The skull is a skeletal element of the head. It distinguishes the facial (visceral) and brain region. The latter has a cavity. It houses the brain.
General information
The facial section is represented by the skeleton of the face, the initial segments of the respiratory tract and the digestive tube. It also contains the palatine, lacrimal, nasal, zygomatic elements, the vomer and the ethmoid bone (the anatomy of this segment will be discussed later). It should be said that the latter lies partially in the department. The parietal, frontal, sphenoid, occipital, temporal elements are distinguished in the brain. There is also a part of the ethmoid bone. In this section, the base and roof (arch) of the skull are distinguished. The brain and facial parts of the skull are connected motionless, except for the lower jaw. She articulates movably using a joint with the bones of the temple.
Brain
The arch contains flat bones. These include scales of the temporal and occipital, as well as the frontal and parietal elements. Flat bones consist of plates of a compact substance (internal and external), between which lies a spongy bone structure (diploea). The connection of the roof elements is carried out by means of seams. At the base of the skull - the lower part - the occipital foramen is located. It connects the cavity with the spinal canal. There are also openings for nerves and blood vessels. Pyramids of the temporal elements act as lateral bones of the base. There are departments of the organs of balance and hearing. Allocate the inner and outer sides of the base of the skull. The first is divided into the back, middle and front central pits. They have different parts of the brain. In the central part in the middle pit is the Turkish saddle. The pituitary gland lies in it. Two condyles lie on the outside of the base, away from the occipital foramen. They are involved in the formation of the atlantooccipital joint.
Front department
The upper jaw is represented by a pair of bones. Inside it is the maxillary sinus. Through the corresponding segments, the walls of the nasal cavity, orbits, and the hard palate are formed. On the side there is a wing-palatine fossa. It communicates with the oral, cranial and nasal cavities, the orbit. The infratemporal and temporal fossae are also present on the same surface. The nasal section opens the cavity of the maxillary, frontal and sphenoid elements, as well as the cells of the ethmoid bone. Jointing of the lower jaw is carried out due to the temporomandibular joints. Next, consider what the ethmoid bone is.
Anatomy, location
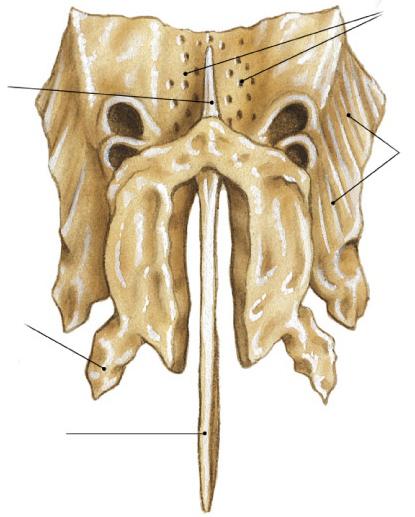
This element serves to separate the cranial and nasal cavities. The ethmoid bone, the photo of which is presented in the article, is unpaired. The segment has a shape close to cubic. The element also has a cellular structure. This is the reason for the name. A segment is located between the sphenoid (posterior), frontal bones and the upper jaw (along the bottom). The element runs along the midline. The ethmoid bone is present in the anterior zone of the base of the brain and facial parts. She is involved in the formation of the nasal cavity and orbits. In the segment there is a plate. From it on the sides are labyrinths. They are covered externally by vertically located orbital surfaces (right and left).
Ethmoid plate
This element is the top of the segment. It is located in the ethmoid notch in the frontal bone. The plate is involved in the formation of the bottom in the anterior cranial fossa. The entire surface of the element is occupied by holes. In appearance, it resembles a sieve, whence its name actually comes from. The olfactory nerves (the first pair of cranial) run through these openings into the cranial cavity. In the midline above the plate there is a cockscomb. Towards the front, it continues with a paired process - the wing. These parts, together with the frontal bone, which lies in front, delimit the blind opening. In some ways, the extension of the ridge is a perpendicular surface. It has an irregular pentagonal shape. It is directed downward towards the nasal cavity. In this zone, the plate, located vertically, is involved in the formation of the upper region of the septum.
Maze
This is a pair formation. It consists of the sinuses of the ethmoid bone (airways that communicate with each other and with the nose). The labyrinth looks as if suspended from the top right and left. The medial surface of the formation is oriented into the nasal cavity and is separated from the perpendicular plate by means of a vertical narrow slit. She, in turn, is in the sagittal (vertical) plane. On the lateral side, the labyrinths are covered with a thin and smooth plate. It is part of the medial surface of the orbit.
Nasal concha
On the medial side, the cells are covered with curved thin bone plates. They represent the middle and upper concha. The lower edge of each hangs freely in the gap. It passes between the perpendicular plate and the labyrinth. The upper portion of each shell is attached to the medial surface of the holes of the labyrinth. The upper shell is attached, respectively, from above, slightly below it and a little forward passes the middle. In some cases, the third element is also found. It is called the "highest shell" and is rather weakly expressed. Between the middle and upper shells lies the nasal passage. It is represented by a narrow gap. The middle stroke is located under the curved side of the corresponding turbinate. It is bounded below by the upper portion of the lower concha. At its posterior edge there is a hook-shaped process, curved down. It is articulated on the skull with the ethmoid process extending from the lower shell. Behind this formation, a large bubble protrudes into the middle course. This is one of the largest cavities, which includes the ethmoid bone. A gap is visible behind and behind the large bubble and the hook-shaped process in front and below. It has the shape of a funnel. Through this gap, the frontal sinus and middle nasal passage are communicated. This is the normal anatomy of the ethmoid bone.
Joint Types
The structure of the ethmoid bone involves a connection with several elements of the skull. In particular, there are joints with the following segments:
- Opener. The ethmoid bone is connected to this element by the upper portion of the anterior margin.
- Upper jaw. The articulation is carried out by the outer side of the lateral masses with the crest of the frontal process and the lower lateral zone with the posterior portion of the inner edge on the orbital surface.
- The frontal bone. The connection occurs by connecting the front edge of the perpendicular element to the nasal spine. Also, the half-cells in the lateral regions and the horizontal plate are articulated with the half-cells in the latticed notch. A seam runs through this section.
- Sphenoid bone. The trailing edge of the horizontal plate is adjacent to the trellis spike. A flexible connection is formed in this section. The posterior edge of the vertical plate is articulated with a comb. At this point there is a seam. The posterior margins in the lateral masses are adjacent to the pre-outer sides of the segment. In this case, a seam is formed.
- Palatine bone. The joint is carried out at the level of the triangle with the lower side of the lateral masses.
- Nasal bones. The joint performs the leading edge of the vertical segment.
- Lacrimal bone. The lateral surface of the same masses is involved in this compound.
- The cartilaginous part of the septum of the nose. The connection is made by the lower front side of the vertical plate.
- Lower concha. The ethmoid bone articulates with it by adjoining the hooked process in the middle cavity to the branch from the lower nasal concha.
Formation
The ethmoid bone has a cartilaginous (secondary) origin. It develops with the four nuclei of their cartilage in the nasal capsule. According to one of the initial elements, it is present in the vertical plate, cocks and lateral masses. Ossification first spreads to the nasal concha. After the process affects the trellis plate. After birth, six months later, the ossification of the orbital surface is noted, and after 2 years, a cockscomb. The vertical plate process only affects 6-8 years of life. Labyrinth holes are finally installed by 12-14 years.
Damage
Due to the fact that the structure of the ethmoid bone is porous, the segment is very susceptible to injury. Often fractures occur in an accident, with a fall, a fight, a front-upward blow in the nose. Bone fragments can freely move through the ethmoid plate, in fact, into the cranial cavity. This can provoke cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) in the nose. The resulting message of the cranial and nasal cavities provokes severe, difficult to eliminate CNS infections. The ethmoid bone has a close relationship with the olfactory nerve. If the element is damaged, the smell sensitivity may deteriorate or completely disappear.