Diphtheria and tetanus are two dangerous diseases, the sources of infection of which are completely different, however, vaccination is often carried out with one combination drug. Its composition includes both diphtheria and tetanus toxoids, which cause the development of stable immunity in the vaccinated individual against diphtheria and tetanus. Vaccination is included in the list of obligatory due to serious consequences, often life-threatening. However, these diseases due to ongoing immunization of the population for many decades are extremely rare. For this reason, some people neglect prevention.
Do I need a vaccine against dangerous infections - diphtheria and tetanus?
There is no consensus on this. Most qualified professionals believe that vaccination against these dangerous infections is necessary. But adherents of the naturalistic theory argue that the human immune system itself is able to cope with infections. Should I get vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus? The right to decide is granted to the parents of the child or to the patient who has reached adulthood. Due to the long-term immunization of the population, most people have antibodies to these infections, which prevents the occurrence of epidemics.
Why are diphtheria and tetanus dangerous?
Tetanus, the causative agent of which is a bacterium - tetanus bacillus, living in the ground, manure and feces, is not a contagious disease. Infection occurs when the pathogen enters through damage to the epidermis and mucous tissues, with the formation of wounds, abrasions, frostbite and burns. The more the surface of the tissue is affected, the greater the likelihood of a disease. The causative agent, falling under the dermis, releases toxins that affect the nervous system. As a result, severe cramps appear, leading to paralysis of the respiratory organs and heart muscle, and death occurs.

Diphtheria is considered a serious infectious disease caused by a bacterium - diphtheria bacillus, which is transmitted by airborne droplets. The causative agent of diphtheria emits toxic substances that affect the oropharynx and bronchi. In this case, a malfunction of the respiratory tract occurs, stenosis of the larynx occurs, which rather quickly, within a quarter of an hour, progresses to asphyxiation. Without emergency medical care, death from suffocation is possible. The only measure to prevent these diseases is recognized as a preventive vaccine against diphtheria and tetanus.
Vaccination frequency
In order to form a stable immunity from dangerous diseases - tetanus and diphtheria, vaccination is carried out throughout the life of an individual according to the following scheme:
- starting from three months, three vaccinations every 45 days;
- 18 months;
- 6-7 years;
- 14-15 years old.
Only with such a frequency of vaccinations does a stable immunity form. If the vaccination schedule is violated for any reason, the child is vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus at the age of 7 using the weakened toxoid ADS-M twice a month, then the first revaccination is carried out after 6–9 months, after 5 years - the second, and then every 10 years. Individuals should monitor the regularity of vaccinations themselves. However, when applying for jobs in some specialties related to the threat of diphtheria or tetanus, business leaders are required to provide information on the availability of vaccination against these diseases. If after the last immunization more than ten years have passed, then three injections must be made, similar to how three-month-old babies are vaccinated.
Contraindications to vaccination
All contraindications are divided into two large groups:
- Relative - any disease that causes a decrease in immunity, fever, low weight of the child, a course of antibiotic treatment just completed, an allergic disease in the acute stage, the first trimester of pregnancy. In this case, the vaccine is postponed until all health problems are resolved.
- Absolute - immunodeficiency of any type, severe allergic reactions of the body to some component of the vaccine. In the first case, they refuse immunization, in the second - they replace the vaccine with an analogue that is similar in action, but without live cultures. For example, a standard vaccine against diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus is replaced by a lightweight ADS that does not contain the components of the pertussis virus, which often produce adverse reactions.
How to reduce side effects?
To reduce the negative effects after vaccination, doctors recommend:
- Reduce the amount of food consumed within three days, starting the day before vaccination. To do this, reduce the concentration and volume of food.
- These days give your baby more fluid.
- With skin rashes, several days before the procedure, the child is given antihistamines.
- You should not sit in line with the child for a long time at the treatment room, it is better to spend some time with him on the street.
- For prophylaxis after vaccination, paracetamol is allowed. Elevated temperature does not affect the production of immunity, so it can be brought down.
Compliance with these simple recommendations will help the child easier to take the vaccine. And according to the guidelines there are few contraindications to vaccination. Mild signs of a cold, slight diathesis, a runny nose are not reasons for refusing vaccination.
Negative reactions after vaccination
Sometimes after vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus, negative symptoms occur, although most children tolerate vaccination without any problems. A local reaction in the injection area and minor changes in the condition of the child may occur:
- redness of the skin;
- slight swelling near the injection site;
- hypodermic seal;
- painful sensations;
- increase in body temperature;
- sweating
- malaise;
- the appearance of a runny nose;
- the occurrence of cough;
- itching
Parents should not worry, all problems will pass on their own in 3 days. To alleviate the symptoms that have arisen, it is best to consult a doctor. In very rare cases, after vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus, the consequences are in the form of severe complications: convulsions, prolonged, continuous crying, encephalopathy, loss of consciousness. In the event of such situations, an ambulance must be called urgently. Sometimes there are also allergic reactions: anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema, which appears immediately after administration of the drug, therefore it is not recommended to leave the clinic for 20-30 minutes. It should be noted that serious consequences arise mainly if the rules for preparing for vaccination are not followed or recommendations are not followed during the recovery period.
Vaccines containing diphtheria and tetanus toxoids
Serum for vaccination containing tetanus and diphtheria toxoids is produced by domestic and imported pharmaceutical companies. There are both multicomponent and mono vaccines. Free vaccination in Russia for children and adults is carried out with domestic drugs:
- DTP is a vaccination against pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus. It is intended for children up to one and a half years. To develop immunity, three vaccinations and one revaccination are necessary.
- ADS - vaccine consists of diphtheria and tetanus toxoid, but does not contain pertussis component. It is prescribed to children after the age of six for revaccination against diphtheria and tetanus. It is also used for babies up to two years old if, after the first vaccination, allergic reactions to pertussis toxoid have been identified.
- ADS-M - differs from ADS in a lower content of antigens.
- AS or AD - mono-preparations containing one component of tetanus or diphtheria. Such vaccinations are given to those who are intolerant of another component that is part of a multicomponent vaccine. The drug AD is convenient to use in the event of an epidemic of diphtheria, and AS in cases of suspected infection with tetanus bacillus.

In the absence of any contraindications, it is always better to be vaccinated with a multicomponent vaccine, in this case, be vaccinated against diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus.
Place for injection in children and adults
Injected substance to enter the body must enter the bloodstream. This happens most quickly in muscle tissue, where there is no fat layer. Therefore, for infants and adults, the vaccine is administered intramuscularly:
- In young children, the most developed muscle is the thigh, and the drug is injected into it. With the right injection, the baby does not have a bump and a strong seal. This is possible just when serum is introduced into the fat layer, where it dissolves for a long time and causes discomfort in the child.
- At the age of six, an injection is made into the shoulder or under the shoulder blade, depending on the physical condition of the baby.
- Adults are vaccinated in the shoulder blade or shoulder area.
It should be recalled that the injection site can not be combed and rubbed so that there are no undesirable reactions: redness, thickening and suppuration.
Vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus in adults
Most people vaccinated in childhood think that they are protected against infections for life and they should not care about vaccination. In fact, there is a revaccination system that supports the body's defenses. And according to the national vaccination calendar for the adult population against diphtheria and tetanus, as well as for children, immunization is provided. In adulthood, the first vaccine is given when 26 years old. After this, revaccination is necessary every 10 years. If the adult was not vaccinated, then he is given two vaccinations with an interval of 45 days and a single booster vaccination 6–9 months after the second vaccination, and then every 10 years. Injection is done with the drug ADS-M - vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus. Adults (whooping cough is much harder and with a large number of complications in young children) do not administer pertussis toxoid. But some experts argue that it is advisable to also vaccinate adults against this disease. To do this, you can use imported drugs containing additionally purified components of pertussis to reduce adverse reactions.
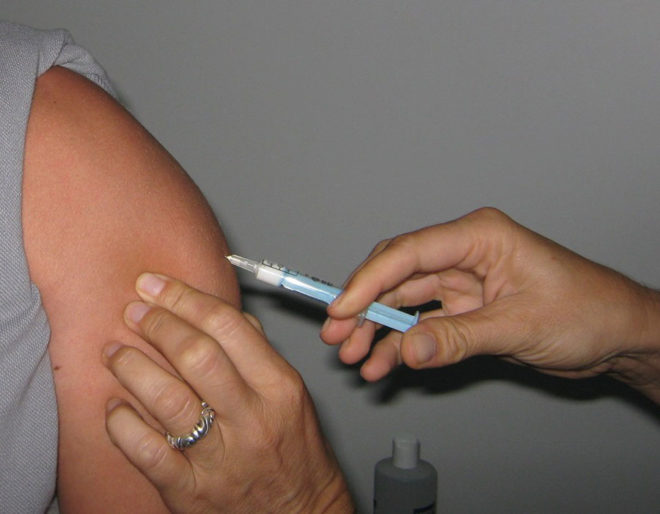
There are special instructions for a number of professions that involve contact with an infection in which there is a risk of infection. For example, forestry and agricultural workers, military, railway workers, medical workers must be vaccinated. Information about immunization is recorded in the health record by a medical professional. Before vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus, adults undergo a medical examination to determine the contraindications, which the drug ADS-M does not have so many. These include: immunodeficiency, an allergic reaction to the components of the drug. Injection may be delayed due to the patient’s illness until his recovery or canceled completely if there are contraindications. Do not vaccinate pregnant women, so as not to harm the development of future crumbs. After vaccination in adults, as in children, mild ailments are possible, which pass on their own. In case of serious complications, consult a doctor.
What to do if you missed the vaccine?
According to the schedule of vaccinations against diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus, an ideal vaccination plan has been developed , according to which the child receives protection from viruses in the optimal time and with the lowest risk of side effects. And this schedule must be adhered to. But in life there are various circumstances: long illnesses, trips or some other situations, and there is a violation of the vaccination plan. You can start vaccinating your baby with DTP vaccine at any time up to the age of 4. In our country, after the child is 4 years old, it is forbidden to use domestic vaccines containing the pertussis component. Therefore, after this milestone, the child is vaccinated with an analogue of DTP, the French drug "Tetracocum" - this is an inoculation against diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus and polio.

Starting from 4 to 6 years old, use the ADS vaccine, and then the ADS-M. Both drugs do not contain pertussis component. If the second vaccination period is missed, DTP continues the vaccination regimen in the same manner as without breaking the schedule. In the event that the third DTP vaccine is missed, it is done, not paying attention to the pass.
French vaccine Pentaxim
Can the imported vaccine Pentaxim replace DTP. Leading experts in this field answer in the affirmative. The only thing that should be noted: vaccination with imported drugs is paid. Pentaxim is not a complete analogue of DTP. As it was previously found out, the domestic vaccine protects babies from three infections, and the imported drug is much more effective, and it protects the baby with one vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus, polio, as well as pertussis and haemophilus influenzae.
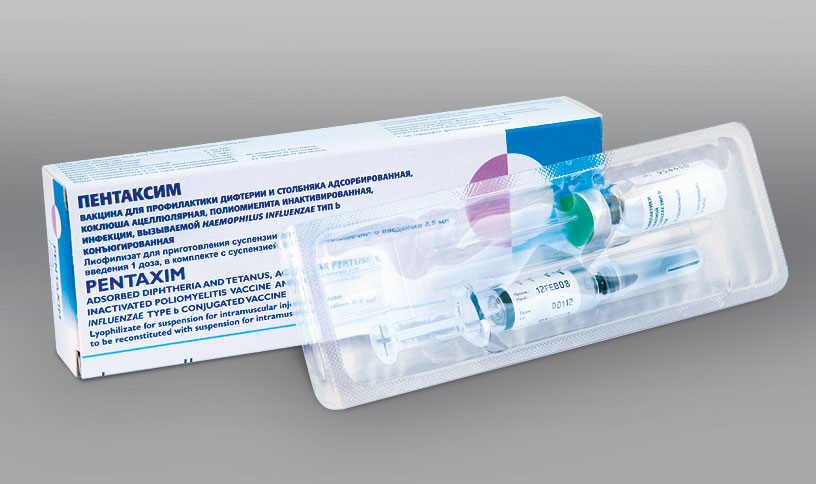
Moreover, protection from whooping cough is very important for a small child, and when vaccinating with DTP, it is precisely this component that most often causes a negative reaction in babies. And therefore, children are often vaccinated with ADS and ADS-M vaccines that do not contain pertussis toxoid. In the Pentaxim preparation, the pertussis component is cleaved and does not contain a shell. As a result, it is much better tolerated by children. In addition, when using it, the number of vaccinations is reduced, which is essential for the baby.
Conclusion
Vaccination against diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus is necessary for adults and children . The danger of contracting these serious diseases is real. It should not be forgotten that some serious ailments do not appear due to the high immunization of the population in the past. Now, when there are voluntary refusals of vaccinations, some of them are returning again. Remember, the risk of complications from diseases is much higher than from vaccination.