The structure and functions of various parts of the body, including bone joints, are studied by anatomy. The elbow joint refers to the bone joints of the free upper limb and is formed as a result of the articulation of the individual parts of 3 bones: the humerus, ulnar and radial.
Joint components
The elbow joint is an unusual bone joint that connects the shoulder and forearm.
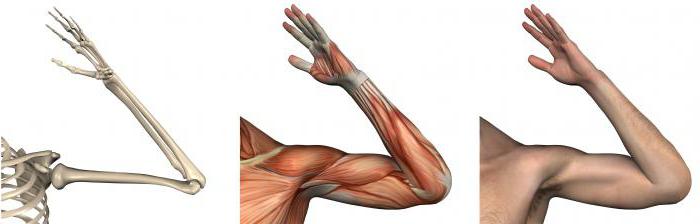 The special structure allows the joint to be attributed to a complex and combined articulation.
The special structure allows the joint to be attributed to a complex and combined articulation.
A complex joint is called one in the formation of which more than two articular surfaces take part. There are three in the elbow:
- articular surface of the distal epiphysis of the humerus (block and head of the condyle);
- the articular surface of the ulna (block and radial notch);
- head and articular circumference of the radius.
A combined joint refers to those joints in which several independent joints are joined by one joint capsule. In the elbow, three independent are combined in one capsule.
The anatomy of the human elbow joint is very unusual; it combines 3 different types of joints in one joint:
- brachiocephalic - uniaxial, block-shaped;
- brachioradial - spherical, but the movement is carried out around two axes (frontal and vertical);
- ray-elbow - cylindrical (rotation around a vertical axis).
Possible elbow movements
The structure of the joint allows you to make a specific set of movements. This is flexion, extension, rotation (pronation and supination).
Joint capsule
The joint capsule surrounds 3 joints. It is fixed in front and on the sides.
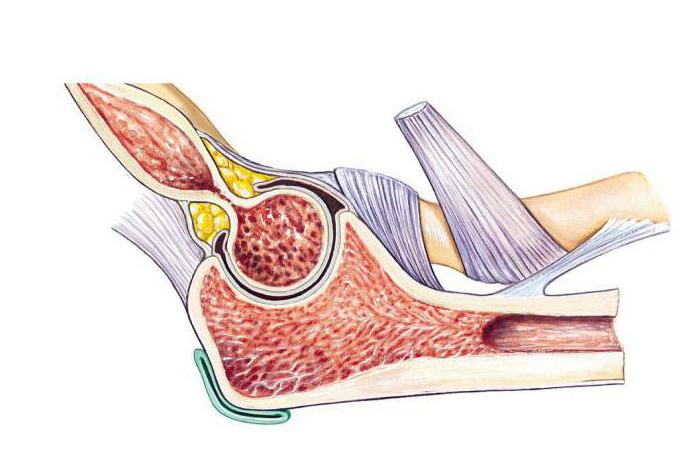 The front and back are quite thin, slightly stretched, but on the sides of it protect the ligaments of the elbow joint. The anatomy of the synovial membrane includes bones that are not covered by cartilage, but are located in the joint.
The front and back are quite thin, slightly stretched, but on the sides of it protect the ligaments of the elbow joint. The anatomy of the synovial membrane includes bones that are not covered by cartilage, but are located in the joint.
Ligaments of the elbow joint
Each bone connection is a complex and thoughtful anatomy. The elbow joint is strengthened by ligaments, which provide its protection and movements in different planes.
The ulnar collateral ligament starts from the base of the humerus (medial condyle), ends on the ulna (block notch).
 The radial collateral ligament starts from the humerus (lateral epicondyle), is divided into 2 bundles, which diverge and bend around the head of the radial bone, are attached to the ulna (radial notch).
The radial collateral ligament starts from the humerus (lateral epicondyle), is divided into 2 bundles, which diverge and bend around the head of the radial bone, are attached to the ulna (radial notch).
The annular and square ligaments fix the radius and ulnar bones.
Lumpy protrusions attached tendons of the elbow joint. The anatomy of this compound is called the "head of the ulna." It is she who most often suffers from injuries and injuries.
In addition to the main ligaments of the joint, the interosseous membrane of the forearm is also involved in the function of fixing the bones. It is formed by strong bundles that connect the radius and ulna. One of these bundles goes in the opposite direction from the others, called the oblique chord. It has openings through which the vessels and nerve pass. The oblique chord is the beginning for a number of muscles of the forearm.
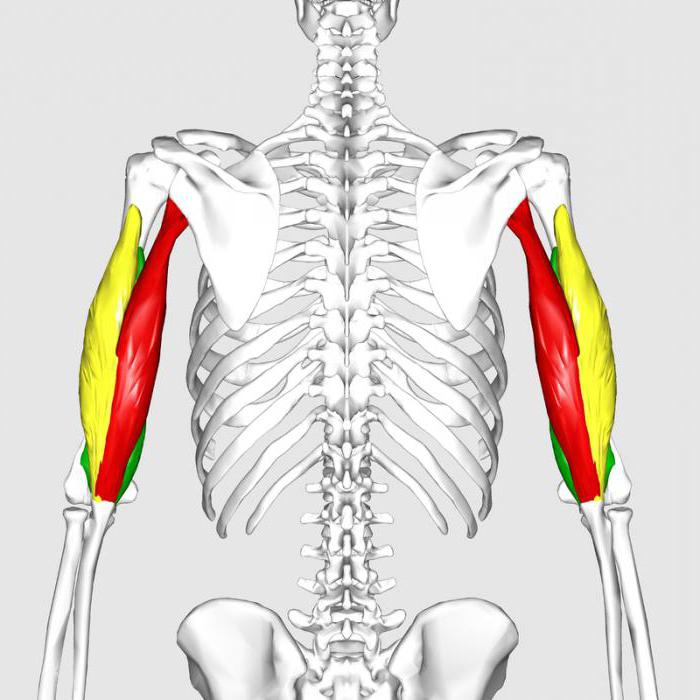
Muscles of the elbow joint, anatomy and their functions
There are several unusual bone compounds in the human body. They are all studied by anatomy. The elbow joint is unusual in its own way. It is protected by a good muscle frame. The coordinated work of all muscles ensures the smooth operation of this bone compound.
All muscles affecting the elbow joint can be divided into 3 groups: extensors, flexors, rotators (they perform pronation and supination).
Joint extensors - triceps muscle of the shoulder (triceps), tensor of fascia of the forearm and ulnar muscle.
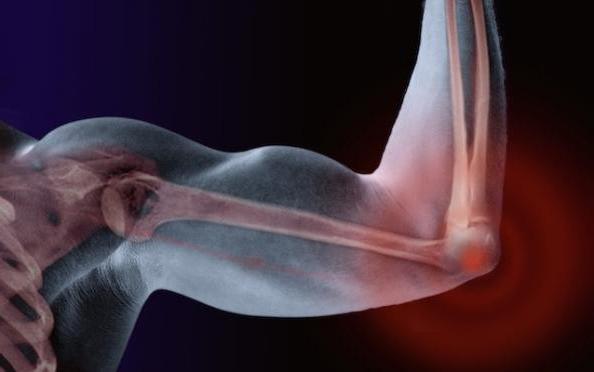 Joint flexors - biceps of the shoulder (biceps), brachioradial and brachial muscles.
Joint flexors - biceps of the shoulder (biceps), brachioradial and brachial muscles.
Pronators - brachioradialis muscle, circular pronator, square pronator perform rotational movements in and out.
Arch support - the biceps of the shoulder, arch support, brachioradius muscle rotate the forearm from the inside.
When performing physical exercises that strengthen these muscles, it is important to remember safety precautions. The elbow joint is very often injured in athletes.
Blood supply to the elbow joint, anatomy
It is very important for the joint to get the nutrients that come to it together with the blood in a timely manner. It comes to all joints and muscles from a group of arteries. They consist of 8 branches that are located on top of the joint capsule.
The network of arteries supplying blood to the joint consists of vessels called anastomosis.
The topographic anatomy of the elbow joint is a very complex vascular connection scheme. Thanks to this scheme, blood flow to the joint is uninterrupted. Outflow is carried out through the veins.
Muscle innervation
What makes the process of movement in the joint possible? There are special nerve formations that innervate the muscles. These are the radial and middle nerves. They pass along the front of the elbow.
Features of the elbow joint, research methods
The elbow joint is very vulnerable, as it is constantly exposed to physical exertion.
Very often, to determine the cause of the pain, the doctor prescribes additional studies. This can be radiography, MRI, ultrasound, tomography, arthroscopy, elbow puncture.
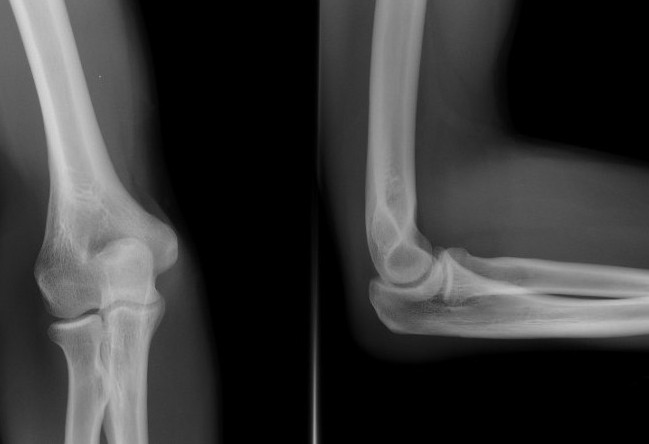 These examinations will reflect the current condition of the bones and ligaments, joint space. A picture of a study will reflect its entire anatomy. The elbow joint is a complex joint that requires caution and a detailed study with the help of additional equipment.
These examinations will reflect the current condition of the bones and ligaments, joint space. A picture of a study will reflect its entire anatomy. The elbow joint is a complex joint that requires caution and a detailed study with the help of additional equipment.
The main method for diagnosing diseases of the elbow is radiography. Pictures are taken in two projections. They allow you to see all the changes in the bones.
To determine the diseases of the soft components of the elbow, doctors use other research methods.
Injuries and illnesses
Regular pain in the elbow may indicate that there are some violations. After the examination, the most common diagnosis is arthrosis. Arthritis happens, and much more.
Arthrosis
It occurs much less frequently than in the knee or hip joints. The risk group includes people whose work is associated with increased loads on the elbow joint, who have suffered an injury or surgery on the elbow, with endocrine or metabolic disorders, with arthritis.
Main symptoms: persistent aching pain that occurs after physical activity. Passes after rest. Clicking or crunching in the elbow. Amplitude limitation.
Arthritis
Inflammation of the joint. There are many possible reasons. They can be infections, allergic reactions, high loads on the joint, malnutrition.
The form of arthritis can be acute or chronic.
The main symptoms: persistent pain, flushing of the skin, swelling, limited mobility of the joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Most often, the elbow joint affects rheumatoid arthritis. Its symptoms: stiffness of movements in the morning, symmetric arthritis (both joints are inflamed), chronic nature of pain, involvement of smaller joints (hands, ankles, wrist, knee joints) in the painful process.
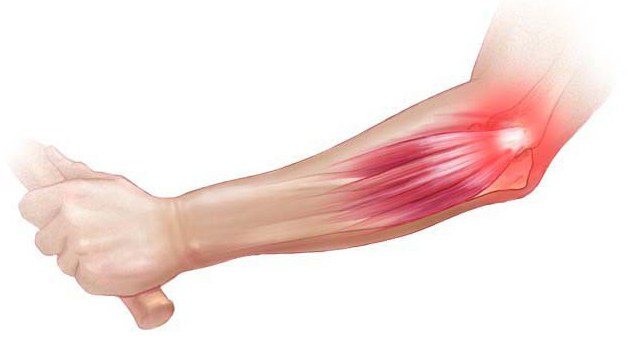
Epicondylitis
A frequent disease in people whose activity is associated with high loads on the elbow joint (tennis, golf, wrestling).
There are 2 types: lateral, medial.
The main symptoms: pain in the area of the damaged epicondyle, which extends to the muscles of the forearm (front or rear). At the onset of the disease, pain occurs after exertion. In the future, pain is felt even from minimal movements.
Bursitis
Inflammation of the articular bag. Most often occurs in people whose activity is associated with permanent injuries of the posterior surface of the elbow.
 The main symptoms: swelling, throbbing pain, swelling in the back of the elbow, limitation of the amplitude of movement. Often, the temperature rises with the main symptoms, a state of general weakness, malaise, and headaches begin.
The main symptoms: swelling, throbbing pain, swelling in the back of the elbow, limitation of the amplitude of movement. Often, the temperature rises with the main symptoms, a state of general weakness, malaise, and headaches begin.
Injuries
Undesirable physical effects on the elbow can result in personal injury. This is a dislocation, bone fractures, sprain, joint hemorrhage (hemarthrosis), muscle damage, rupture of the joint capsule.
The listed injuries and illnesses are most common in everyday life. In order to protect themselves from them, preventive measures should be taken: to avoid excessive exertion, give yourself a timely rest, the prevention of traumatic situations at work, the observance of the diet are important, moderate physical training and joint gymnastics are needed .