The body of many living organisms consists of tissues. The exceptions are all unicellular, as well as some multicellular, for example, lower plants, which include algae, as well as lichens. In this article we will look at the types of tissue. Biology studies this topic, namely its section - histology. The name of this industry comes from the Greek words "fabric" and "knowledge." There are so many types of fabrics. Biology studies both plant and animal. They have significant differences. Tissues, types of tissues, biology has been studying for quite some time. For the first time they were described even by such ancient scholars as Aristotle and Avicenna. Biology continues to study tissues and types of tissues further - in the 19th century such famous scientists as Moldenhauer, Mirbel, Gartig and others studied them. With their participation, new types of cell populations were discovered, and their functions were studied.
Types of Tissues - Biology
First of all, it should be noted that the tissues that are characteristic of plants are not characteristic of animals. Therefore, biology can divide types of tissues into two large groups: plant and animal. Both combine a large number of varieties. We will consider them further.
Types of Animal Tissues
Let's start with what is closer to us. Since we belong to the kingdom of Animals, our body consists precisely of tissues, the varieties of which will now be described. Types of animal tissues can be combined into four large groups: epithelial, muscle, connective and nervous. The first three are divided into many varieties. Only the last group is represented by only one type. Next, we consider all types of tissues, structure and functions that are characteristic of them, in order.
Neural tissue
Since it is only one species, we start with it. The cells of this tissue are called neurons. Each of them consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. The latter are the processes along which an electrical impulse is transmitted from cell to cell. The neuron has one axon - it is a long process, there are several dendrites, they are smaller than the first. In the body of the cell is the nucleus. In addition, the so-called Nissl bodies are located in the cytoplasm - an analogue of the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, which generate energy, as well as neurotubules, which are involved in conducting an impulse from one cell to another.
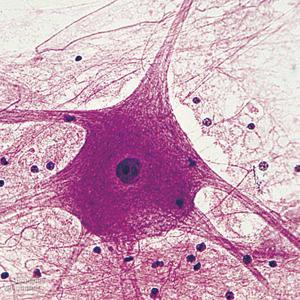
Depending on their functions, neurons are divided into several types. The first type is sensory, or afferent. They conduct an impulse from the senses to the brain. The second type of neurons is associative, or switching. They analyze the information that came from the senses, and generate a response impulse. Such types of neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord. The last variety is motor, or efferent. They conduct an impulse from associative neurons to organs. Also in the nervous tissue there is an intercellular substance. It performs very important functions, namely it provides a fixed arrangement of neurons in space, participates in the removal of unnecessary substances from the cell.
Epithelial
These are types of tissues whose cells are tightly adjacent to each other. They can have a diverse shape, but are always located close. All different types of tissues of this group are similar in that there is little intercellular substance in them. It is mainly presented in the form of a liquid, in some cases it may not be. These are the types of body tissues that provide its protection, and also perform a secretory function.
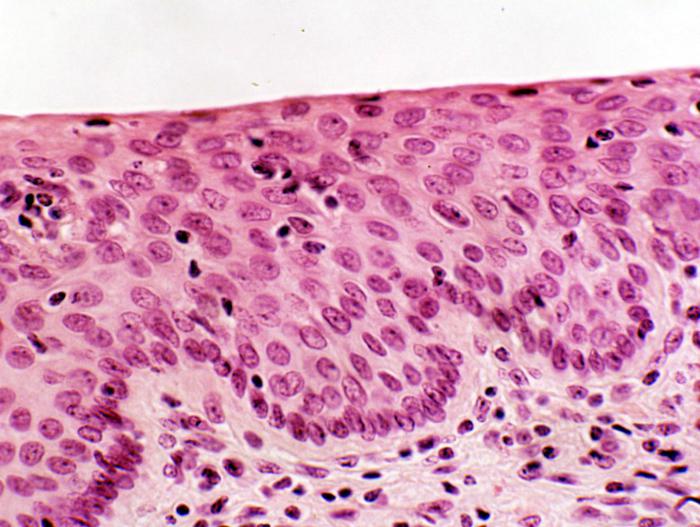
This group combines several varieties. This is a flat, cylindrical, cubic, sensory, ciliary and glandular epithelium. From the name of each one can understand what kind of cells they are made of. Different types of epithelial tissues differ in their location in the body. So, the flat lining the cavity of the upper organs of the digestive tract - the oral cavity and esophagus. The cylindrical epithelium is located in the stomach and intestines. Cubic can be found in the renal tubules. The sensory lining of the nasal cavity, on it there are special villi that provide the perception of odors. Cells of the ciliary epithelium, as its name implies, have cytoplasmic cilia. This type of tissue lines the airways below the nasal cavity. The cilia that each cell has have a cleansing function - they filter to some extent the air that passes through the organs covered by this type of epithelium. And the last variety of this group of tissues is the glandular epithelium. Its cells perform a secretory function. They are located in the glands, as well as in the cavity of certain organs, such as the stomach. The cells of this type of epithelium produce hormones, earwax, gastric juice, milk, sebum and many other substances.
Muscle tissue
This group is divided into three types. The muscle is smooth, striated and cardiac. All muscle tissues are similar in that they consist of long cells - fibers, they contain a very large number of mitochondria, since they need a lot of energy to carry out movements. Smooth muscle tissue lines the cavity of the internal organs. We cannot control the contraction of such muscles ourselves, since they are innervated by the autonomic nervous system.
The cells of striated muscle tissue are characterized in that they contain more mitochondria than in the first. This is because they need more energy. The striated muscles can contract much faster than smooth muscles. It consists of skeletal muscles. They are innervated by the somatic nervous system, so we can consciously control them. Muscular heart tissue combines some of the characteristics of the first two. It is able to contract as actively and quickly as striated, but is innervated by the autonomic nervous system, as well as smooth.
Connective tissue types and their functions
All tissues of this group are characterized by a large amount of intercellular substance. In some cases, it appears in a liquid state of aggregation, in some in a liquid state, and sometimes in the form of an amorphous mass. Seven types belong to this group. It is dense and loose fibrous, bone, cartilage, reticular, fat, blood. In the first variety, fibers predominate. It is located around the internal organs. Its functions are to give them elasticity and their protection. In loose fibrous tissue, amorphous mass prevails over the fibers themselves. It completely fills the gaps between the internal organs, while the dense fibrous forms only peculiar shells around the latter. She also plays a protective role.
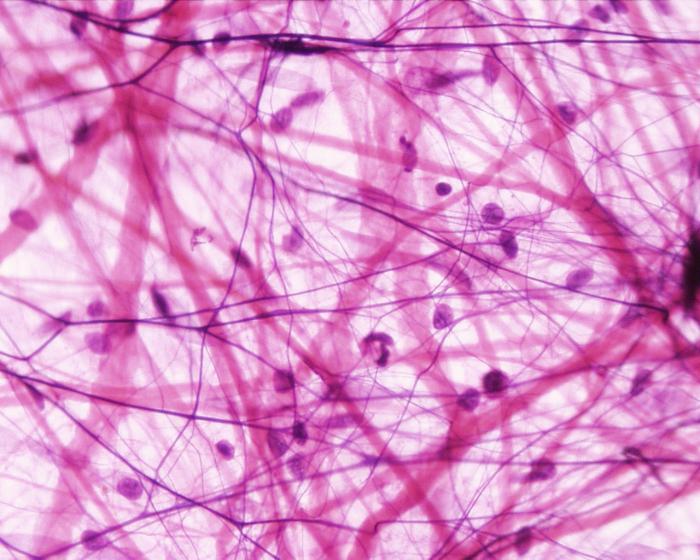
Bone and cartilage tissue form the skeleton. It performs a supporting function in the body and partly protective. Inorganic substances predominate in the cells and intercellular substance of bone tissue , mainly phosphates and calcium compounds. The metabolism of these substances between the skeleton and blood is regulated by hormones such as calcitonin and parathyrotropin. The first maintains the normal state of bones by participating in the conversion of phosphorus and calcium ions into organic compounds stored in the skeleton. And the second, on the contrary, with a lack of these ions in the blood, provokes them from skeletal tissue.
Blood contains a lot of liquid intercellular substance, it is called plasma. Her cells are quite original. They are divided into three types: platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. The former are responsible for blood coagulation. During this process, a small blood clot forms, which prevents further blood loss. Red blood cells are responsible for the transport of oxygen throughout the body and providing them with all tissues and organs. They may contain agglutinogens, which exist in two types - A and B. In the blood plasma, the content of agglutinins alpha or beta is possible. They are antibodies to agglutinogens. For these substances, the blood group is determined. In the first group, no red agglutinogens are observed on red blood cells, and two types of agglutinins are immediately found in plasma. The second group has agglutinogen A and agglutinin beta. The third is B and alpha. In the fourth plasma, there are no agglutinins, but on the red blood cells there are agglutinogens A and B. If A occurs with alpha or B with beta, the so-called agglutination reaction occurs, as a result of which the red blood cells die and blood clots form. This can happen if you transfuse the blood of an inappropriate group. Considering that only red blood cells are used during transfusion (plasma is screened out at one of the stages of donor blood processing), then a person with the first group can only be transfused with blood of his own group, with the second - blood of the first and second groups, with the third - of the first and third groups, with the fourth - any group.
Also, D antigens can be on red blood cells, which determines the Rh factor, if they are present, the last positive, if absent, negative. Lymphocytes are responsible for the immune system. They are divided into two main groups: B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes. The former are produced in the bone marrow, the latter in the thymus (the gland located behind the sternum). T-lymphocytes are divided into T-inductors, T-helpers and T-suppressors. Reticular connective tissue consists of a large number of intercellular substance and stem cells. They form blood cells. This tissue forms the basis of bone marrow and other blood forming organs. There is also adipose tissue, the cells of which contain lipids. It performs a spare, heat-insulating and sometimes protective function.
How are plants arranged?
These organisms, like animals, consist of a combination of cells and intercellular substance. We will describe the types of plant tissues further. All of them are divided into several large groups. These are educational, integumentary, conductive, mechanical and basic. Types of plant tissues are numerous, since several belong to each group.
Educational
These include apical, lateral, intercalary and wound. Their main function is to ensure plant growth. They consist of small cells that actively divide and then differentiate, forming any other kind of tissue. The apical ones are at the tips of the stems and roots, the lateral ones are inside the stem, under the coverslips, the insertion ones are at the bases of the internodes, and the wound ones are at the site of damage.
Coverslips
They are characterized by thick cell walls consisting of cellulose. They play a protective role. There are three types: epidermis, peel, cork. The first covers all parts of the plant. It can have a protective wax coating, also on it are hairs, stomata, cuticle, pores. The crust is different in that it has no pores; in all other characteristics, it is similar to the epidermis. Cork is the dead integumentary tissue that forms the bark of trees.
Conductive
These fabrics come in two varieties: xylem and phloem. Their functions are the transport of substances dissolved in water from the root to other organs and vice versa. Xylem is formed from vessels formed by dead cells with hard membranes; there are no transverse membranes. They transport fluid up.
Phloem - sieve tubes - living cells in which there are no nuclei. Transverse membranes have large pores. Using this type of plant tissue, substances dissolved in water are transported down.
Mechanical
They also come in two types: these are collenchyma and sclerenchyma. Their main task is to ensure the strength of all organs. Collenchyma is represented by living cells with woody membranes that fit tightly together. Sclerenchyma consists of elongated dead cells with hard membranes.
The main
As their name implies, they form the basis of all plant organs. They are assimilative and spare. The first are in the leaves and the green part of the stem. In their cells are chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. Organic matter accumulates in the storage tissue, in most cases it is starch.