Nothing testifies to human health more reliably than indicators of the cardiorespiratory system. As you can easily guess from the name, we will talk about the relationship of the circulatory and respiratory systems in our body, their functions and purpose.
What role does
Even minimal physical activity is impossible without the mechanism of coordinated transport of oxygen to the heart and brain. If you suspect a cardiovascular disease, the patient is referred for diagnostic procedures, the results of which will give an objective idea of the state of the cardiorespiratory system. Specific changes in it lead to a malfunction in the work of the whole organism. According to some reports, the number of people suffering from diseases of the heart, blood vessels and lungs in Russia is almost 20 million people, of which more than a million are children under the age of 15.
The prevalence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system obliges modern society to the need to study their pathogenesis and etiology, so the assessment of the aerobic power of the body is a mandatory procedure. The cardiorespiratory system is a complex consisting of two different, but at the same time interconnected systems. To understand how the main processes of the body’s vital activity proceed, consider the structure and principle of operation of each of them.
The cardiovascular system
Thanks to its constant and uninterrupted operation, blood circulation throughout the body is ensured. In the structure of the cardiovascular system, the main elements are the heart - a kind of pump that pumps blood, and blood vessels - hollow tubes through which blood is transported. In addition to blood, lymph flow is also important, which is conditionally considered part of the vascular system.
The nutrition of each cell with oxygen and the course of metabolic processes depend on the state of the cardiorespiratory system. Interacting with the internal systems of the body, the heart and blood vessels immediately respond to any changes in the conditions of the internal environment to ensure maximum efficiency of their work.
Even during sleep and rest, the cardiorespiratory system does not stop working, continuing to satisfy the tissue's need for oxygen. The heart, blood vessels and lungs have a diverse purpose. Why is a cardiorespiratory system needed? It performs the following functions:
- exchange;
- excretory;
- homeostatic;
- transport;
- protective.
The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen and nutrients to each cell of the body, removing carbon dioxide and end products of metabolism from it. Blood moving through arteries, veins, and capillaries delivers hormones from the endocrine glands to their final receptors, participates in maintaining a stable temperature regime, and controls the body’s pH. It is the cardiovascular system that helps prevent dehydration and infectious diseases.
How does the cardiorespiratory process proceed?
Many works of scientists are devoted to the study of methods for studying the state of the cardiorespiratory system. Independent work is also carried out by students of the corresponding profile of medical universities. All these developments are of great importance. Thanks to the research work, it became known what the cardiorespiratory system is and what processes take place in it.
The human heart consists of two atria, which serve as receiving chambers, and two ventricles that pump blood. The heart as a pump promotes non-stop blood circulation through large and small vessels, which are the structure of the circulatory system. The blood flowing in the capillaries not only transports oxygen and nutrients to internal organs and tissues, but also collects the products of their metabolism. With them, she goes back to her heart. Such blood is called deoxygenated.
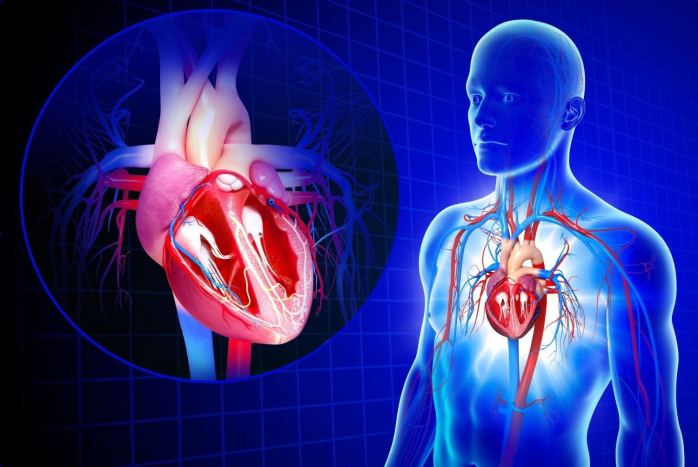
Fluid tissue enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava. From the right atrium, blood is sent to the right ventricle, where it is pumped through the open valve into the pulmonary arteries, and from there directly into the right and left lungs. The right side of the heart is responsible for the pulmonary part of the blood circulation, therefore it sends blood to the respiratory system, which has passed throughout the body, for its subsequent reoxygenation. Once the lungs are filled with oxygen, the enriched blood goes through the pulmonary veins and returns to the left atrium. Oxygenated blood flows here, which supplies oxygen to all tissues and organs, flowing from the open atrioventricular left mitral valve into the left ventricle and aorta, and then to all body tissues.
Natural ventilation - what is it?
The process of moving air to the lungs and back is called breathing. Anatomical ventilation is provided in two stages - inhalation and exhalation. Air enters the lungs through the nose; the mouth is used when the need for air exceeds the amount that can enter the lungs through the nose. Moreover, it is more correct and more beneficial to breathe through the nose, since the air that passes through the nasal concha is warmed and cleaned of dust, allergens, viruses and bacteria that are retained by the ciliary epithelium and the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. Mouth breathing does not provide the same thorough filtration of the air mixture entering the body, which increases the likelihood of developing respiratory infections.
The smallest element of the human cardiorespiratory system is the pulmonary alveolus - part of the lungs in which gas exchange occurs. Alveoli are numerous respiratory units. From the nose and mouth, air moves to them through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles.
The lungs are not attached to the ribs. The respiratory organs seem to be suspended due to the pleural cavity enveloping the lungs. They contain a thin layer of pleural fluid, necessary to eliminate friction during respiratory movements. In addition, pleural cavities are connected not only with the lungs, but also with the inner surface of the chest.
What happens during exercise
The muscle demand for oxygen increases suddenly with increasing activity, against the background of which a large consumption of nutrients is required. In addition, there is an acceleration of metabolic processes, which leads to an increase in the number of decay products. Prolonged physical activity provokes an increase in body temperature, the level of concentration of hydrogen ions in soft tissues and blood, and a decrease in the acidity of the internal environment.
Regulation of respiration plays a huge role in increasing physical activity. Most often, changes in the level of muscle activity adversely affect the state of the cardiorespiratory system. One common occurrence is shortness of breath experienced by people who do not have proper physical preparation. Increased loads lead to a sharp increase in the concentration of arterial carbon dioxide and the level of H + ions in the blood. A signal about these changes enters the respiratory center, as a result of which the frequency and depth of ventilation increase.
All these specific changes in the cardiorespiratory system help to achieve the main goal, which consists in meeting the increased physical needs and ensuring maximum efficiency of its functioning.
Intensive lung work
To ensure full pulmonary ventilation and gas transportation, the body spends a lot of energy. Most of it is used by the respiratory muscles in the process of ventilation. If a person is inactive, is at rest, only 2% of the total amount of energy expended utilizes the respiratory muscles. If the frequency of inspirations and expirations increases, so do the energy costs. With intense physical work, the respiratory system can use more than 15% of the energy. Oxygen is required for all its elements: the diaphragmatic septum, intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles.
The process of natural ventilation of the lungs is carried out at high energy costs, but even the maximum physical load does not lead to arbitrary intake and exit of air. This is the maximum arbitrary ventilation. There is an opinion that it is pulmonary ventilation that is the limiting factor during debilitating physical activity in athletes. The cardiorespiratory system, according to experts, is working at full strength, which ultimately leads to wasting glycogen reserves and respiratory muscle fatigue. These changes are observed during prolonged training, a multi-kilometer race, etc.
Scientists who conducted experiments with rats came to the conclusion that in insufficiently “trained” rodents, during intensive physical activity, the level of glycogen in the respiratory muscles decreased. And despite the fact that it remained practically unchanged in the muscles of the hind limbs, a cardiorespiratory syndrome arose in the test animal, which is characterized by tachycardia, severe shortness of breath, and in severe cases, pulmonary edema.
The volume of inhaled air during physical activity can increase several times, and the resistance of the airways remains the same as that characteristic of a state of rest due to the expansion of the laryngeal gap and bronchi. Blood entering the cardiovascular bed does not lose oxygen saturation even at maximum effort. Thus, the cardiorespiratory system is able to satisfy the need for intensive breathing both with short and long-term physical activity.
It should be borne in mind that excessive oxygen uptake can lead to some problems. Abnormally narrow airways or impaired patency can lead to specific changes in the cardiorespiratory system. Asthma, for example, provokes narrowing of the bronchioles and swelling of the mucosa, which ultimately increases the strength of ventilation resistance and provokes shortness of breath. An indicator characterizing the maximum performance of the cardiorespiratory system is a satisfactory state of the respiratory system. Despite the fact that the relationship between physical activity and impaired airway has been established a long time ago, doctors can not yet determine the exact mechanism for the development of an asthmatic attack against a background of increased activity.
Pulse on hand: how many strokes are considered normal?
Heart rate is the simplest and at the same time informative indicator, which is taken into account when conducting cardiorespiratory monitoring. Everyone knows how to measure heart rate - you need to feel for bullets in the wrist or carotid artery and count the number of beats per minute. In these areas, the amount of work performed by the heart to meet the increased requirements of the body is reflected.
The difference in indicators in a person at rest and in a person during cardiorespiratory loading is obvious. The average heart rate is about 60-80 beats per minute. Interestingly, in athletes, the cardiorespiratory system at rest shows more modest results. Their heart rate can be 28-40 beats, which is considered the norm and is explained by a high level of training and physical endurance developed over the years of training. In people who are much less likely to encounter intense loads on the cardiorespiratory system, the heart rate can reach 90-100 beats per minute.
With age, the pulse decreases. External factors (for example, high temperature, lack of oxygen, high atmospheric pressure, etc.) can affect the heart rate. With an increase in the intensity of work, the pulse becomes faster. If the level of physical activity is under control (it can be measured using various devices), an approximate amount of oxygen consumed can also be calculated using a special formula.
The determination of labor intensity in terms of oxygen consumption is not only accurate, but also the most suitable when examining different people, or the same person, but under different circumstances. The maximum heart rate increases in proportion to an increase in the intensity of physical labor up to overwork. By the way, as this state is reached, the heart rate gradually stabilizes.
The maximum heart rate can be determined taking into account age, as it becomes lower as a person grows older. The heart rate drops at a rate of 1 beat per year from 10-15 years. It should be borne in mind that individual indicators can differ significantly from the average values.
Blood circulation during exercise
The cardiorespiratory system is a complex structure in which one of the main roles belongs to blood circulation. When a person begins to engage in physical education or work, his blood flow is distributed differently. Under the influence of the sympathetic nervous system, blood leaves those vessels where its presence is currently optional, and is directed to the muscles that are actively involved in the work. In a person who is at rest, the cardiac output of blood in the muscles is only 15-20%, and when playing sports it can reach 85%. Blood supply to muscle tissue increases due to a decrease in blood supply to the abdominal organs.

In the event of a change in temperature, the predominant amount of blood is sent to the skin. The sympathetic nervous system also takes care of this. The purpose of redistribution is to compensate for the heat that is released into the external environment, sending it from the depths of the body to the periphery. At the same time, increased skin blood flow automatically reduces the intensity of blood supply to muscle tissue. It is not surprising that the characteristic of the cardiorespiratory system in people involved in sports in hot weather, demonstrates insufficiently high results.
The skeletal muscles involved in the work experience an urgent need for more oxygen, which is satisfied by accelerated blood circulation due to sympathetic stimulation of blood vessels in those areas where blood flow is temporarily limited. For example, the vessels leading to the organs of the digestive system can narrow, after which the blood flow is redirected to the muscles that need more blood. The vessels of the muscles expand, due to which there is a rush of blood. In the process of performing physical activity, the rate of metabolic reactions occurring in muscle tissue increases, which leads to the accumulation of metabolic decay products. Active metabolism causes an increase in acidity and temperature in the muscles.
Myocardial functionality
The medical name for the heart muscle is myocardium. The wall thickness of the main human "motor" depends on what kind of load is regularly placed on its cameras, of which the left ventricle is the most powerful. Reducing, she pumps blood and sends it through the entire circulatory system. If a person is not active, but just sitting or standing, his myocardium will be energetically contracted. This allows you to cope with the action of gravity, which leads to the accumulation of blood in the lower extremities.
If the left ventricle is hypertrophied, that is, the thickness of its muscle wall is increased in comparison with other chambers of the heart, this means that the heart had to constantly work in conditions of increased demands. When playing sports or other intense exertion, accompanied by increased breathing, myocardial activity becomes as active as possible. If muscle demand for blood increases, the requirements for the left ventricle also increase, so over time it increases in size similar to skeletal muscle.
The coordination of heart contractions depends on the signal being given to perform the contraction. The conduction system of the heart is responsible for the implementation of this function. : , . 70-80 .
, , , . – . . – . , – .
60 , 100-120 . . , , . – , , , , , , .
, , . , - , . , 200-400 – , .
Ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia is an equally serious disorder requiring urgent medical attention. This violation is a serious threat to the life of the patient. With ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia, three or more premature ventricular contractions occur, which can lead to flickering. Unlike flutter, flickering does not allow the myocardium to control the process of contraction of ventricular tissue. The heart loses its ability to pump blood. Ventricular fibrillation often leads to death of patients suffering from chronic heart failure and other diseases.
Severe forms of arrhythmia are a direct indication for the use of a defibrillator, with which it is possible to return a satisfactory sinus rhythm. Emergency measures help restore breathing and support vital functions. Engaged in sports that require the development of high cardiorespiratory endurance, a person can find a low heart rate. In this case, we are not talking about bradycardia. An increase in heart rate during active muscular work is not considered tachycardia. Both bradycardia and tachycardia usually occur in people at rest.
Features of the cardiorespiratory system in children and adolescents
Some experts identify the so-called puberty of the heart, since it is during puberty that pronounced changes are observed in cardiovascular activity. Compared with the level of development of the cardiorespiratory system in children 7-10 years old, the cardiovascular apparatus in adolescents becomes more functional and resilient.
At the same time, the process of formation of the heart and blood vessels differs among representatives of different sexes. In girls, myocardial mass increases faster, but less evenly. In turn, the sizes of the heart and aorta in boys are larger than in girls. During puberty, profound changes in the structure of the heart muscle occur, and the diameter of the fiber and core increases. Myocardium grows rapidly, and blood vessels slower, which is why the lumen of the arteries in relation to the size of the heart becomes smaller. This change can lead to circulatory disorders and increased pressure during exercise.
Heart rate is a labile indicator that changes under the influence of internal and external factors (increase in air temperature, manifestation of emotions, sports training, etc.). At the same time, the pulse during physical work can increase to 160-180 beats per minute, which leads to an increase in the volume of pushed blood. Mental stress acts on the child’s cardiorespiratory system, which is expressed by increased heart rate, a temporary increase in blood pressure and adverse changes in hemodynamics.
An equally important criterion for the functioning of the respiratory system is the vital capacity of the lungs - the amount of air that a person exhales after a deep breath. A sharp jump in the general growth and development rates of the entire respiratory apparatus, including the nasal passages, larynx, trachea, and the general surface of the lungs, occurs during the pubertal period. In adolescents, the volume of the lungs in comparison with the lungs of the newborn is increased 10 times, and in adults - 20 times.
The most intensive lung growth is observed between 12 and 16 years old, with boys having more lung capacity than girls. In general, adolescents have higher cardiorespiratory parameters, including natural ventilation of the lungs, the amount of oxygen consumed, and the performance of the circulatory system than in younger schoolchildren.
This article discusses all the elements of the human cardiorespiratory system, its features, including adaptation to physical activity and increase endurance. When planning to play sports, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances of your body and properly distribute the load. The condition of the cardiorespiratory system is an important indicator of health.