In our article, we will consider the structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. These organisms differ significantly in the level of organization. And the reason for this is the structural features of genetic information.
Structural features of prokaryotic cells
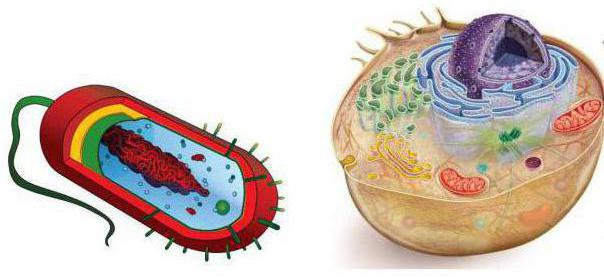
Prokaryotes are all living organisms whose cells do not contain a nucleus. Of the representatives of the five modern Realms of wildlife, only one belongs to them - Bacteria. Prokaryotes, whose structure we are considering, also include representatives of blue-green algae and archaea.
Despite the absence of a formed nucleus in their cells, they contain genetic material. This allows you to store and transmit hereditary information, but limits the variety of methods of reproduction. Reproduction of all prokaryotes occurs by dividing their cells in two. They are not capable of mitosis and meiosis.
The structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes
The structural features of prokaryotes and eukaryotes that distinguish them are quite significant. In addition to the structure of genetic material, this also applies to many organelles. Eukaryotes, which include plants, fungi and animals, contain mitochondria, the Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, and many plastids in the cytoplasm. In prokaryotes, they are absent. The cell wall, which is in both those and others, differs in chemical composition. In bacteria, it contains complex carbohydrates pectin or murein, while in plants it is based on cellulose, and in fungi - chitin.
Discovery story
The structural and vital features of prokaryotes became known to scientists only in the 17th century. And this is despite the fact that these creatures have existed on the planet since its inception. In 1676, they were first examined under an optical microscope by its creator Anthony van Levenguk. Like all microscopic organisms, the scientist called them "animalikules." The term "bacteria" appeared only at the beginning of the 19th century. He was proposed by the famous German naturalist Christian Ehrenberg. The concept of "prokaryotes" arose later, in the era of the creation of an electron microscope. Moreover, at first, scientists established the fact of differences in the structure of the genetic apparatus of the cells of different creatures. E. Chutton in 1937 proposed combining organisms on this basis into two groups: pro and eukaryotes. This division exists to this day. In the second half of the 20th century, a difference was discovered among the prokaryotes themselves: archaea and bacteria.
Features of the surface apparatus
The surface apparatus of prokaryotes consists of a membrane and a cell wall. Each of these parts has its own characteristics. Their membrane is formed by a double layer of lipids and proteins. Prokaryotes, whose structure is quite primitive, have two types of cell wall structure. So, in gram-positive bacteria, it consists mainly of peptidoglycan, has a thickness of up to 80 nm and is tightly attached to the membrane. A characteristic feature of this structure is the presence of pores in it, through which a number of molecules penetrate. The cell wall of gram-negative bacteria is very thin - up to a maximum of 3 nm. It is not tight to the membrane. Some representatives of prokaryotes also have a mucous capsule on the outside. It protects organisms from drying out, mechanical damage, creates an additional osmotic barrier.
Prokaryotic organelles
The cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes has its own significant differences, which are primarily the presence of certain organelles. These constant structures determine the level of development of organisms as a whole. In prokaryotes, most of them are absent. The synthesis of protein in these cells occurs on the ribosomes. Water prokaryotes contain aerosomes. These are gas cavities that provide buoyancy and regulate the degree of immersion of organisms. Only prokaryotic cells contain mesosomes. These folds of the cytoplasmic membrane occur only during the use of chemical methods of fixation during the preparation of prokaryotic cells for microscopy. Organelles of the movement of bacteria and archaea are cilia or flagella. And attachment to the substrate is carried out drank. These structures formed by protein cylinders are also called villi and fimbriae.
What is a nucleoid?
But the most significant difference is the structure of the gene of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. All these organisms possess hereditary information . In eukaryotes, it is located inside the formed nucleus. This two-membered organelle has its own matrix called nucleoplasm, membrane and chromatin. Here is carried out not only the storage of genetic information, but also the synthesis of RNA molecules. Subunits of ribosomes, the organelles responsible for protein synthesis, are subsequently formed in the nucleoli from them.
The structure of prokaryotic genes is simpler. Their hereditary material is represented by a nucleoid or nuclear region. DNA in prokaryotes is not packed into chromosomes, but has a circular ring structure. The nucleoid also includes RNA and protein molecules. The latter functionally resemble eukaryotic histones. They are involved in DNA doubling, RNA synthesis, restoration of chemical structure and nucleic acid breaks.
Features of life
Prokaryotes, whose structure is not difficult, carry out rather complex processes of life. This is nutrition, respiration, reproduction of their own kind, movement, metabolism ... And all this is capable of only one microscopic cell, the sizes of which range from up to 250 microns! So we can only talk about primitiveness relatively.
The structural features of prokaryotes also determine the mechanisms of their physiology. For example, they are able to receive energy in three ways. The first is fermentation. It is carried out by some bacteria. This process is based on redox reactions during which ATP molecules are synthesized. This is a chemical compound, the splitting of which in several stages produces energy. Therefore, it is not in vain called the "cell battery". The next way is breathing. The essence of this process is the oxidation of organic substances. Some prokaryotes are capable of photosynthesis. Their examples are blue-green algae and purple bacteria , which contain plastids in the cells. But archaea are capable of chlorophyll-free photosynthesis. During this process, carbon dioxide is not fixed, but ATP molecules are directly formed. Therefore, in fact, this is real photophosphorylation.
Type of food
Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, the structure of which allows them to carry out various methods of nutrition. Some of them are autotrophs. These organisms themselves synthesize organic matter during photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is located in the cells of such prokaryotes. Some bacteria receive energy through the breakdown of certain organic compounds. Their type of nutrition is called chemotrophic. Representatives of this group are iron and serobacteria. Others absorb only finished compounds. They are called heterotrophs. Most of them lead a parasitic lifestyle and live only inside the cells of other creatures. A variety of this group are saprotrophs. They feed on waste products or decaying organic matter. As you can see, the ways of eating prokaryotes are quite diverse. This fact contributed to their widespread distribution in all habitats.
Breeding forms
Prokaryotes, whose structure is represented by one cell, multiply by dividing it into two parts or by budding. This feature is also due to the structure of their genetic apparatus. The process of binary division is preceded by doubling, or DNA replication. In this case, the nucleic acid molecule is first untwisted, after which each thread is duplicated according to the principle of complementarity. The resulting chromosomes diverge towards the poles. Cells increase in size, a constriction forms between them, and then their final isolation occurs. Some bacteria are also capable of forming asexual reproduction cells - spores.
Bacteria and archaea: hallmarks
For a long time, archaea, along with bacteria, were representatives of the Kingdom of Drobyanka. Indeed, they have many similar structural features. This is primarily the size and shape of their cells. However, biochemical studies have shown that they have a number of similarities with eukaryotes. This is the nature of enzymes under the influence of which the processes of synthesis of RNA and protein molecules occur.
By the method of nutrition, most of them are chemotrophs. Moreover, the substances that break down in the process of obtaining energy of the archaea are more diverse. These are complex carbohydrates, and ammonia, and metal compounds. Among archaea and autotrophs. Very often they enter into a symbiotic relationship. There are no parasites among archaea. Most often in nature, commensals and mutualists are found. In the first case, the archaea feed on the substances of the host organism, but do not bring him any harm. In contrast to this kind of symbiosis, with mutualistic relationships, both organisms benefit. Some of them are metagens. Such archaea live in the digestive system of humans and ruminant mammals, causing excessive gas formation in the intestines. These organisms reproduce by binary division, budding, or by fragmentation.
Archaea have mastered almost all habitats. They are especially diverse in the composition of plankton. Initially, all archaea were assigned to the group of extremophiles, since they are able to live in hot springs, and in reservoirs with increased salinity, and at depths with significant pressure.
The value of prokaryotes in nature and human life
The role of prokaryotes in nature is significant. First of all, they are the first living organisms that arose on the planet. Scientists have established that bacteria and archaea arose about 3.5 billion years ago. The theory of symbiogenesis suggests that some organelles of eukaryotic cells originated from them. In particular, we are talking about plastids and mitochondria.
Many prokaryotes find their application in biotechnology in order to obtain medicines, antibiotics, enzymes, hormones, fertilizers, herbicides. Since ancient times, man has been using the beneficial properties of lactic acid bacteria for the manufacture of cheese, kefir, yogurt, and pickled foods. With the help of these organisms, water and soil are cleaned, and ores of various metals are enriched. Bacteria form the microflora of the intestines of humans and many animals. Along with archaea they carry out the cycle of many substances: nitrogen, iron, sulfur, hydrogen.
On the other hand, many bacteria are the causative agent of dangerous diseases, regulating the number of many species of plants and animals. These include plague, syphilis, cholera, anthrax, diphtheria.
So, prokaryotes are called organisms whose cells lack a formed nucleus. Their genetic material is represented by a nucleoid consisting of a circular DNA molecule. Of modern organisms, prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea.