Anatomy and physiology play an important role in the membranes of the brain (spinal and brain). Particular attention is paid to their features, structure and functions, since the functioning of the entire human body depends on them.
What is the meninges ?
The medulla is the connective tissue membrane structure that surrounds both the spinal cord and the brain. It may be as follows:
- solid;
- spider web;
- soft or vascular.
Each of these species is present both in the brain and in the spinal cord and is a single whole, passing from one brain to another.
Next, we will talk about the dura mater.
Anatomy of the membrane covering the brain
The dura mater of the brain is a formation with a dense texture, which is located under the inner surface of the skull. Its thickness in the arch area varies from 0.7 to 1 mm, and at the base of the cranial bones - from 0.1 to 0.5 mm. In places where holes, vascular grooves, protrusions and sutures are located, as well as on the base of the skull, it fuses with the bones, and in other areas its connection with the bones of the skull is more loose.
In the process of development of pathologies, the described membrane may detach from the cranial bones, as a result of which a gap is formed between them, which is called the epidural space. In places where it is present, with the violation of the integrity of the cranial bones, the formation of epidural hematomas.
From the inside, the walls of the dura mater of the brain are smoother than from the outside. There, it loosely connects to the arachnoid underneath with the help of a multilayer accumulation of specific cells, rare connective tissue filaments, thin vascular trunks and nerves, as well as pachyon granulations of the arachnoid. Normally, between these two shells there is no space or gap.
In some places, it is possible to delaminate the hard shell of the brain, as a result of which two leaves are formed. Between them there is a gradual formation of venous sinuses and the trigeminal cavity - the location of the trigeminal node.
The processes extending from the hard shell
Between the brain formations, 4 main processes depart from the dura mater. These include:
- Sickle of the big brain. Its location is the sagittal plane located between the hemispheres. Its front part enters this plane especially deeply. In the place where the cockscomb is located, located on the ethmoid bone, is the beginning of this process. Further, its convex edge is attached to the lateral ribs of the sulcus located on the superior sagittal sinus. This process of the meninges reaches the occipital protrusion and then goes into the outer surface, which forms the outline of the cerebellum.
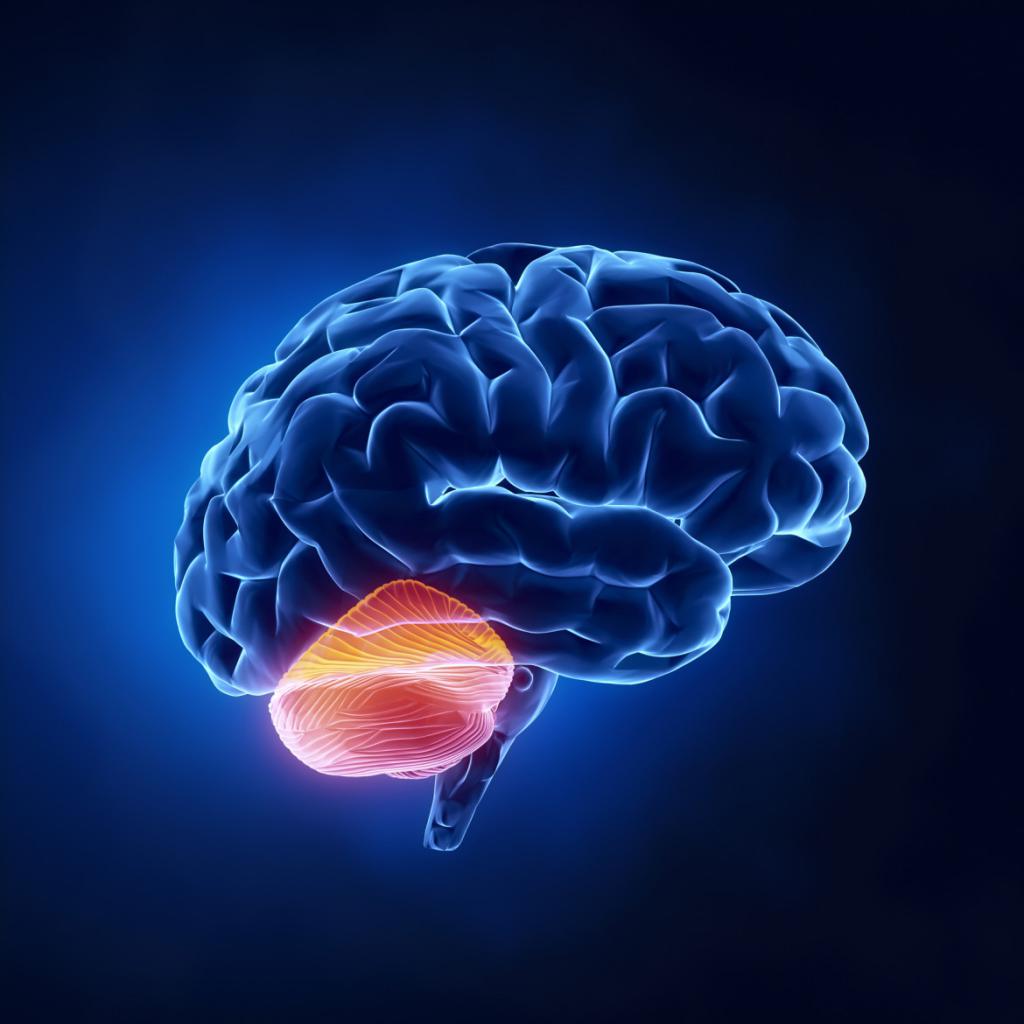
- Cerebellum sickle. It originates on the inner occipital protrusion and along its crest goes to the posterior edge of a large opening in the back of the head. There, he passes into two folds of the dura mater, the task of which is to limit the posterior opening. A cerebellum sickle is located between the cerebellar hemispheres in the area where its posterior notch is located.
- Bast cerebellum. This process of the dura mater is stretched over the fossa of the posterior cranial surface, between the edges of the temporal bones, as well as the grooves located on the transverse sinuses of the back of the head. It separates the cerebellum from the occipital cerebral lobes. The cerebellum will look like a horizontally located plate with the middle part drawn up. Its free edge, located in front, has a concave surface, forming a notch of the mark, which limits its hole. This is the location of the brain stem.
- Diaphragm saddles. The appendix received this name due to the fact that it is stretched over the Turkish saddle and forms its so-called roof. Below the diaphragm of the saddle is the pituitary gland. In its middle there is a hole through which passes the funnel holding the pituitary gland.
Spinal cord anatomy
The thickness of the dura mater of the spinal cord is less than that of the brain. With its help, a bag (dural) is formed, in which the entire spinal cord is placed. A thread from a hard shell departs from this bag, leading downward, subsequently attached to the coccyx.
There is no intergrowth between the hard membrane and periosteum, resulting in the formation of an epidural space, which is filled with loose unformed connective tissues and internal venous vertebral plexuses.
With the help of a hard shell, the formation of fibrous vaginas located near the roots of the spinal cord is carried out.
Hard Shell Functions
The main function of the dura mater is to protect the brain from mechanical damage. They perform the following role:
- Provide blood circulation and its removal from the vessels of the brain.
- Due to its dense structure, they protect the brain from external influences.
Another function of the dura mater is to create a shock-absorbing effect as a result of cerebrospinal fluid circulation (in the spinal cord). And in the brain, they take part in the formation of processes that delimit important areas of the brain.
Pathology of the dura mater
Pathologies of the meninges may include: developmental disorders, damage, diseases associated with inflammation, as well as tumors.
Developmental disorders are rare and often occur against the background of changes in the formation and development of the brain. In this case, the hard shell of the brain remains underdeveloped and defects in the skull itself (windows) are possible. In the spinal cord, pathology in development can lead to local cleavage of the hard shell.
Cranial or spinal cord injury can result in damage.
Inflammation in the dura mater is called pachymeningitis.
Inflammatory disease in the lining of the brain
Often the cause of the inflammatory process in the dura mater of the brain becomes an infection.
In the practice of doctors, there is a development in patients with hypertrophic (basal) pachymeningitis or HPM. It is a manifestation of pathology in the described structure. More often this disease affects men at a young or middle age.
The clinical picture of basal pachymeningitis is represented by inflammation of the membranes. This rare pathology is characterized by a local or diffuse thickening of the dura mater at the base of the brain, most often in places where the sickle or cerebellum is located.
In the case of the autoimmune variant of GPM, by examining the cerebrospinal fluid, pleiocytosis, an increased protein content, and also the absence of microbial growth can be detected.
Pathology of the hard membrane of the spinal cord
Often, external pachymeningitis develops. In the process of its development, inflammation occurs, affecting the epidural tissue, after which inflammation spreads to the entire surface of the hard shell of the spinal cord.
Diagnosing an ailment is difficult enough. But the incidence of spinal pachymeningitis is higher than the development of pathologies associated with inflammation in the hard shell of the brain. To identify it, it is necessary to build on the patient's complaints, medical history, as well as laboratory tests of cerebrospinal fluid and blood.
Tumors
Dura mater can undergo the development of both benign and malignant tumors. So in the described structures or their processes, meningiomas can develop, growing towards the brain and compressing it.
Damage to the dura mater by malignant tumors most often occurs due to metastases, as a result of which single or multiple nodes are formed.
Diagnosis of such a pathology is carried out by examining cerebral or cerebrospinal fluids for the presence of tumor cells.