An integral part of any living organism that can only be found on the planet is the intercellular substance. It is formed from components known to us - blood plasma, lymph, collagen protein fibers, elastin, matrix and so on. In any organism, cells and intercellular substance are inextricably linked. And now we will consider in detail the composition of this substance, its functions and features.
general information
So, intercellular substance is one of the many types of connective tissue. It is present in various parts of our body, and its composition changes depending on the location. As a rule, such a binding substance is secreted by supporting trophic tissues, which are responsible for the integrity of the work of the whole organism. The composition of the intercellular substance can also be characterized in general. These are blood plasma, lymph, protein, reticulin and elastin fibers. This fabric is based on a matrix, which is also called an amorphous substance. In turn, the matrix consists of a very complex set of organic substances, whose cells are extremely small in size compared with the main known microscopic elements of the body.
Features of Binding Tissue
The formed intercellular substance in tissues is the result of their activity. That is why its composition depends on what part of the body we are considering. If we talk about the embryo, then in this case the type of substance will be the same. Here it appears from carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and embryonic connective tissue. In the process of growth of the body, its cells become more diverse in their functions and content. As a result, the intercellular substance also changes. It can be found in the epithelium and in the bowels of internal organs, in the bones of a person and in his cartilage. And in each case, we will find an individual composition, the identification of which can only be a knowledgeable biologist or physician.
The most important fiber of the body
In the human body, the intercellular substance of the connective tissue performs the main supporting function. It is not responsible for the operation of a specific organ or system, but supports the vital activity and interconnection of all components of a person or animal, from the deepest organs to the dermis. On average, this binder component represents from 60 to 90 percent of the total body weight. In other words, this substance in the body is a supporting framework that provides us with vital functions. Such a substance is divided into many subspecies (see below), the structure of which is similar to each other, but not completely identical.
We dig even deeper - the "matrix"
The intercellular substance of the connective tissue itself is the matrix. It performs a transport function between various systems in the body, serves as its support and, if necessary, transmits various signals from one organ to another. Thanks to this matrix, a metabolism occurs in a person or in an animal, it participates in the locomotion of cells, and is also an important component of their mass. It is also important to note that in the process of embryogenesis, many cells that were previously independent or belonged to a certain internal system, become part of this substance. The main components of the matrix are hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans and glycoproteins. One of the most prominent representatives of the latter is collagen. This component fills the intercellular substance and is found in literally every, even the smallest corner of our body.
The internal structure of the skeleton
The formed bones of our body are composed entirely of osteocyte cells. They have a pointed shape, a large and solid nucleus, and a minimum of cytoplasm. Metabolism in such "petrified" systems of our body is made thanks to the bone tubules, which perform a drainage function. The intercellular substance of bone tissue itself is formed only during bone formation. This process is carried out thanks to osteoblast cells. They, in turn, after the completion of the formation of all tissues and compounds in a similar structure are destroyed and cease to exist. But at the initial stages, these bone cells secrete intercellular substance through the synthesis of protein, carbohydrates and collagen. Once the tissue matrix is formed, the cells begin to produce salts that turn into calcium. In this process, osteoblasts seem to block all metabolic processes that occurred inside them, stop and die. The strength of the skeleton is now maintained due to the fact that osteocytes function. If some kind of trauma happens (fracture, for example), then osteoblasts renew and begin to produce intercellular substance of bone tissue in large quantities, which allows the body to cope with the disease.
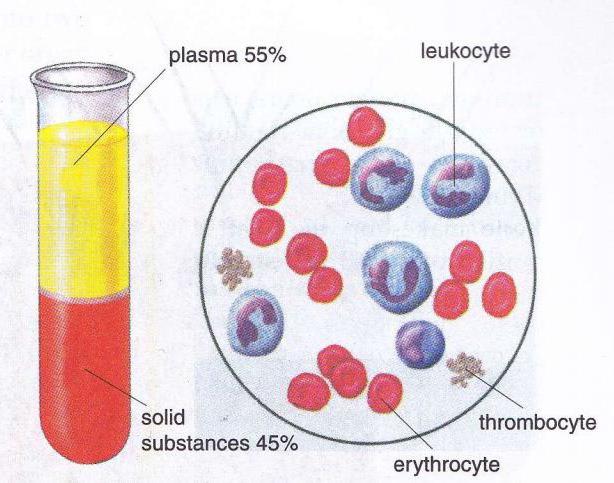
Features of the structure of blood
Everyone knows very well that such a component as plasma is part of our red liquid. It provides the necessary viscosity, the possibility of blood sedimentation and much more. Thus, the intercellular substance of the blood - this is plasma. Macroscopically, it is a viscous liquid, which is either transparent or has a slight yellowish tint. Plasma always collects in the upper part of the vessel after deposition of other basic blood elements. The percentage of such intercellular fluid in the blood is from 50 to 60%. The basis of the plasma itself is water, which contains lipids, proteins, glucose and hormones. Plasma also absorbs all metabolic products, which are then disposed of.
The types of proteins that are in our body
As we already understood, the structure of the intercellular substance is based on proteins, which are the end product of the work of cells. In turn, these proteins can be divided into two categories: those that have adhesive properties, and those that eliminate cell adhesion. To the first group we mainly include fibronectin, which is the main matrix. It is followed by nidogen, laminin, as well as fibrillar collagens, which form fibers. On these tubules are transported various substances that provide metabolism. The second group of proteins is release agents. They include various glycoproteins. Among them, we will name tenascin, osteonectin, thrompospondin. These components are primarily responsible for the healing of wounds and injuries. They are also produced in large quantities during infectious diseases.
Functionality
Obviously, the role of intercellular substance in any living organism is very large. This substance, consisting mainly of proteins, is formed even between the hardest cells, which are at a minimum distance from each other (bone tissue). Due to its flexibility and the tubule-conductors in this "semi-fluid" metabolism occurs. This may highlight the products of processing the main cells, or it may receive useful components and vitamins that have just been ingested with food or in another way. The intercellular substance penetrates our body completely, starting with the skin and ending with the cell membrane. That is why both western medicine and eastern medicine have long come to the conclusion that everything in us is interconnected. And if one of the internal organs is damaged, then this can affect the condition of the skin, hair, nails, or vice versa.
Perpetual motion machine
The intercellular substance present in the tissues of our body literally ensures its vital activity. It is divided into many different categories, can have a different molecular structure, and in some cases the functions of a substance vary. Well, let us consider what types of such connective matter are and what is characteristic of each of them. We’ll probably only miss the plasma here, since we have already studied enough of its functions and features and will not repeat ourselves.
Intercellular simple connection
Traced between cells that are at a distance of 15 to 20 nm from each other. In this case, the connecting tissue is freely located in this space and does not interfere with the passage of useful substances and waste products from the cells through their tubules. One of the most famous varieties of such a connection is the "castle". In this case, the bilipid membranes of cells located in space, as well as part of their cytoplasm, are compressed, forming a strong mechanical bond. Various components, vitamins and minerals, which ensure the body's work, pass through it.
Intracellular tight connection
The presence of intercellular substance does not always mean that the cells themselves are at a great distance from each other. In this case, with their similar adhesion, the membranes of all the components of an individual body system are tightly compressed. Unlike the previous version - the “lock”, where the cells also touch, here such “sticking-in” prevents the passage of various substances through the fibers. It is worth noting that this type of intercellular substance most reliably protects the body from the environment. Most often, such a dense fusion of cell membranes can be found in the skin, as well as in various types of dermis, which envelops the internal organs.
The third type - desmosome
This substance is a kind of sticky bond that forms above the surface of cells. This can be a small area with a diameter of not more than 0.5 microns, which will provide the most effective mechanical connection between the membranes. Due to the fact that desmosomes have a sticky structure, they very tightly and reliably glue cells together. As a result of this, metabolic processes in them occur more efficiently and quickly than under the conditions of simple intercellular substance. Such sticky formations are found in intercellular tissues of any type, and all of them are interconnected by fibers. Their synchronous and consistent work allows the body to respond to any external lesions as soon as possible, as well as process complex organic structures and transfer them to the necessary organs.
Cell nexus
This type of contact between cells is also called gap. The bottom line is that here only two cells take part, which are tightly adjacent to each other, and at the same time there are many protein canals between them. Metabolism occurs only between the specific two components. Between the cells, which are so close to each other, there is an intercellular space, but in this case it is practically inactive. Further along the chain reaction, after the exchange of substances between the two components, vitamins and ions are transmitted further and further through the protein channels. It is believed that this method of metabolism is the most effective, and the healthier the body, the better it develops.
How the nervous system works
Speaking of metabolism, transport of vitamins and minerals throughout the body, we missed a very important system, without which not a single living creature can function - a nervous one. The neurons of which it consists, in comparison with other cells of our body, are located at a very large distance from each other. That is why this space is filled with intercellular substance, which is called the synapse. This type of connective tissue can only be located between identical nerve cells or between a neuron and the so-called target cell, into which an impulse must arrive. A characteristic feature of the synapse is that it transmits a signal only from one cell to another, without immediately spreading it to all neurons. In this chain, information reaches its “target” and notifies a person of pain, malaise, etc.
Short afterword
The intercellular substance in the tissues, as it turned out, plays an extremely important role in the development, formation and further vital activity of every living organism. Such a substance makes up a large part of the mass of our body, it performs the most important function - the transport, and allows all organs to work harmoniously, complementing each other. The intercellular substance is able to independently recover after various injuries, bring the whole body into tone and correct the work of certain damaged cells. This substance is divided into many different types, it is found both in the skeleton and in the blood, and even in the nerve endings of living things. And in all cases, it signals to us what is happening to us, makes it possible to feel pain if the work of a certain organ is disrupted, or the need to obtain a certain element when it is not enough.