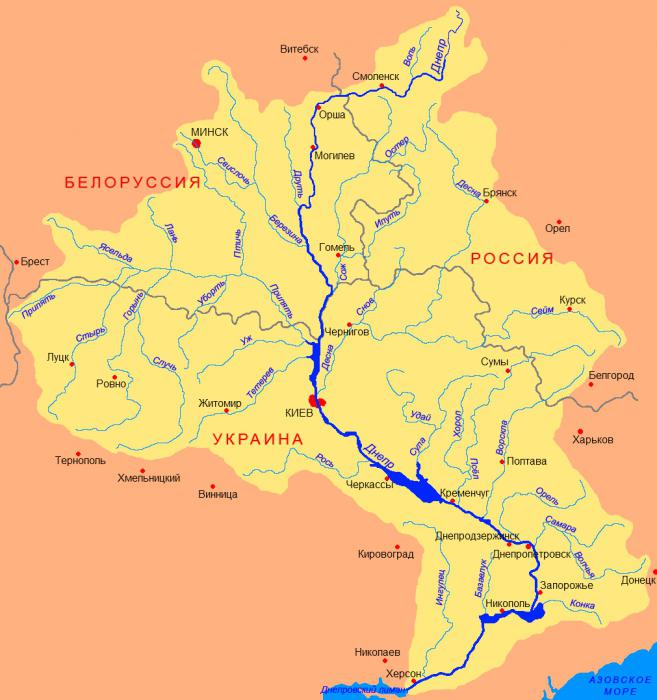
The Pripyat River is the largest and most important right tributary of the Dnieper. Its length is 775 kilometers. Water flow flows through Ukraine (Kiev, Volyn and Rivne regions) and Belarus (Gomel and Brest regions). The catchment area exceeds 114 thousand square kilometers. Pripyat originates between the villages of Rogovye Smolyary and Budniki on the Volyn Upland. In the upper reaches of the river its valley is expressed rather weakly, in the lower reaches - somewhat more clearly. The width of the floodplain in the upper reaches does not exceed 4 kilometers, in the lower - up to 15. The river slope is 0.08 meters per 1 kilometer. In the upper reaches of the Pripyat, it looks like a channel, below it becomes winding. In the middle course there are many old women and meanders, the river has many channels and small islands. The width of the water stream at the source is no more than 40 meters, at the Kiev reservoir, where the Pripyat River flows, up to 5 kilometers.
River life
The Pripyat River has a mixed water supply, mainly from snowmelt. Its regime is characterized by a long flood in the spring. It begins in early March, and in the cold years - in mid-April. High water can last up to 3.5 months. It is accompanied by large-scale spills. At this moment, in the upper reaches, water can rise by 2 meters, in the middle - by 3.5, and in the lower reaches - up to 7 meters. The summer low-water period is short-term, as it is constantly interrupted by rain floods. Autumn is almost annually characterized by a significant rise in water. The annual runoff is 14.5 cubic kilometers. Of these, up to 65% fall in the spring. Pripyat freezes only by mid-December. There are many swamps in the river basin that determine the color of the water in the river.
Water flow location
The Pripyat River on the map begins in the Lyuboml district of the Volyn region of Ukraine, along which 204 kilometers flow. Then a water stream crosses the border of Belarus and follows 500 km along the Polesskaya lowland. His path lies among the Pinsk swamps. Here the valley is weak, the coast is swampy. The river often breaks into sleeves. At the beginning of the lowland, the bottom is unstable, sandy, by the end the number of rifts on the river increases. The remaining 50 kilometers of Pripyat again flows in Ukraine, where it ends its journey in the Kiev reservoir, just south of Chernobyl. The river is connected by channels with the Mukhavets (a tributary of the Western Bug) and Shchara (a tributary of the Neman). The Pripyat River is flat. It is characterized by low bogging - up to 15%.
Inflows, settlements, lakes and canals of Pripyat
The Pripyat River has many tributaries, but the most important are Ptich, Styr and Goryn. The latter is the largest water stream (from the flowing in). The Dnieper-Bug Canal eventually connects Pripyat with the Bug, thus forming a waterway to Europe. Or the Black Sea with the Baltic. The Dnieper-Neman Canal makes the river part of the route from Ukraine to Latvia - to the Kaunas reservoir. There are other non-navigable "small" channels. For Polesie lowland is characterized by a large lake. Only on the right bank of Pripyat are more than 2.5 thousand lakes. The largest on the river are two Belarusian cities - Mozyr and Pinsk. The two most famous Ukrainian settlements are the “dead cities” of Pripyat and Chernobyl.
Chernobyl
On the territory of the Chernobyl exclusion zone, Pripyat is the largest water body. The river bypasses the area from the east and then flows into the Kiev reservoir. Directly in the area of accommodation, the channel was artificially changed. Today it is a canal with a length of 11 kilometers. Navigation is open on it. An artificial channel was laid in order to pass the Pripyat nuclear power plant cooler. Now these two water bodies are separated by a dam and are located at a distance of 300 meters. The channel has a depth of up to 4 meters and a width of up to 160. Pripyat plays an exceptional role in the removal of radionuclides from the exclusion zone. Researches of scientists have shown that, unlike other ways (such as air, biogenic, technogenic), water makes an order of magnitude more harmful substances. The desert Pripyat flows through the desert exclusion zone - a river whose photos show its banks with ship cemeteries. The water stream carries radionuclides in the reservoir of Kiev. Pripyat (river) in Belarus is not contaminated with harmful substances.
The economic importance of Pripyat
Water is the primary resource for any state. Pripyat supplies about 35% for the needs of the national economy: industrial enterprises, agricultural land, for drinking needs and for transport. Only for the needs of one person per day is calculated up to 550 liters. But water bodies, including Pripyat, are becoming shallow, and the government of Belarus faces the most acute problem of protecting the country's water resources. A comprehensive project is being developed, which envisages not only savings, but also the purification of water bodies and their protection. In Belarus, the maximum amount of cargo is transported along Pripyat, especially along the route on which the Dnieper-Bug Canal is located.
The nature of Pripyat
On the territory of four regions of Belarus in 1999, a unique Republican landscape reserve “Middle Pripyat” was created. The purpose of its organization is to preserve the ecosystem of the river floodplain. The ministers of the reserve are busy with the conservation of endangered and rare species of plants and animals. The reserve area is more than 90 thousand square kilometers. If earlier the description of the Pripyat River reported on the diversity of coastal nature, then in recent decades there has been a decline. Now, gradually, nature is recovering. Only geese during their migration stop here up to 50 thousand individuals annually. On the territory of the Middle Pripyat 72 species of plants were registered, of which 24 were endangered. The fauna is represented by 36 species of mammals, 182 - birds, 10 - amphibians, 6 - reptiles. Of these, 67 species are threatened with extinction.
Fishing in Pripyat
In Pripyat, up to the exclusion zone, 37 species of fish live. Fishermen on the river all year round. Summer fishing begins in late April or early May. Pike, asp, perch, roach, bream, sabrefish, ide, carp, catfish, pike perch, silver bream and roach are well caught here. In June, fishermen take revenge for a long break. For example, at the village of Konkovichi, all kukans are hung with pikes. Feeders are caught on feeders everywhere and always. Other fish need to be caught in accordance with the solar schedule. One misfortune is a lot of vileness. By September, the pike peck literally at the first cast. But the most successful fishing in the fall is trolling. At this time, the river is very quiet: the fish do not beat, the birds do not sing. You can catch almost everything: maggots, poppers, wobblers, turntables. In winter, many fishermen are attracted to the Norovli area. But there is a reserve, and you need to go down the ice downstream.
Tourism
On the river and along Pripyat in the summer there are many tourists. Who walks, exploring the beauties of nature and local attractions, and who rafts or kayaks. There are developed routes by local travel agencies, but you can go on a trip yourself. Water tourism is relevant from June to September. The length of the routes is an average of 100 kilometers. The path begins at the city of Pinsk. The main attractions along the banks of the river are reserves and reserves. At the end of the route you can admire the ancient city of Belarus, Mozyr, which was first mentioned in chronicles in the 16th century. In Pripyat river cruises pass through the territory of Belarus.