Direct blood transfusion is rare and for exceptional reasons. The procedure is not always possible due to the problem of finding a suitable donor, and its implementation is fraught with a lot of risks and difficulties. How is direct transfusion performed? What are the indications and contraindications for the procedure? How is a donor chosen? What are the possible complications?
Transfusion Rules
To avoid the dangerous consequences of direct blood transfusion, the rules of the procedure are strictly observed in medical institutions. Blood transfusion should be carried out in a completely aseptic environment, that is, disinfected. Before transfusion, it is mandatory to conduct certain studies (regardless of the data that are already known from the patient’s medical record): determining the group affiliation of the donor material and the Rh factor, checking the compatibility of the donor and recipient.
The use of biological material that has not been tested for syphilis, serum hepatitis and AIDS is prohibited. The volume of biological material taken at one time should not exceed 500 ml. When a preservative solution is added, blood can be stored at a temperature of four to nine degrees Celsius for twenty-one days. Material frozen at a temperature of liquid nitrogen (-196 degrees) is allowed to be stored for years. Blood transfusion is carried out for newborns exclusively taking into account the individual dosage, with great care and according to indications.
Donor training
Of great importance for direct blood transfusion is the preparation of the donor. It can be a person from eighteen to forty-five years of age, without contraindications. The results of a preliminary medical examination, tests (absence of hepatitis B, AIDS, syphilis) should be known. After donating blood, the donor is given warm tea with sugar, a hearty dinner. To rest on the day of blood sampling, the donor is given a leave from work. Direct transfusion is carried out in the operating room or in a special sterile room. Even if there are fresh test results, the doctor must conduct blood tests of the patient and the donor, compare biocompatibility, and make biological tests.
Blood Transfusion Technique
A common method for the treatment of various diseases and relief of emergency conditions is the indirect transfusion of freshly frozen plasma, blood, erythrocyte or platelet mass. The procedure must be carried out correctly, according to strictly approved instructions, which are the same for the Moscow blood transfusion station, and for regional and foreign ones. The responsibility for the recipient's health does not lie with the junior staff, but directly with the doctor.
The blood transfusion algorithm is as follows:
- Preparing the patient for the procedure, collecting an anamnesis, finding out the presence of chronic diseases and (in women) pregnancies, determining the group according to the AB0 system and Rh factor.
- The selection of donor material and its assessment of suitability for use by the macroscopic method. Additional check on the Rh and AB0 systems.
- Conducting blood compatibility tests for transfusion in a biological and instrumental way. A small amount (about 5 ml) of blood is placed in a special apparatus and a drop of serum is added. After being monitored. If gluing of the red blood cells does not start, this means that the recipient and the donor are compatible. Another way to check is the introduction of a few ml of donor blood to the patient and monitoring his condition.
- Transfusion. The bag of biological material must first be at room temperature for half an hour. The procedure is carried out with a disposable aseptic dropper at a speed of 36 to 65 drops per minute. The patient should be in a horizontal position and in complete peace of mind.
- Filling out a blood transfusion protocol by a doctor.
- Observation of the recipient during the day, especially carefully the first three hours.
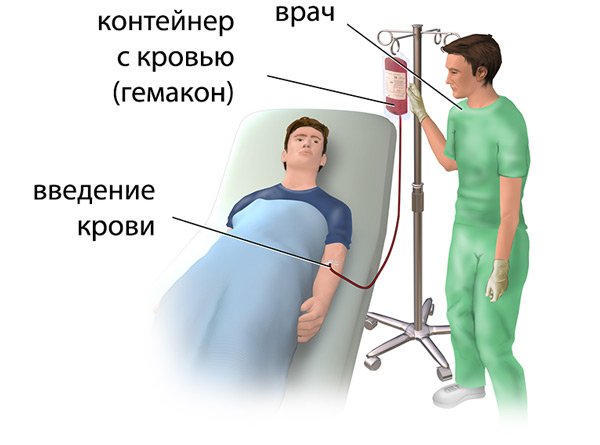
Direct transfusion
Direct blood transfusion is carried out in emergency cases, that is, quite rarely. The advantage of this method is the fact that biological material retains all the properties, the disadvantage is the need for complex hardware. Transfusion performed in this way can cause embolism of arteries and veins (blockage of blood vessels by foreign particles or gas bubbles).
Indications for transfusion
Indications for direct blood transfusion are coagulation disorders in the absence of the effect of other methods of therapy. In general, the main indications for transfusion (in any way) are:
- severe anemia (hemoglobin level less than 70 g / l), which is characterized by severe weakness, increased heart rate with little physical activity or at rest, dizziness, severe headache, visual impairment, and so on);
- hemolytic disease of the newborn - a congenital disease due to incompatibility of the blood of the fetus and mother by antigens;
- significant emergency blood loss due to injuries or emergency conditions (uterine, intestinal bleeding, stroke, tumor or cerebral thrombosis);
- incessant bleeding (a patient’s loss of more than 30% blood within a few hours);
- severe intoxication;
- surgery with significant blood loss;
- an overdose of certain types of drugs, including indirect anticoagulants that disrupt the blood coagulation process (Sinkumar, Warfarin, Pelentan, Neodicumarin and others);
- some kidney and liver diseases;
- dermatological diseases with ulcers;
- DIC-syndrome, characterized by the formation of blood clots in the vessels and leading to multiple massive hemorrhages.
Contraindications to transfusion
Direct blood transfusion can cause disturbances in processes that fully ensure the vital activity of the body, so doctors always evaluate not only indications, but also the presence or absence of contraindications. In this case, data on previous transfusions (if any) are of great importance. The risk group consists of patients with cancer, prolonged septic processes, blood pathologies, women who have had a complicated birth or cesarean section, the birth of children with jaundice, miscarriages.
Absolute contraindications to direct blood transfusion are heart failure, purulent inflammation of the lining of the heart muscle, third-stage hypertension, general disturbances in protein metabolism, impaired brain blood flow, allergic condition, cardiosclerosis, myocarditis. Relative contraindications are aortic aneurysm, active endocarditis, acute thrombophlebitis, pronounced hypertension, a tendency to allergies, severe coronary artery disease.
Possible complications
Directly during the direct transfusion procedure, complications may occur due to errors during the procedure. One of these is blood coagulation in the system. To prevent this, instrumental methods that ensure a continuous flow of blood should be used. The inner surface of the tubes in such devices is coated with silicone, which prevents the formation of blood clots.
The presence of blood clots in the transfusion system may result in pushing the clot into the patient’s blood vessels and arteries. This threatens the development of thromboembolism. In this case, the patient has a feeling of anxiety, chest pain, shortness of breath and cough, blood pressure rises sharply, the neck veins swell, the skin in the face, chest and neck turns blue. The appearance of these symptoms requires an immediate termination of the procedure and the beginning of emergency care measures.
Blood group compatibility
When donating blood, the biological material must be checked according to the Rh and AB0 systems, as well as for AIDS, syphilis and serum hepatitis. According to the AB0 system, biological material is divided into 4 groups, according to Rh - into two groups according to the presence or absence of a special antigen on the surface of blood cells. Rhesus negative and Rh positive blood are incompatible. In this case, a "positive" person can transfuse Rh- blood, but not in the reverse order.
The first group is universal, the second can be transfused with people from the second and fourth, and for the person with the second group - the first and second. Blood of the third group can be transfused for people with the third and fourth, and for patients with the third - the first and third. The fourth can only be transfused to a recipient with the same group, but for a person with 4 groups, any biological material is suitable for blood transfusion.
Universal donor
Today, in the course of direct transfusion, it is forbidden to use any biological material, except for blood of the same group and Rh factor as that of the recipient. In rare emergency cases, a universal donor may be used. What blood type should a universal donor be with? This is the owner of the biological material of the first group with a negative Rh factor.