Probably, many people know that yeast is mushrooms. And what about the further classification of these representatives of the kingdom? Yeast is known to belong to the fungi of the ascomycetes and basidiomycetes. What does this mean? Let's try to figure it out together.
Yeast - Mushrooms
Moreover, unicellular mushrooms. They lost mycelium as a result of evolutionary processes, as they believe, in connection with the transition to living in liquid substrates, which are rich in organic matter and very favorable for the vital activity of these organisms. In total, there are up to one and a half thousand species. All yeast are unicellular mushrooms.
Dimensions
Single isolated cells of these fungi reach up to 7 microns in diameter, but some grow to 40 microns. However, some yeast-like ones still form mycelia at the stages of their life cycle, and in some cases the fruiting body. Currently, for example, baker's yeast are the first eukaryotes whose genome has been identified and deciphered.
Bit of history
Yeast - mushrooms, "domesticated" by man, and for a long time. They have long been used for thousands of years for culinary purposes: baking, creating the conditions of fermentation. Bakery existed already in Ancient Egypt and, obviously, yeast was used. And in some countries in ancient times, along with baking unleavened (for example, matzo or pita bread), the production of yeast bread was also gaining popularity. The Egyptians already knew about beer yeast more than six thousand years ago, and with the help of these organisms people made this foamy drink.
Interestingly, for a new sourdough in many farms from ancient times used the remains of the old. So, according to scientists, there was a selection of yeast, there were species that are not found in the wild. And many people consider some types of yeast to be a product of exclusively human activity (for example, cultivated cereals: wheat, rye, and others).
Zymology
This is the name of science that describes and studies the life and activity of these organisms. Yeast belongs to mushrooms, their pure culture was first isolated in 1881 in Denmark, and in 1883 it was already used for the production of beer. At the end of the 19th century, a classification of yeast was created, and in the 20th century, collections and identifiers of known cultures appear. Yeast belongs to the mushrooms of the Ascomyceta until the middle of the last century. Scientists observed their sexual cycle, generalizing as a taxonomic group (marsupials). But in Japan, one of the scientists induced the reproduction of yeast-basidiomycetes. Thus, experts came to the conclusion that yeast fungi (photo below) were formed in the process of evolution independently among these two departments of the kingdom (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes). The data was also confirmed by molecular biological research of organisms. They are not a taxon, but, most likely, a special life form.
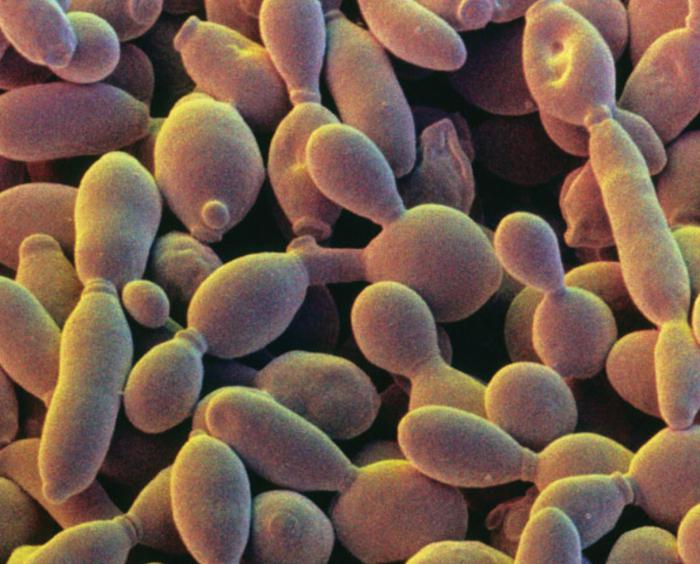
Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
So, the yeast belongs to the fungi of the ascomycete and basidiomycetes (more precisely, to two different departments). All of them are the kingdom of higher mushrooms. They can be distinguished by the characteristics of life cycles and some other signs: vapors in DNA, the presence of urease. Ascomycetes, or marsupials, are a fairly extensive department, which includes up to thirty thousand species (by the way, truffles known to everyone belong to this department, as well as morels and lines). Among all - and yeast, which are considered scientists secondarily unicellular organisms.
Habitat
Typically, these organisms live in places that are rich in sugars - substrates on the surface of fruits and berries, leaves. They can eat plant vital products: nectar, secretions, wound juices. Do not disdain and dead phytomass. They can live both in soil litter from organic matter and in natural water masses. Some yeast is also present in the intestines of insects that feed on wood. A lot of yeast and leaves that are affected by aphids.
Application
Some types of yeast crops have long been in demand in cooking, baking and distillation of alcohol. Kvass, bread, beer, wine cannot do without these tiniest helpers. All of these, known to mankind for a long time, yeast belong to the fungi of the ascomycete division. To produce strong alcohol, they are involved in distillation at the fermentation stage. Nowadays, some yeast cultures are used in a wide range of biotechnologies: the production of fuel and food additives and enzymes. And in science they are used as experimental cultures for research by geneticists.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Bakery uses the Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture, known as baker's yeast. They produce alcoholic fermentation, enhancing the taste and aroma of a bread product (alcohol then evaporates during baking). In addition, carbon dioxide formed in the mass causes the dough to rise, giving the dough porosity and softness.
- In nature, yeast cultures develop naturally on grape berries, which are noticeable as a whitish coating. But true wine yeast is considered Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which are quite rare on clusters. It is this variety that is used for the most part for the preparation of wine material. As a result of processing the sugars contained in grape juice by yeast, ethanol is produced, and yeast, when the degree is increased, die. And to make champagne, the finished wine is fermented again, adding a yeast culture.
- In brewing, germinated barley grain (malt) and yeast from the bottom and top fermentation are used. Malt is ground, boiled, mixed with water and fermented using Saccharomyces cerevisiae or some other types of yeast. Kvass is made in approximately the same way, but in addition to yeast, lactic acid bacteria are also used.
- The above yeast, widely used in the national economy, belong to the order of ascomycetes fungi. Associations of yeast and bacteria are also popular for making drinks: for example, Kombucha or Tibetan mushroom. They have many useful properties for the human body, and the regular use of these drinks prevents all kinds of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other internal organs.