There are two main types of blood tests - clinical (it is also called general) and biochemical. Both types of analysis may include a different number of studies. Therefore, they talk about a general and extended blood test. This applies to the first type of research. In the second case, we are talking about a biochemical and biochemical extended blood test.
Jab
In the case of a routine examination, patients are prescribed a routine clinical blood test. In another way, it is called a "general blood test (KLA)." With its help, hemoglobin content is estimated, the number of formed elements - platelets, red blood cells, white blood cells, the leukocyte formula, color index and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are determined. Given these indicators, the doctor can identify the inflammatory process and establish its stage, anemia, assess the condition of the vascular wall. This is a nonspecific analysis, that is, for example, an increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood will not tell about a specific pathology, but will report on its presence and on the general condition of the body.
When an Advanced UAC Appointed
In the event of any abnormalities or when examining the blood of patients with already established diseases, more specific studies are prescribed. These include a clinical advanced blood count. The latter includes a more detailed study of the cellular composition of the blood. Results may include erythrocyte, leukocyte, and platelet indices.
For example, if you suspect a myocardial infarction, the doctor will need to know the ESR, the number of leukocytes, since their change indicates this disease, and also by the degree of deviation from the norm of these indicators, you can determine the duration of the disease. These indicators are included in the usual list of a general blood test.
If the KLA data indicate a pathology such as anemia, then to determine its cause, you must pass an extended blood test, including red blood cell indices.
What includes advanced UAC
A general extended blood test may include the following groups of indicators:
1. Common indicators:
- hemoglobin concentration,
- red blood cell count
- white blood cells
- platelet count
- color indicator
- hematocrit.
2. Red blood cell indices:
- the average volume of red blood cells,
- the average hemoglobin (Hb) in the red blood cell,
- the average concentration of hemoglobin (Hb) in the red blood cell,
- normoblasts
- delta hemoglobin.
3. Platelet indices:
- average platelet volume
- the width of the distribution of platelets by volume,
- thrombocrit
- immature granulocytes.
4. Leukoformula:
- lymphocytes
- neutrophils
- basophils,
- eosinophils,
- monocytes.
5. Analysis for reticulocytes:
- reticulocytes
- hemoglobin content in reticulocytes,
- immature reticulocyte fraction,
- adjusted reticulocyte count,
- reticulocyte production index.
The complex of the obtained research results in terms of the UAC is called a hemogram. It is a table in which indicators, their norm, units of measurement and the result of the study are indicated.
What diseases are prescribed for advanced KLA?
The doctor will prescribe a general extended blood test in the following cases:
- diagnosis of diseases of the blood system and blood formation,
- identification of inflammatory diseases,
- evaluation of the treatment.
It is indicated for other pathologies. The main groups of diseases in which an extended general blood test can be prescribed are:
- anemia
- hemorrhagic diathesis - bleeding disorders,
- hemoblastoses - oncological diseases of the blood.
Some of these diseases are characterized by a change in the number of formed elements (for example, the number of red blood cells decreases during anemia), some are characterized by a change in structure (for example, with sickle cell anemia), some are accompanied by a change in the number of blood cells and their properties. The last group of diseases is called blood cancer. Therefore, the hemogram includes indicators of the number of blood cells (for example, the number of platelets) and indicators of changes in the size and other properties of the cells (for example, the width of the distribution of platelets by volume).
Normal values of UAC indicators
The table shows the normal values of the UAC indicators. The norm of an extended blood test is a rather conventional concept. Although the composition of human blood is fairly constant, many factors can affect the result. In addition, in different population groups - children, pregnant women, athletes - the norm is slightly different. Therefore, the decoding must be carried out by a doctor.
| Indicator | Units | Norm women | Norm men |
| ESR | mm / h | up to 30 years: 8-15 after 30 years: no more than 25 | up to 30 years: 2-10 after 30 years: no more than 15 |
| Hemoglobin | g / l | 115-140 | 140-160 |
| White blood cells | x10 9 / l | up to 30 years: 4.2-9 after 30 years: 3-7.9 | up to 30 years: 4.2-9 after 30 years: 3-8.5 |
| Red blood cells | x10 12 / l | 3.5-4.7 | 3.9-5.5 |
| Hematocrit | % | up to 30 years: 35-45 after 30 years: 35-47 | under 30 years old: 39-49 after 30 years: 40-50 |
| Reticulocytes | % | 2-12 |
| Red blood cell volume | fl | 80-100 |
| The average content of Hb in the red blood cell | pg | 27-31 |
| The width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume | % | 11.5-14.5 |
| Color indicator | | 0.85-1 |
| Platelets | g / l | 150-380 | 180-320 |
| Average platelet volume | fl | 7.4-10.4 |
Decryption of the extended UAC
Deciphering an extended blood test is difficult, even for a therapist. Only a narrow specialist who directs the patient to this study should deal with it. After all, the diagnosis cannot be made according to one or two indicators, it is necessary to take into account the whole complex of indicators, plus clinical signs and additional studies.
For example, consider an indicator such as the width of the distribution of platelets by volume. A completely incomprehensible name for an ordinary person, even if he knows that platelets provide blood coagulation. It shows the heterogeneity of platelets in their volume. Platelets in size are:
- normal
- giant - pathological,
- large - young
- small ones are old.
It is possible to establish whether this platelet is young or old, that is, no longer fulfilling its functions, only by their size - volume. The indicator indicates what percentage of the total number is occupied by small and too large cells. Normally, they should be no more than 15-17%. A change in the indicator indicates a pathology in the bone marrow leading to excessive platelet production, for example, true polycythemia, myelogenous leukemia, myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia. However, a change in this indicator can be observed with other pathologies, including helminthic invasions and Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, only a change in this indicator cannot indicate any particular pathology, but can only complement a whole range of studies.
Blood chemistry
The work of each organ is accompanied by the release of certain substances into the blood - enzymes, hormones, cell metabolism products. In case of an organ disease, the amount or composition of these substances in the blood will change. Therefore, biochemical analysis will assess the functional state of various systems and organs and the state of metabolism in general.
When prescribing advanced biochemical AK
An advanced biochemical blood test can include about 40 indicators. However, there is no need to examine the blood for all these indicators. From the entire list, the doctor will choose those studies that will clarify the condition of a particular organ or systems. For example, with myocardial infarction, a large number of certain enzymes and myoglobin protein enter the bloodstream. Therefore, the establishment of the activity of the enzymes AST, ALT, LDH, CF and their isoenzymes will tell the doctor about the presence of a heart attack and indicate its duration. These indicators are included in the usual list of biochemical studies. However, the most specific indicator of myocardial infarction is the level of troponins in the blood. This analysis is not performed for all patients; it is included in the list of an extended analysis of blood biochemistry and is prescribed only if a heart attack is suspected.
A second example of the purpose of an additional biochemical study is to determine the cause of anemia. If anemia is suspected, the patient will be prescribed a blood test for iron content, which is part of an extended blood test.
What includes advanced biochemical AK
The usual form of "blood test for biochemistry" includes about 20-30 indicators. At the initial examination, the GP sees only a few indicators that need to be checked. Usually this: total protein, total bilirubin, glucose, urea, enzyme activity - AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase.
If any disease is suspected, an extended blood test is prescribed to establish an accurate diagnosis, which indicates the condition of a particular organ. For example, if you suspect atherosclerosis, the list of tests will include, in addition to total cholesterol: triglycerides, high density lipoproteins (HDL), low (LDL) and very low density (VLDL). The list can be further expanded by examining the content of lipoprotein a, apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B.
Decoding of a biochemical blood test
If necessary, the following biochemical studies can be included in the list of advanced biochemical blood tests:
| Biochemical indicator | Value |
| Glucose (or blood sugar) | An indicator of carbohydrate metabolism, a marker of problems in the endocrine system or liver. The indicator provides control of blood sugar in diabetes. Overweight patients should monitor this indicator and take an analysis more often. |
| Bilirubin | The level of direct bilirubin shows the ability of the outflow of bile from the gallbladder, the level of indirect indicates the condition of the liver. |
| Urea (or residual nitrogen) | Protein processing product. It is excreted by the kidneys, so the level shows their condition. |
| Creatinine | The level shows the functioning of the kidneys and energy metabolism in the body. It is considered in combination with urea. |
| Cholesterol (or cholesterol) | The indicator of fat metabolism. Patients with cardiovascular disease should monitor this indicator. |
| AST | An intracellular enzyme, therefore, normally in the blood its activity is minimal. It enters the bloodstream (increased activity is detected in the analysis) with damage to an organ, most often the heart, liver, pancreas. |
| ALT | An intracellular enzyme, therefore, normally in the blood its activity is minimal. It enters the bloodstream (increased activity is detected in the analysis) when damage is predominantly to the liver. |
| Amylase | An enzyme, a change in activity indicates a pathology of the stomach or pancreas. |
| GTF | The enzyme, a change in activity indicates a violation of the liver, biliary tract. |
| LDH | The enzyme, its various isoforms are localized in different organs. Therefore, a change in the activity of certain isoforms indicates damage to a particular organ, for example, LDH 4 - the liver. |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Enzyme activity shows the state of the bile ducts, bones, intestines, kidneys, and placenta. |
| Total protein | The level indicates the intensity of metabolism as a whole, about the availability of nutrients. |
| Albumen | The main blood protein, a decrease in the level indicates dehydration, an increase is rare. |
| Triglycerides | Energy substrates. The indicator of fat metabolism. |
| Blood iron | It is part of the hemoglobin of red blood cells. A decrease in the indicator confirms the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia. |
Blood sampling procedure
Typically, for a general analysis, blood is taken from a finger, and for biochemical and other species from a vein. However, if you need a detailed general analysis, then more material will be required, and it is difficult to take a lot of blood from a finger. Anyone who has ever donated blood from a finger remembers how hard the paramedic squeezes only a few drops.
For an extended analysis, blood will be taken from a vein, usually from the ulnar fossa or from the veins of the forearm or hand. The hand is freed from clothes. Place an oilcloth under the elbow. The hand is lowered down. A tourniquet (venous cuff) is placed slightly above the elbow on a napkin or underwear. The paramedic senses a pulse and finds the most filled vein. Then you need to clench your fist several times, then clamp it.
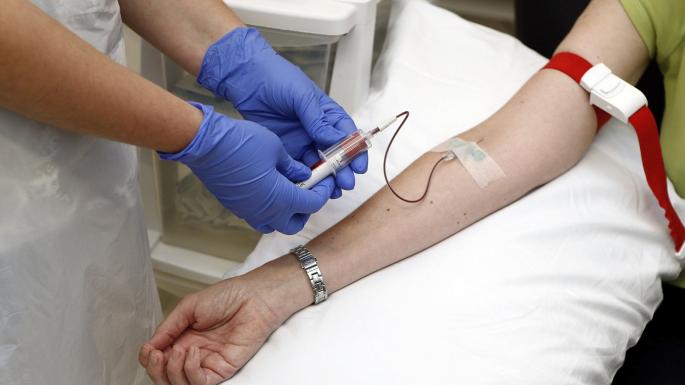
Blood is taken using vacuum systems. It is collected in several test tubes, outwardly different in the color of the caps. Each tube is designed for its own - one or more analyzes. For example, hematological studies are carried out only in whole - not clotted blood. To prevent blood clotting, special reagents are added to the test tube. These tubes have purple (EDTA) or green (heparin) caps. On the contrary, all biochemical analyzes are carried out with serum. She settles during blood coagulation. To do this, use silicon dioxide. Silicon dioxide tubes have red caps.
After taking the blood, the tourniquet will be removed first, only then the needle will be removed from the vein. An alcoholic cotton ball is applied to the puncture site. You need to hold your hand in your elbow and hold it like this for about 3-5 minutes. If you hold your hand badly, a hematoma is formed. Therefore, there is no need to check whether there is blood from the puncture or not. Keep your hand held for at least 3 minutes!