Parasitic infections are a diverse range of symptoms and diseases that are caused by the entry of eggs or an adult parasite into the human body. Often, the first signs of the disease cannot be detected for several days, and in some cases several months or even years. This is due to the life cycle of parasites and their main functions: good camouflage and maintaining one's own life by receiving nutrients from the host organism.
Types of parasites and their characteristics
Parasitic infections, depending on certain properties of their manifestation, are divided into three groups:
1. Ectoparasites.
The main localization is the surface of the human body. These include lice, fleas, ticks and bugs. They feed mainly on human blood, although in some cases, such as, for example, with ticks that cause demodicosis, the main food is the secret of the sebaceous glands or dead cells of the epithelium (skin).
The first signs of a parasitic infection are fairly easy to recognize, as they cause itching and burning in their habitats. Some ectoparasites are carriers of serious diseases: typhoid, anthrax, encephalitis and trypanosomiasis. They cause enormous damage to human health, even death.
2. Endoparasites (protozoa).
Mostly affect the internal organs. By their structure they are unicellular, hence the name - protozoa. Despite this, they can lead to severe forms of illness. The main diseases of this group are parasitic blood infections caused by toxoplasma, and intestinal infections provoked by amoeba or giardia.
3. Helminths.
They are the causative agents of the most common forms of parasitic infections. In the human body, their developmental cycles mainly take place in the intestines and tissues, where the onset of symptoms of diseases begins.
Roundworms (nematodes)
These are parasites, whose body is in the cross section of a circular shape. Sexual signs are easily distinguishable. Females are usually larger than males. But also in representatives of this class hermaphrodites are found. All nematodes go through developmental stages: an egg, a larva, an adult. This class includes:
- Pinworm. Enterobiosis causes the disease. Mostly affects children of preschool and primary school age.
- Whispers. Trichocephalosis causes the disease. Has a distinctive body shape. 2/3 of the body length has a thin diameter resembling human hair or thread. The other end of the body is of a larger diameter, the intestine is located in it.
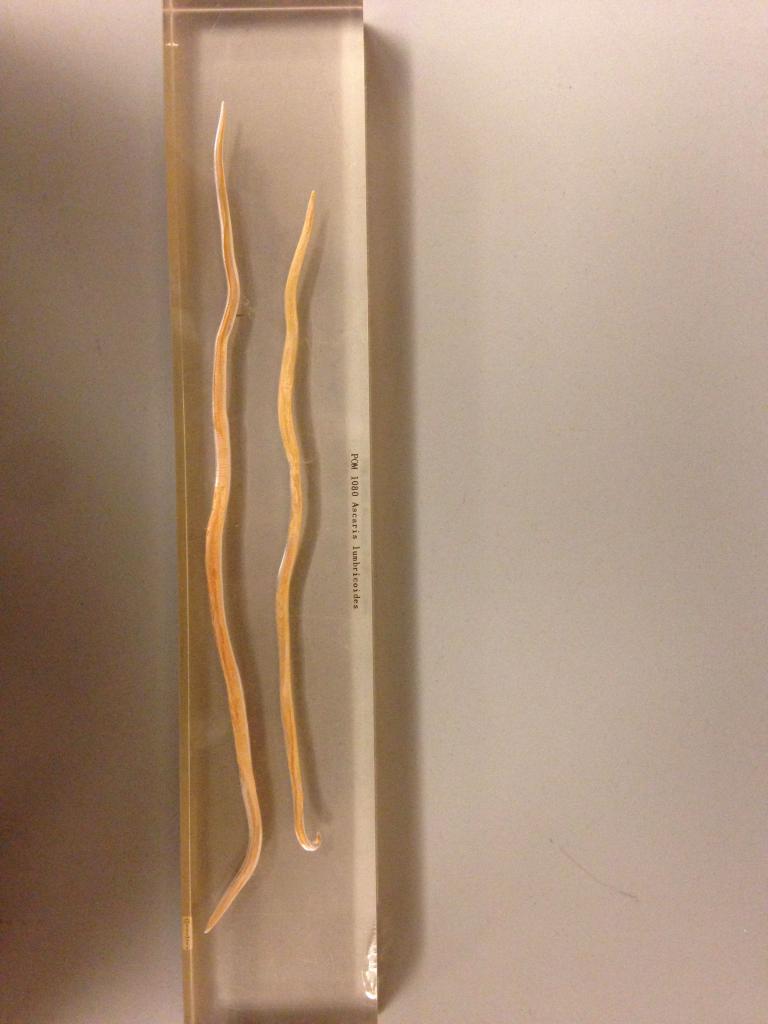
- Ascaris. Ascaridosis causes the disease. Adult individuals reach a size of 25 cm (males) and 40 cm (females). After the larva enters the human body, it passes through the stomach and enters the small intestine. From there, it passes through the pores with a blood stream to the liver, then to the heart and then to the lungs, where it develops within 7-10 days. Then the larvae begin to rise to the larynx. Upon reaching the oral cavity, they are re-swallowed. After entering the small intestine, the larvae can no longer re-enter through the pores into the bloodstream due to their large size. There they grow to adults within 2-3 months. After this, reproduction begins and the cycle repeats. The female can lay more than 200 thousand eggs per day.

Tapeworms (cestodes)
These are parasites whose body resembles the shape of a tape. A distinctive feature of this class is the lack of a digestive system. These include:
- Echinococcus. Causes echinococcosis. This parasite has a small size (2-9 mm) and consists of several segments and suction cups. The uterus of a mature individual contains a large number of eggs, inside of which there are larvae. The main places of localization of echinococcus are the liver and lungs. There, it causes a chronic disease called echinococcal cyst.
- Bull tapeworm. Causes a disease teniarinhoz. At the larval stage, it has an intermediate host - cattle. Once in the human body, it develops in the small intestine to the tape stage. The body of an adult parasite has up to 1000 segments, and in length it can reach 4-10 meters.
- Pork tapeworm. Causes a disease of teniosis. Outwardly very similar to a bull tapeworm. Also has intermediate hosts: pigs, dogs, camels, hares and rabbits. In humans, it parasitizes in the intestines. The size of an adult in length does not exceed 4 meters.
- The tape is wide. Causes the disease diphyllobothriasis. It lives in freshwater bodies of water. As an intermediate host uses crustaceans and fish. In the human body, it parasitizes in the small intestine. In length, an adult can reach several meters.
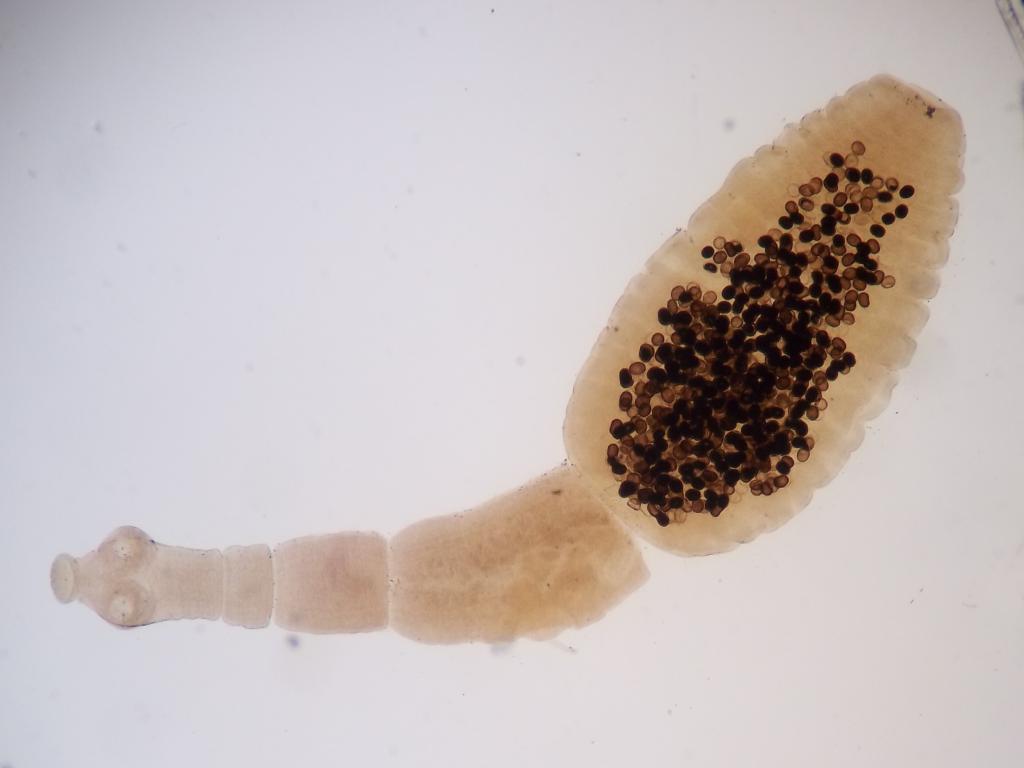
Flatworms (trematodes)
During their life cycle, these parasites can change several intermediate hosts. In humans, they can parasitize in any organ. This group includes:
- Schistosomes. Schistosomiasis causes the disease. In the human body can get in contact with an infected fresh water. The parasite penetrates the skin and enters the circulatory system, where it begins to multiply actively. Females can produce from 300 to 3000 eggs per day. Further, with the flow of blood, eggs spread throughout the body and continue their development in any organ. The length of their body does not exceed 0.1-0.2 cm.
- Hepatic flukes. Opisthorchiasis causes disease. The length of an adult varies from 3 to 5 cm. When it enters the human body, it parasitizes in the bile ducts, gall bladder, liver and pancreas. It is fixed in these organs with the help of suction cups located on the body.
Ways of penetration of parasites into the human body
- Alimentary infection is considered the most common. A person becomes infected with a parasite when eating poorly washed vegetables and fruits. Of particular danger is meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. Also, a person is infected with a parasitic infection if the rules of personal hygiene are not followed. For example, do not wash your hands before eating.
- The transplacental pathway. A parasitic infection is transmitted from a pregnant woman through the placenta to the baby. For example, diseases such as toxoplasmosis, malaria or hookworm.
- Perkutanny way. The parasite penetrates the human body through the skin. These are mainly schistosomes and hookworms.
- Contact way. The parasite is transmitted through dirty hands, contaminated personal belongings, and linen. So most often lice, scabies itch, pinworms are transmitted.
- Transmission path. Infection occurs after the bite of insects that are carriers of parasites. For example, malaria.
Symptoms
Many parasitic diseases in the early stages are not symptomatic. This is due to the stages of development of the pathogen. Each individual parasite species manifests itself differently as it grows. Common common symptoms of a parasitic infection include:
- Itching
- Redness of the skin by the type of urticaria.
- Diarrhea.
- Constipation.
- Flatulence.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Cramping and pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Weight loss without the use of diets and increased physical activity
- Fever.
- High body temperature (38-40 ˚) for a long period.
- Prolonged bouts of dry cough.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Pain in the muscles.
- Disorders of a psycho-emotional nature.
Diagnostics
If you suspect the presence of parasitic diseases, you must pass a number of tests. Diagnosis of parasitic infections allows you to determine the presence or absence of a parasite, its type and location in the body. The data obtained will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Diagnostic methods include:
I. Study of feces. Allows you to determine the presence of most types of parasites that live in the intestine. Feces excrete their eggs, larvae and body segments. There are two types of analysis:
- A fecal sample for eggs and helminth larvae is examined. The analysis is delivered to the laboratory, where the doctor makes smears and examines them under a microscope. This method is often used, but it is not accurate enough. In order to make a final diagnosis, the patient must take this analysis up to three times with small time intervals. This is due to the life cycle of the parasites and the laying of eggs that are detected by this research method.
- Scraping (flushing) from the folds of the anal passage. This analysis is used to detect only one type of helminth - pinworms. In children, parasitic infection is more common than in adults. For this reason, such an analysis is carried out mainly for children. The laboratory assistant moistens a cotton or glass eye stick in water or glycerin and rinses off the perianal folds. Next, the resulting material is applied to a glass slide and examined under a microscope. Also, this analysis is done by another method: the laboratory assistant glues a piece of adhesive tape to the anus, presses and peels off. Then the adhesive tape is glued to the slide and is also examined under a microscope. The parasite is diagnosed quite accurately. Using these methods, the laboratory technician manages to examine not only helminth eggs, but sometimes adults as well.
II. Examination of cerebrospinal fluid, sputum, duodenal contents (bile), urine. Assign according to the results of a patient survey to determine the presence of a parasite and determine its localization. The analysis of these biological fluids is examined using microscopy and macroscopy. First, the obtained sample is examined for the presence of adults, and then microscopy is performed to detect eggs and larvae of parasites.
III. Blood test. Modern methods of blood testing for parasitic infections make it possible to determine the presence and type of pathogen with high accuracy. Three types of such diagnostics are used:
- Serological reactions. They determine the presence of parasite antibodies in the patient's blood serum. This method is considered highly specific, but inferior to PCR diagnostics.
- PCR diagnostics. This method is based on the detection of parasite DNA in any biological fluid that was taken for analysis.
- Genetic research. It consists in the detection of the parasite genome in a patient’s blood sample. This method is used much less often than all others, but has high accuracy.
IV. Examination of biopsy material and lymph nodes. For this analysis, the doctor performs an excision of a small area of the organ, tissue or the entire lymph node and sends it for histological examination. Thus, the presence or absence of parasites is diagnosed.
Test preparation guidelines
Before taking tests for parasitic infections, you need to properly prepare for them. If the recommendations are followed, the accuracy of the diagnosis is increased, since there are no interfering factors in the material that affect the effectiveness of research methods.
Preparation for stool analysis:
- You should stop taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and antacids. The use of drugs and other drugs containing bismuth and iron is also unacceptable.
- If an X-ray study was performed using barium or a colonoscopy, in which an enema was used to cleanse the intestines, then a stool analysis can be taken only after 2-3 days.
- It is not recommended to take feces in case of the onset of menstrual bleeding or exacerbation of hemorrhoids.
Preparation for blood test:
- It is necessary to stop taking pharmacological drugs that affect the blood formula.
- Three days before the test, you should follow a light diet, do not eat fatty foods, give up alcohol.
- A blood test for parasitic infections is taken on an empty stomach. Small amounts of clean drinking water are allowed.
For the rest of the analyzes, most often it does not require special preparation. It will only be necessary to follow the doctor's recommendations.
Treatment
Unfortunately, the symptoms of parasitic infections cannot always be detected in the initial stages of the disease. In such cases, treatment begins late. It is important to understand: the longer the parasite is in the body, the more difficult it will be to get rid of it.
Therapy of infectious and parasitic infections is divided into two areas:
- Symptomatic treatment. It is aimed at eliminating the clinical manifestations of the disease. These include a decrease in body temperature, getting rid of redness and itching, normalization of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The etiological treatment of parasitic infections is aimed at getting rid of the pathogen.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. It is applicable for alveococcosis, echinococcosis and some types of infection with trematodes.
When dehydrating the body, saline solutions are prescribed: Trisol, Disol, Regidron, 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
To reduce irritation, hyperemia and itching of the skin, the following creams are used: Fenistil, Hydrocortisone, Gistan, Advantan.
Anthelmintic therapy is carried out using the following drugs: Nemozol, Vermox, Pirantel, Dekaris, Vermakar, Mebendazole.
Antimalarial drugs: Delagil, Primakhin, Quinine Sulfate, Malaron, Fansidar.
Only a doctor can prescribe treatment for parasitic infections based on laboratory data and a patient survey.
Prevention
It is very important to observe the prevention of parasitic infections. In most cases, this will help prevent pathogens from entering the body.
Preventive measures include:
- Observance of personal hygiene rules: it is necessary to wash hands before eating food, after visiting the toilet room, going home from the street.
- Rinse vegetables and fruits well.
- Be sure to conduct sufficient heat treatment of meat, fish and seafood.
- As drinking water, do not use tap water, since it can not always be cleaned of parasites. The use of home filters will not help as an additional cleaning. The best option is to use boiled or bottled water.
- If pets live at home, then they need to be dewormed once every six months. You should also limit contact with the pet if it has signs of parasitic diseases and contact a veterinary clinic.
- It is necessary to iron underwear (especially for children) after washing.
- After visiting exotic countries, when working with land, as well as employees of children's institutions, it is recommended to be examined once a year for the presence of parasitic infections and, if necessary, to carry out preventive measures with medicines.