The most important role in the treatment of a rare disease is played by diagnostics, which makes it possible to differentiate the disease with a number of other health disorders. The treatment of Still's disease is long, but the prognosis for patients who turned to a specialist on time is generally good.
Medical history
The disease was first discovered in 1897 thanks to the physician George Still. But at this time, Still's disease was considered only one form of rheumatoid arthritis. Only in 1971, Eric Bywaters published studies highlighting the disease from a number of problems with similar symptoms.
Medical statistics indicate that both male and female representatives can get a rare disease equally. However, most patients who see a doctor with symptoms of Still's disease and receive a confirmatory diagnosis are children under 16 years of age. Given the very young age of most patients, the diagnosis is complicated, since it is difficult for parents who first notice symptoms in a child to have such an “age” problem.
Causes of the disease
The etiology of the development of the disease is still unclear. Numerous studies aimed at identifying the factor that triggered Still's disease in adults and children have failed. According to the generally accepted hypothesis, the disease is the result of exposure to infectious or viral agents on the body, but there is no evidence to support this claim.
Doctors tried to associate the disease with pregnancy, the use of medications, including female hormones, stress and other factors. According to some sources, Still's disease is an autoimmune disorder. It is reliably proved only that in the active phase the disease is characterized by changes in the concentration of cytokines. Perhaps in the future, medicine will be able to identify the cause of the disease, thereby simplifying its diagnosis and accelerating the recovery of patients.
Symptoms of Still's disease in adults
Still's disease, the symptoms of which are similar to a number of other diseases, is diagnosed by several indicators:
- The fever that occurs with Still's disease differs from the fever inherent in a number of infectious diseases in its inconstancy. Traditionally, the temperature throughout the day is kept within normal limits, but rises to 39 degrees and above twice a day. At the same time, in a fifth of patients, a decrease in temperature indicators and improvement in the patient’s well-being are not observed, which significantly complicates the diagnosis.
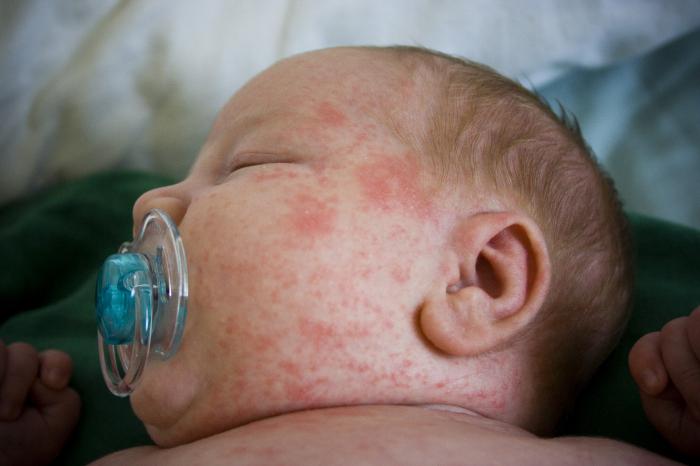
- At the peak of the temperature rise, the patient has skin rashes, represented by pink papules or macules. Most often, the rash is located on the trunk and in the proximal extremities, less often - the picture of the rash is presented on the face. In a third of patients, the rash rises above the skin, occurring mainly in places of friction and compression. A similar symptom is called the Kebner phenomenon. The rash is not always accompanied by an itch, and its rather pale pink color and periodic disappearance make the symptom invisible to the patient. To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors are forced to expose the patient to heat, activating the manifestation of rashes. It can be a warm shower or a warm towel. The atypical manifestations of the disease are: alopecia, erythema nodosum, petechial hemorrhages. But in practice, such symptoms are extremely rare.
- The initial stage of Still's disease is characterized by the appearance of myalgia and arthralgia. In this case, only one joint is affected at first. Over time, the disease covers other joints, taking on the character of polyarthritis. First of all, the knee, ankle, wrist, hip, temporomandibular, metatarsophalangeal joints are affected. But a feature of the disease, most typical for most cases, is the development of arthritis of the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands. This is what makes it possible to differentiate Still's disease from rheumatic fever, systemic lupus erythematosus, or rheumatoid arthritis.
- In 65% of patients with the disease, lymphadenopathy occurs. Half of the patients have enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Moreover, in some cases, lymphadenitis takes on a necrotic character.
- At the beginning of the disease, patients note a pronounced burning sensation in the throat, which is permanent.
- Cardiopulmonary manifestations, such as aseptic pneumonitis, cardiac tamponade, valve vegetation, and respiratory distress syndromes, are also characteristic of Still's disease.
- Patients also have ophthalmic disorders. This is complicated cataract, tape-shaped degeneration of the cornea of the eye, iridocyclitis.

Still's disease in children
The symptomatology of the disease in children does not differ from the adult. However, manifestations of Still's disease in childhood can be blurred, which leads to late diagnosis and untimely treatment. Sometimes polyarthritis in childhood leads to disability. To avoid this, parents should be extremely attentive to the physical condition of the child. And at the first symptoms of the disease, contact a qualified specialist. The neglected Still's disease in children can provoke a disproportionate growth of the limbs, which will require surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since the specific symptoms of the disease are practically absent, the diagnosis is difficult. In every twentieth case, Still's disease is interpreted as an unexplained fever. In some cases, the diagnosis of sepsis. And only after a series of unsuccessful courses of antibacterial therapy and a number of additional tests, the doctors conclude that this is Still's disease in adults. Treatment and rehabilitation - long-term procedures and requiring constant medical supervision. The same applies to children.
When making a diagnosis, symptoms are taken into account in the form of fever, swelling of the joints, an increase in lymph nodes and inflammation of the throat, as well as other indicators obtained using an echocardiogram, computed tomography, and ultrasound. A blood test showing platelet and white blood cell counts is also required. In Still's disease, the patient is characterized by a decrease in the level of red blood cells. In adult patients, C-reactive protein and ferritin are elevated. Moreover, tests for antinuclear antibodies and rheumatoid factor are usually negative.
Treatment during remission
Comprehensive and phased treatment is carried out both in the active phase of the disease, and during the period of remission. In the first case, the procedures are performed in a hospital, in the second - the patients receive the necessary therapy, being on outpatient treatment or in sanatorium-and-spa institutions. Therapy includes medical treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures, physiotherapy exercises and massage.
Treatment during exacerbation of the disease
During an exacerbation of the disease, patients take NSAIDs, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids. The treatment is always long. That is why both the patient himself and his relatives need to stock up on a large dose of patience. Still's disease in adults and children is a serious disease, and it is possible to cope with it only with timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment.
Forecast
After treatment, three forms of the development of the disease are possible. The best of them is the spontaneous recovery observed in a third of patients with a rare diagnosis. Another third of patients have a periodically recurring form of the disease. The most difficult option is chronic Still disease in adults. Treatment, recovery and rehabilitation in this case may include not only traditional therapy, but also arthroplasty, which allows to restore joints damaged by the disease.