of the platform in Norway, Sweden and Finland, the Baltic Crystal Shield is located. Here, in the south of Sweden, there is the Middle Swedish Lowland. Its length from north to south and from west to east, respectively, is 200 km and 500 km. The altitude here does not exceed 200 m.
But in the north of Sweden and Finland, the Norland Plateau is located. Its maximum height is 800 meters above sea level.
The hill is characterized by a small section of Norway, which includes the East European platform. The shape of the relief here takes on a mountainous character. Yes, this is not surprising, since the hill gradually in the west passes into the most real mountains, called the Scandinavian mountains. But these mountains are already derivatives of the Caledonian folding, not directly related to the platform described in this review, which is depicted on a tectonic map.
Rivers
Now let's take a look at the main bodies of water that are located on the territory of the platform we are studying. After all, they are also relief-forming factors.
The largest river of the East European platform and Europe as a whole is the Volga. Its length is 3530 km, and the basin area is 1.36 million square meters. km This river flows from north to south, while on the surrounding lands forming the corresponding floodplain landforms of Russia. The Volga flows into the Caspian Sea.
Another major river on the Russian platform is the Dnieper. Its length is 2287 km. She, like the Volga, flows from north to south, but, unlike her longer sister, flows not into the Caspian Sea, but into the Black Sea. The river flows through the territory of three states at once: Russia, Belarus and Ukraine. At the same time, about half of its length falls precisely on Ukraine.
Other large and well-known rivers of the Russian platform include the Don (1870 km), the Dniester (1352 km), the Southern Bug (806 km), the Neva (74 km), the Don tributary Seversky Donets (1053 km), the Volga Oka tributaries (1499 km) and Kama (2030 km).
In addition, in the most southwestern part of the platform, the Danube River flows into the Black Sea. The length of this great river is 2960 km, but it flows almost completely beyond the borders of the platform we are studying, and only the mouth of the Danube is on its territory.
Lakes
Available on the territory of the Russian platform and lake. The largest of them are located in the north-west of Russia. This is Europe’s largest freshwater lake Ladoga (an area of 17.9 thousand square kilometers) and Lake Onega (9.7 thousand square kilometers).
In addition, in the south of the Russian platform is the Caspian Sea, which, in fact, is a salt lake. It is the largest body of water in the world that does not have access to the world's oceans. Its area is 371.0 thousand square meters. km
Minerals
Now let's explore the mineral resources of the East European platform. The bowels of this territory are very rich in gifts. So, in the east of Ukraine and south-west of Russia is one of the largest coal basins in the world - Donbass.
On the territory of Ukraine there are also Kryvyi Rih iron ore and Nikopol manganese pools. These deposits are associated with access to the surface of the Ukrainian shield. Even greater iron reserves are available on the territory of the Kursk magnetic anomaly in Russia. True, there the shield did not come out, but very close to the surface.
In the area of the Caspian depression, as well as in Tatarstan, there are quite large oil deposits. They are also on the territory of the southern oil and gas region in Ukraine.
On the territory of the Kola Peninsula, production of apatites on an industrial scale has been established.
Actually, these are the main minerals of the East European platform.
Soils of the Russian platform
Are the soils of the East European Platform fertile? Yes, it is in this region that one of the most fertile soils in the world. Especially valuable soil types are located in the south and in the center of Ukraine, as well as in the chernozem region of Russia. They are called chernozems. These are the most fertile soils in the world.
The fertility of forest soils, in particular gray soils, which are located north of the chernozems, is much lower.
General characteristics of the platform
Landforms of Russia are quite diverse. Among them, plains occupy a special place. Just the East European platform forms the largest flat complex in Europe. Relatively high highlands can be found only on its periphery. This is due to the antiquity of this platform, on which mountain-forming processes have not been going on for a long time, and weathering has smoothed the hills that existed here millions of years ago.
Nature has endowed the region with huge mineral reserves. Particularly noteworthy are coal and iron ore deposits, in terms of which the Russian platform is one of the world leaders. There are also reserves of oil and some other minerals.
This is the general characteristic of the East European platform, its relief, minerals stored in the bowels, as well as the geographical features of this area. Of course, this is a fertile land that provides its residents with all the necessary resources, which, if used properly, will be the key to prosperity.