So the world is arranged that each of us is surrounded by thousands of microscopic creatures. With the naked eye, we do not see them, but we touch them every minute. Some “invisibles” help us, others kill, and still others can bring harm and benefit. The yeast-like mushrooms of the Candida genus are just such microbes that do not prevent us from living happily, but in certain situations they begin to behave aggressively, causing candidiasis or thrush. Because these microorganisms do not always cause harm, they are called opportunistic. In total, 186 species of fungi from the genus Candida have been discovered, but only two dozen species are dangerous. They will be discussed in this article.
Candida mushroom genus: characteristic features
Candida is a yeast genus. Most of their species are completely harmless, live in the body of Kombucha, in kefir, in other dairy products, as well as in the human digestive tract, being part of the microflora of a healthy intestine. Mushrooms of the genus Candida are aerobes, that is, they lead an active life in the presence of oxygen. They can exist in two forms - yeast and micellar.
The yeast mushrooms are round or oval blastospores and multiply by budding. In the micellar form
, fungal cells lengthen, turning into pseudomycelia. Unlike the true one, there are no partitions in it, but there are constrictions. Blastospores are located on them, and chlamydiospores with a double shell are located on terminal extensions. In micellar form, fungi can mate.
Mushrooms of the Candida genus differ from other dimorphic creatures in that they can be in their host’s body in two of their forms at once, and not change them depending on the temperature of the environment.
An important property of candida is that they can ferment maltose and glucose.
According to recent studies, candidiasis is caused by approximately 20 species of these fungi, and the most dangerous are C. albicans (60%) and C. tropicalis (20%). The remaining 18 species are less widespread and have no significant effect on the incidence of candidiasis.
Brief description of pathogenic species
The most common fungi of the genus Candida, called C. albicans. Their carriers are approximately 8 out of 10 people. Basically, these fungi enter the baby’s body at birth and live without inconvenience in the mouth, esophagus and intestines. In women, they are also part of the vaginal microflora. It is this type of candida that is most often responsible for the occurrence of candidiasis.
The second dangerous species is called C. tropicalis. These fungi are able to penetrate the blood and colonize peripheral organs with its help. Recent studies have revealed a feature of Candida C. Tropicalis to work in tandem with Serratia marcescens and Escherichia coli, and lead to Crohn's disease.
Not very common, but considered the most dangerous, are yeast fungi of the genus Candida species C.Krusei. They are resistant to the medicine "Fluconazole" used in the treatment of fungal infections, therefore it is important to correctly differentiate the type of pathogenic fungus that affected the patient.
Candida species of C. glabrata was considered non-pathogenic. They exist only in yeast form and reproduce only by budding. Most often, Candida Glabrata is found on urinary catheters, where it forms thin biofilms. This fungus causes urogenital candidiasis.
Candida species C. parapsilosis often causes sepsis. It can infect wounds, especially if foreign objects get into them.
Species of fungi C. Rugosa and C. Lusitaniae and others from the genus Candida are extremely rare. For example, C. Lusitaniae was detected in only 30 patients between 1979 and 1990.
Ways of infection
The conditionally pathogenic yeast-like fungi of the Candida genus in the process of evolution have developed mechanisms to help them lead a parasitic existence. They are able to withstand long-term freezing and drying. They can enter the human body with unwashed and insufficiently processed foods, with dirty hands and other objects, for example, C. parapsilosis fungi infect wounds when foreign objects enter them, including unsterilized medical instruments, and C. Glabrata fungi with urinary or intravenous catheters. Most often, infection with fungi of the species C. Albicans occurs, and from the first minutes of the baby’s life. This happens during childbirth, if the vagina of the woman in labor is populated by these microbes. There is also an assumption that C. Albicans penetrates the baby’s body at the embryo stage, as fungi have been repeatedly found in amniotic fluid. If a woman in labor is included in that small percentage of people who are not carriers of mushrooms, her baby during the first years of life can become infected through a nipple, toys, and so on. Panic because of this is not worth it, since candida, once in the body of their master, behave quietly, even help him, controlling the growth of other pathogens.
When Candida infection becomes a disease
A person can be a carrier of these microbes all his life, while remaining completely healthy. Mushrooms of the genus Candida become pathogenic only when their reproduction is out of control. Causes:
- pregnancy;
- various infections;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- hypo - or vitamin deficiency;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- taking corticosteroids;
- hormonal disorders.
The main cause of candidiasis is low immunity. This condition can occur in many situations, including poor nutrition, poor living conditions, and frequent stresses.
In addition, the sudden growth of Candida species occurs with the following concomitant diseases:
- AIDS (or HIV infection);
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- hypothyroidism;
- some blood diseases;
- vaginosis.
Pathogenicity factors
The size of one fungus of the genus Candida is only 2-5 microns, so they can only be examined under a microscope. Those white or yellowish-gray films that grow on agar or plaque visible on the affected areas of the body are entire colonies of fungi, numbering hundreds of thousands of individual microorganisms. Once in the host organism, how do mushrooms of the genus Candida behave? Studies of microbiologists have shown that each fungus tends to begin adhesion, that is, to adhere tightly, we can say, to grow into human epithelial cells. This germs succeed the easier, the lower the immunity of their victim, and the higher her endocrine disorders. The most active clutch fungus of the species C. Albicans. Once on the mucous membranes, it adheres in 100% of cases. The most passive fungus is the species C.Krusei. It may not be fixed at all, that is, infection does not occur. Surface proteins, surface proteins, and some molecules, such as polysaccharides and glycoproteins, and saliva molecules in the mouth, help fungi to invade. In general, Candida are glycogenophiles (they like glycogen), therefore, most often they colonize tissues where it contains a lot, for example, the mucous membranes of the vagina and oral cavity. When thrush occurs, fungi of the Candida genus in a smear taken from these organs are detected with a high probability, which makes it possible to accurately diagnose.
At the initial stage of adhesion, the fungi are in yeast form, but they quickly rebuild, forming long strands (hyphae) that penetrate more easily into damaged host cells, and are less prone to phagocytosis of leukocytes.
Having consolidated and settled down, parasites in the process of their life release various poisons into the host organism:
- candidotoxin (a protein that acts on basophils and mast cells and causes a pseudo-allergic reaction);
- 6 types of low molecular weight toxins (increase vascular permeability, lower blood pressure);
- lipid toxins (cause local leukocyte reaction and lead to the appearance of granulation tissue).
Candidiasis in children
As noted above, infants are infected by Candida either in the womb or during childbirth at the time of passage of the birth canal. In the future, the fungus can enter the infant in the oral cavity with a poorly processed nipple, rattles, from the nipples of an infected mother. Symptoms of the baby becoming infected with thrush are as follows:
- white, curd-like plaque on the tongue, on the inner surface of the gums and cheeks;
- moodiness;
- refusal of food.
Without treatment, the fungus continues to settle and soon appears on the lips of the baby.
Mushrooms of the genus Candida in the intestine are manifested by symptoms of dysbiosis, such as:
diarrhea
- lethargy;
- temperature;
- weight loss.
Diarrhea in infants is dangerous because it entails rapid dehydration, so a sick child must be hospitalized. Only in a hospital setting can you provide him with the necessary treatment (droppers) to prevent fluid loss.
In addition to the digestive tract and the oral cavity, thrush in babies can occur on the skin. In this case, not white, but red spots appear, similar to diaper rash. The child becomes very moody, as any touch of erosion causes him suffering. Most often, cutaneous candidiasis in infants appears in the folds on the legs, on the buttocks and in the groin area. This is preceded by diaper rash, being in the diaper for too long, poor hygiene and inappropriate (synthetic, too tight) clothing.
Treatment of childhood candidiasis
If fungi of the Candida genus begin a pathogenic process in the oral cavity of a child, treatment is usually carried out locally. It consists in the treatment of places where white plaque is observed, with special preparations. Previously, doctors attributed lubricating a child’s mouth with brilliant green. This medicine helps well, but dries mucous membranes. Now apply "Akriderm", "Fukortsin", solutions of borax in glycerin.
In order to prevent it, you need to boil nipples and bottles in the first months of life, wash the rattles. Mom should treat the nipples with antifungal drugs before feeding.
With symptoms of dysbiosis, infants are given feces for bacterial sowing. It is believed that fungi of the genus Candida in feces in children under the age of 12 months can be present in amounts of not more than 103 CFU / g, and older than 12 months in the amount of 104 CFU / g. If the indicator is exceeded, prescribe drugs that restore the microflora and strengthen the immune system.
With skin candidiasis, the affected areas are lubricated with antifungal ointments - nystatin, levorin. It is very useful to bathe a child with the addition of a string of decoction, calendula, and chamomile into the water. All linen and diapers must be ironed, and diapers should be changed often enough, without waiting for them to be fully filled.
If the above methods of treatment do not help, the child will undergo an additional examination and prescribe antifungal therapy.
Candidiasis in women and men
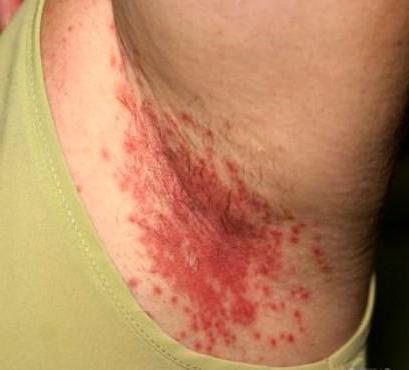
In adults, Candida fungi can, like in children, infect the oral cavity, skin, intestines. Candidiasis in the mouth is manifested by a cheesy plaque, capturing the tongue, gum, palate, inner side of the cheeks and is accompanied by painful sensations. Sometimes the mucous membranes ulcerate. Candidiasis on the skin is characterized by red spots in the places where the fungus is introduced (under the arms, under the breasts of women, in the groin, less often under the knees). These spots itch and peel, and ulcerate when combed.
But most often, adults suffer from candidiasis of the genitourinary organs. In women, mushrooms settle in the vagina and on the vulva, so the disease was called vulvovaginitis. At the initial stages, its symptoms are as follows:
- white (like sour milk) vaginal discharge;
- itching, not passing, but, on the contrary, worse after washing and in the morning;
- unpleasant smell of underwear;
- pain during intercourse.
The most indicative symptom is Candida mushrooms in a swab taken from the vagina.
Without treatment, signs of the disease worsen. Pain appears not only during intercourse, but also with every urination, the vaginal mucosa swells, ulcerates, the discharge becomes thicker.
In men, candida infection is called balanoposthitis. Symptoms
- allocation of a curdled appearance from the penis;
- itching, pain during urination;
- soreness of sexual intercourse.
In addition to the genitourinary system, Candida fungi parasitize on the external organs of people. Infection of the nails is called "onychia", and of the prungalon roller - "paranichia." The causes of these diseases can be barbs, manicure with infected tools.
Candida genus analysis
The presence of candidiasis is established by the results of such studies:
- a smear from the oral cavity or vagina;
- sowing;
- IFA;
- PCR.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe urine and blood tests.
If the smear is planned to be taken from the vagina and / or urethra, it is not allowed to wash before it, and you can urinate only 2 hours before taking the smear, not later. If you plan to take a smear from your mouth, do not brush your teeth before doing this.
For sowing, feces, sputum, urine, scrapings from affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes are used. Three days later, they get an answer whether or not Candida mushrooms are in the material. Norm is a negative result. If the tests confirm the presence of the fungus, determine its appearance and sensitivity to medications.
An ELISA is called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. It helps to identify antibodies to the fungus and track the dynamics of the process. The research material for ELISA is blood from a vein. As a rule, it is carried out in conjunction with Bakseeding.
The most accurate is the analysis of PCR, which means a polymer-chain reaction of fungal DNA molecules. It determines the presence of a pathogen even at the very initial stage of the disease. The material for PCR is sputum, excretion, blood.
Treatment
If the patient has found fungi of the genus Candida, treatment is carried out with medication. Inside they write out:
- "Fluconazole."
“Nizoral.”
- "Diflucan."
Ointments are used externally:
“Clotrimazole.”
“Sertocanazole.”
“Miconazole.”
- Suppositories with pumaficin and other agents that suppress the growth of the fungus. Anti-inflammatory ointments may also be prescribed.
Treatment of pregnant women is carried out only by external means. Only in some cases, "Pumacin" is prescribed orally.
With candidiasis of the genitourinary tract, both sexual partners are treated.
In addition to antifungal drugs, vitamins and other immunity enhancing agents are prescribed.