All living organisms, with the exception of algae, are composed of various tissues. Body tissues are collections of cells similar in structure, united by a common function. So what are they?
Plant tissue
There are such types of plant tissues:
- educational;
- main;
- coverslip;
- conductive;
- mechanical.
All of them carry out their functions. For example, an educational one provides plant growth, and all other types of tissues are formed from it. The integumentary tissue has a protective function. In addition, gas exchange occurs through it. Conducting provides the transport of substances throughout the plant. Mechanical tissue also plays a protective role. It is present in plants with a woody stalk. The main body tissues are responsible for the formation and accumulation of nutrients.
Human tissue
There are many types of animal tissues, which, in turn, are divided into species.
The animal organism is built of four types of tissue:
- epithelial;
- muscular
- Nervous
- connecting.
All types of tissues of the human body are divided into types. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Epithelium: varieties and functions
Tissues of living organisms of this type perform mainly a protective function.
The epithelium, first of all, can be divided into single-layer and multi-layer. In the first, there is only one row of cells located close to each other. The second consists of several layers of cells.
The shape of cells distinguish between flat, cubic and cylindrical epithelium. Depending on the specific functions performed by the tissue, ciliary, glandular and sensitive, or sensory epithelium is also secreted.
Different types of epithelial tissue are found in different parts of the body of animals and humans. So, the flat lining the oral cavity and the cavity of the esophagus, cubic - the renal tubules, cylindrical - the stomach and intestines. Ciliary epithelium is located inside the respiratory tract, sensitive (sensory) in the nasal cavity, glandular in the glands.
Muscle tissue: characteristic
The muscle tissues of the human body are divided into three types:
- striated muscles;
- smooth muscles;
- heart muscle.
Muscle tissue cells are called myocytes, or fibers. The tissue of this species is able to contract due to the content of contractile proteins in the cells: actin and myosin.
The striated muscles have thin, long cylindrical fibers with several nuclei and a large number of mitochondria that provide the cell with energy. This type of tissue consists of skeletal muscle. Their main function is to move the body in space. They can also play a protective role. This applies, for example, to the abdominal muscles, which protect internal organs from damage.
Smooth muscles, unlike striated muscles, cannot be controlled consciously. Such tissues of the human body line some internal organs, such as the intestines and uterus. They also consist of sphincters - circular muscles, which narrow the hole when narrowing. Animals have upper and lower esophageal sphincters, the pylorus of the stomach, several sphincters of the duodenum; sphincters of Oddi, Mirizzi, Lutkens and Helly, located in the organs of the pancreatic system; sphincters of the colon, as well as sphincters of the urethra. In addition, the pupil sphincter is also present in animals and humans, due to which it narrows and expands. Smooth muscles have spindle-shaped cells containing one core. Muscles of this type are contracting not as fast and actively as striated.
The heart muscles are similar to striated and smooth. Like a smooth one, her person cannot control it consciously. However, it is capable of contracting as quickly and actively as striated. The fibers of the heart tissue intertwine with each other, forming a strong muscle.
Neural tissue
It is not subdivided into species. Cells of such tissue are called neurons. They consist of a body and several processes: one long axon and several shorter dendrites. In addition to neurons, neuroglia are also present in the nervous tissue. It consists of small cells with numerous outgrowths. Neuroglia plays a supporting function, provides the cell with energy, and also forms specific conditions for the formation of a nerve impulse.
Connective tissues: varieties, functions, structure
This type of fabric has many types:
- dense fibrous;
- loose fibrous tissue;
- blood;
- lymph;
- bone;
- cartilaginous;
- fatty;
- reticular (mesh) tissue.
Despite the fact that they all belong to the connective, these tissues are quite different in their structure and functions. The main similarity of all these tissues is the presence of a large amount of intercellular substance. Consider the features of the main types of connective tissue.
Reticular tissue: features
This is one of the most important connective tissue. Reticular tissue forms the organs of hematopoiesis. It contains cells from which blood cells are formed . Reticular tissue forms the red bone marrow - the main hematopoietic organ of humans and animals, as well as the spleen and lymph nodes.
Reticular tissue has a complex structure. It consists of reticular cells (reticulocytes) and reticular fibers. The cells of this tissue have a light cytoplasm and an oval nucleus. On its surface, it has several processes, with the help of which the cells connect together and form something like a network. Reticular fibers are also arranged in the form of a lattice, branch and connect to each other. Thus, the network of reticular fibers together with the network of reticulocytes form the stroma of the blood-forming organs.
Reticulocytes can be secreted from the cell network and differentiate into macrophages or hematopoietic cells. Macrophages are special white blood cells that are part of the phagocyte group. They are able to carry out phagocytosis - capture and absorption of particles, including other cells. The main task of macrophages is to fight against pathogenic bacteria, viruses and protozoa.
Bone and cartilage
They perform protective and supporting functions in the body. Their main feature is that the intercellular substance is solid and consists mainly of inorganic substances. As for the cells, they are in four types of bone tissue : osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and osteogenic. All of them differ in structure and function. Osteogenic cells are those from which the other three types of bone cells are formed. Osteoblasts are mainly responsible for the synthesis of organic substances that make up the intercellular substance (collagen, glycosamine glycans, proteins). Osteocytes are the main cells of the tissue, they have an oval shape and a small amount of organelles. Osteoclasts are large cells with several nuclei.
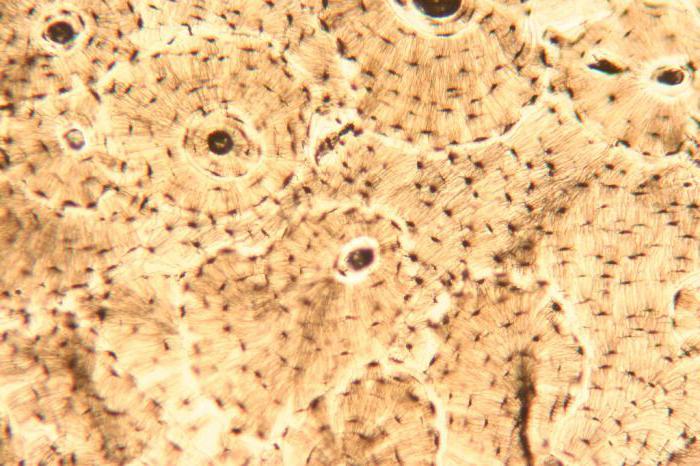
Cartilage is divided into several varieties. These are hyaline, fibrous and elastic cartilage. The main feature of this type of tissue is the presence of a large amount of collagen in the intercellular substance (about 70%). Hyaline cartilage covers the surface of the joints, forms the skeleton of the nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi, is part of the ribs, sternum. Fibrous cartilage can be found in intervertebral discs, as well as in places where tendons are attached to bones. Elastic forms the skeleton of the ear.
Blood
It has a huge amount of liquid intercellular substance called plasma. It is 90% water. The remaining 10% are organic (9%) and inorganic (1%) substances. The organic compounds that make up the blood are globulins, albumin and fibrinogen.
The cells of this tissue are called blood cells. They are divided into red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells. The former perform a transport function: they contain hemoglobin protein, which is able to carry oxygen. Platelets provide blood coagulation, and white blood cells are responsible for protecting the body from pathogens.