According to medical statistics, every fourth death in the world could have been prevented with timely resuscitation. Cardiac and respiratory arrest (clinical death) may occur as a result of a serious illness or accident. Saving lives in such situations depends on how quickly and correctly assistance is provided. Therefore, each person should know how the cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the victim is carried out.
Terminal states
The cessation of vital functions occurs gradually. Death states are called terminal. In medicine, the following stages of dying are distinguished:
- Predagonia. The patient is severely depressed or completely absent. The skin turns pale or acquires a bluish tint. The pulse on the wrist is not felt, but is felt on the carotid and femoral arteries. Pressure drops 2 times less than normal, and sometimes to zero. Breathing becomes rare.
- Terminal pause. This stage is not always noted. It consists in a very short (1 to 15 seconds) respiratory arrest.
- Agony. In this condition, the higher parts of the brain do not control the life of the body. The pulse becomes threadlike or not detected at all. Breath is superficial, consciousness is absent.
- Clinical death. At this stage, circulatory and respiratory arrests occur. Due to the lack of oxygen, the metabolism drops sharply and is maintained only due to the oxidation of glucose. There is an expansion of the pupils, the absence of their reaction to light stimuli. Muscle tone is absent. You can still bring the dying person back to life, but there’s only 5-6 minutes left.
- Biological death. Irreversible changes are occurring in all organs and systems of the body. The proteins and cornea of the eyes become cloudy and dry. There is also a deformation of the pupil when pressing on the sclera (a symptom of "cat's eye"). Late symptoms include numbness and the appearance of cadaveric spots.

In connection with the development of resuscitation, at present, one can distinguish such a concept as "brain death." Sometimes doctors managed to resume the patient’s blood circulation and breathing after prolonged clinical death. However, irreversible changes occurred in the central nervous system. The human brain was actually dead with a working heart. Breathing in such cases was carried out through a special apparatus. This is called "brain death" or a chronic vegetative state.
If you know how the cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the victim is carried out, then a person can still be saved even at the stage of clinical death.
Indications for resuscitation
Stopping breathing and blood circulation is an indication for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. How to determine that the victim needs immediate help? The following symptoms indicate a critical condition:
- lack of breathing and consciousness;
- lack of heartbeat;
- the skin changes color, becomes bluish or pale;
- lack of reflexes and muscle tone.
With such signs, it is necessary to have time to assist the dying man no later than 5 minutes. If a person was in icy water or received severe frostbite, then resuscitation can help, even when 15 minutes have passed since the cessation of blood circulation and breathing. Delay in such situations is unacceptable, otherwise irreversible changes will begin in the body, and it will be impossible to help a person. Therefore, it is useful to study in advance how cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the victims is carried out.
When shouldn’t resuscitation be performed?
All measures make sense only if biological death has not occurred.
A person should not be reanimated if more than 25 minutes have passed since the moment of respiratory arrest.
According to the rules of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, emergency care is discontinued if all activities do not give effect within 30 minutes.
In case of an incurable severe disease with exhaustion of the body, resuscitation is not performed.
Objectives and stages of resuscitation
The algorithm and stages of cardiopulmonary resuscitation are called the "survival chain." All emergency measures are aimed at restoring breathing, blood circulation, and then the work of all other organs. First of all, you need to make sure that there is no pulse (on the neck) and the cessation of respiratory movements. This takes no more than 1-2 minutes. Then you must immediately call an ambulance and immediately begin pre-medical measures. The following stages of assistance can be distinguished:
- cleansing the mouth and preventing tongue retraction;
- artificial respiration;
- Indirect cardiac massage
- heart defibrillation;
- life support, drug therapy, rehabilitation measures.
People without a medical education need to learn how the cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the victim is carried out in the first three stages. Further, the patient is assisted by doctors in special intensive care units or intensive care units.
How is resuscitation performed?
After calling the resuscitation team, they begin to restore breathing. In seriously ill patients, particles of vomiting and blood often get into the larynx and trachea. It is also important to prevent tongue retraction. To restore the patency of the respiratory system, you must perform the following steps:
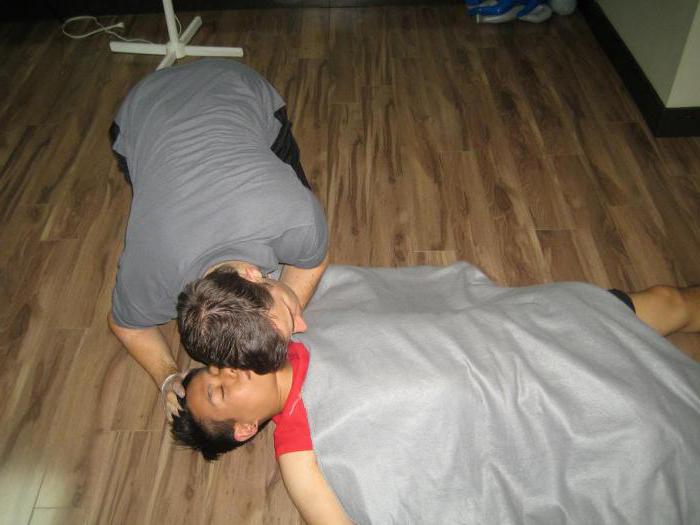
- Lay the person on his back, turn his head to the side, wipe the oral cavity with a napkin or handkerchief, removing foreign particles;
- Then turn your head straight and tilt back as far as possible. Keep one hand on the patient's forehead and the other under the chin, thus fixing the head in a tilted position. This will help the tongue maintain a normal position in the mouth and prevent sinking.
- If the patient has dentures, then they can be left in the mouth, but only if they are intact and not broken.
Next, they begin to restore breathing. For this, artificial lung ventilation is performed using the following methods:
- Blowing air from the mouth of the resuscitator into the mouth of the victim. The carer needs to stand on the side of the patient. Put one hand on the victim’s forehead, and the other under the neck, and abruptly throw his head back, and hold the wings of the nose with your fingers. Make a sharp exhalation from your mouth to the patient's mouth. The volume of exhaled air should be 500-700 ml. Then step back and allow the victim to exhale. Such injections need to be done 12 times in one minute.
- Blowing air from the mouth of the resuscitator into the victim’s nose. In this way, assistance is provided if the patient has a broken jaw or cannot open his mouth. It is necessary, as in the first case, to throw back the patient's head and at the same time strongly cover his mouth, pressing the lower jaw to the upper. Then they cover the patient’s nose with their mouth and blow air into it. The tidal volume and frequency of blowing are the same as in the first method.
To prevent infection, with mechanical ventilation, insufflation should be done through a thin scarf or gauze.
If the patient does not have a heartbeat, blueness or pallor of the skin is observed, then air blowing is carried out together with an indirect heart massage. To do this, follow these steps:
- The patient is laid on a hard surface.
- Two strong and quick injections are made, then one hand is placed on the lower part of the patient’s sternum, and the palm of the other hand is placed on top. With force commit pressure on the chest of the victim. It is necessary to make 60 such movements per minute lasting 30 seconds. Depth of pressure should be about 5 cm.
- In this case, it is necessary to alternate the injection of air and pressure on the sternum. If the resuscitator works alone, then for every 2 pushes 15 artificial breaths are made. In just a minute, 12 injections and 60 pressures are done. If 2 resuscitators work, then one conducts artificial respiration, and the second does a heart massage.
Assessment of the effectiveness of resuscitation measures
How to find out that the first aid was provided correctly, and the victim began to come to life? The following criteria for the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation can be distinguished:
- Respiratory movements - raising and lowering in the chest area.
- The skin takes on a pink tint.
- A narrowing of the pupils is observed.
- Sensation of pulsation in the carotid artery.
Features of resuscitation of pregnant women
How is cardiopulmonary resuscitation performed in pregnant women? When providing assistance, it must be borne in mind that during the period of gestation, the vessels are squeezed by an enlarged uterus.
If there was a cardiac arrest in the pregnant woman, then it is necessary to lay the woman on the left side and carefully, with light movements of the hands, move the uterus to the left side.
When performing a heart massage, hands should be placed 5-6 cm higher than in a normal case. Without stopping, do about 100 taps on the sternum.
Features of resuscitation of children
How is the correct cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the child carried out? Newborns are inflated simultaneously in the mouth and nose. For this, the baby's head is thrown back; the resuscitator grabs the child’s nose and mouth with his mouth and blows air. Per minute, you need to do 25-30 injections of 30 ml.
With a heart massage, children under 10 years of age are given 80 pressures per minute. For newborns, this procedure is carried out with two fingers (index and middle), do 120 clicks per minute.
Medical resuscitation
After the first stages of resuscitation, further assistance to the patient is provided by doctors. The patient is taken to a special department of the hospital (intensive care unit or intensive care unit), where they perform electrical defibrillation of the heart and intracardiac administration of medications.
Now you know how the cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the victim is carried out. But saving a person, it is important to remember precautions. Some resuscitation measures can only be carried out by a doctor. There is such a technique for rescuing a patient with a stopped heart, such as precardial shock. This is punching the lower middle part of the sternum. This method often leads to the fact that a stopped heart starts working again.
It is very important to remember that only resuscitators can use this technique. In no case should you save the patient yourself. Such a stroke can be life-saving if a person's heart stopped, but can cause death if the patient continues to have a heartbeat. People without a medical education should confine themselves to providing primary care.