In pathological physiology, compliance with the dynamics of indicators in the field of morphology, biochemistry, and the functionality of the human body is considered the norm. All of them may vary depending on the quality of the environment. Under normal conditions, the biological system adapts perfectly to virtually any environment, which means its full viability.
The optimism of the working process of a biological type system means the maximum performance of protective functions with minimal energy consumption. The state of the body can always be determined on the basis of such an aspect as the rate of reactions.
The difference between the norm of reactions and pathology
The possible range of variability of genetic traits, which directly depends on the environment, is what the rate of reaction is. Pathology is considered a condition with an insufficient or excessive degree of response at the biological level. The rate of reactions may be different.
The difficulty in determining these concepts is the frequent variability of functional and metabolic indicators - this depends on the physical condition of the person. It is worth noting that during the development of the pathological process, damage and defense reactions always appear. There are times when these signs transform into each other.
Everyone knows that health is called a state of well-being from a physical, psychological and financial point of view, and not just the absence of illness or an external defect. Many tests and vaccinations allow an accurate assessment of the state of the human body. The reaction rate is an important component of diagnosis.
Why do we need a test of Pirke (Mantoux reaction)
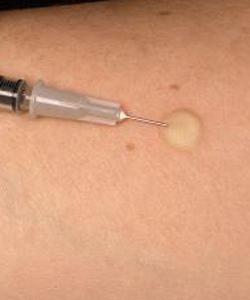
All children have a “button” immediately after the first year of life, then everyone goes through this procedure at school. A sample is taken to check the human body for the presence of tubercle bacillus. The Mantoux reaction is determined by the size of the inflammation at the injection site. On the skin immediately after the test you can see a slight irritation - this is a specific reaction to an injection of tuberculin. This process is caused by the protective actions of T-lymphocytes - it is these blood particles that are responsible for immunity at the cellular level. The essence of the test is that the introduced microbacteria act as a magnet for beneficial microorganisms, moving them closer to the skin. Most often, only lymphocytes that are “familiar” with the tuberculosis component of the vaccine respond to tuberculin. If the body contains Koch sticks, the reaction will be intense. Accordingly, in this case, the test has a positive result.
Test accuracy
Inflammation from the introduction of tuberculin is considered a type of allergic process. It is worth noting that a positive test result is not evidence of the presence of the disease - it is recommended to conduct more detailed studies, for example, fluorography and sputum culture. Only after receiving all the necessary data, doctors can identify the exact diagnosis.
The reaction rate in children and adults for the test of Pirke differs significantly in size. It is also important to note that the older generation rarely passes this test for tuberculosis.
Mantoux reaction: the norm in an adult
Before the appointment of the sample Pirke specialist conducts a preliminary examination. With the revealed signs of the disease, this procedure can be performed as an diagnosis for an adult, but most often specialists use x-rays.
A varied Mantoux reaction is possible. The norm in an adult is a papule, the size of which does not exceed 21 mm. The test is used to identify infected patients, but not patients. It is known that an adult can acquire tuberculosis with a constant Mantoux, therefore, fluorography is considered a more effective way to determine.
Heredity
Under the influence of the environment several factors can change. For a particular organism, a different rate of response of a sign is possible, but it never goes beyond the norm. For example, height, weight and physical strength may depend on a good diet, and rabbit color is inherited. In other words, organisms do not inherit certain qualities, but the ability to display certain properties in a variety of conditions. From one generation to another, the norm of the reaction of the attribute passes.
Modification Type Variability
A broad reaction rate is quantitative traits that are controlled by polygenes (weight, milk quality, skin pigmentation). The region of variability can be varied. A narrow reaction rate characterizes other properties and is modified very weakly (blood type or eye color).
Possible urine reaction
The main factor in the pathology is low or high acidity (pH). The norm of the urinary environment is observed when eating the right food. In this case, the reaction is considered neutral (pH = 7) or slightly acidic (pH varies from 5 to 7). These indicators are used to study adults and children who eat mixed foods. All breastfed babies who are breastfed have a neutral or alkaline reaction. Acidity is directly dependent on food. With an alkaline reaction, we can conclude about the consumption of a large number of vegetables, soda or bread. Increased acidity occurs after ingestion of protein and fatty foods, white bread, and also as a result of long abstinence from food. A different urine reaction is possible, the norm also changes.
Urine density
This moment is also of great importance during the examination. A person is considered healthy if the indicators range from 1003 to 1028 units. In this case, the acceptable reaction rate is values from 1001 to 1040. The changes are affected by proper nutrition and the use of sufficient water. The increase in indicators depends on the consumption of meat, potency, vomiting or diarrhea. A decrease in density may be due to vegetarianism.
The value of organic matter in urine
These microorganisms are characteristic of the variability of the norm. A general urinalysis gives doctors a complete picture of the required amount of organic substances. Most often, such components are identified as:
- protein;
- bilirubin;
- amount of glucose;
- urobilin;
- bile type acids (pigments);
- indican;
- ketone bodies.
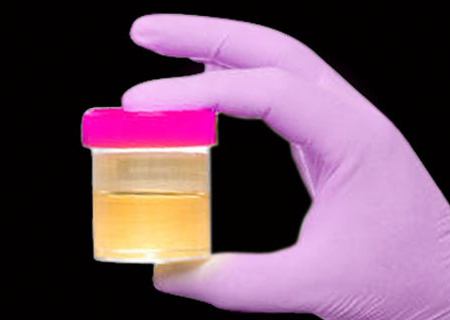
These biological elements can be defined in various ways. Today, most commonly used are automatic-looking analyzers and test strips. The first type is able to immediately indicate the concentration of biological substances, and the second method is used only for the purpose of screening determination and provides an answer in the form "there is / is no organic structure in the urine." The norm when taking a test in a healthy person can be protein (0.03 grams) or urobilinogen (6-10 micromoles per day). All other of the above substances in the urine are absent, otherwise this indicates the presence of the disease. There are always exceptions, for example, a heavy load, hypothermia or overheating, excessive emotions - all this easily provokes an increase in protein to 3-5 g, but also indicates that the urine reaction is normal. An increase in the level of this element can still be due to a large number of red blood cells, bacteria or white blood cells.
Sediment in urine
When the stage of determining the physical properties of the taken material and the presence of organic substances in it is completed, the liquid is worked out in a special centrifuge. The resulting precipitate is examined in a laboratory under a microscope. Such a process helps determine the exact amount of the following biological substances: white blood cells, red blood cells, cylinders, epithelium, crystals of salts, mucus, bacteria.
Information on organic matter in urine sediment
A general analysis gives a complete picture of the content of various elements in the body, by the amount of which it is easy to determine the presence of a particular disease.
White blood cells
The generally accepted norm of white blood cells in a healthy person is:
- 0-3 - in men;
- 0-5 - in women.
If in the analysis of urine there is a significant increase in the data of organic elements, we can safely state the presence of an inflammatory process in the human body.
Red blood cells
In the absence of disease, elements are not observed in the resulting pellet or unit cells are present. It is worth noting that there are pathological and physiological causes of the occurrence of these substances. The first option is associated with a disease of the genitourinary system. Physiological reasons are: excessive physical exertion; prolonged standing condition; taking sulfa drugs or anticoagulant drugs. Such options mean fluctuations in the norm and do not always indicate the presence of diseases.
Cylinders
These substances have the following types:
- hyaline;
- grainy;
- waxy;
- epithelial;
- leukocyte count;
- erythrocyte.
All of the above elements, in addition to the first, should be absent in the urinary sediment. Hyaline-type cylinders can occur in a healthy person under the influence of:
- cold water (shower, dousing, etc.);
- physical process;
- overvoltage;
- work at high temperatures (hot types of production, hot weather on the street).
In these cases, the detected substances are not considered pathologies, but are in the nature of ordinary fluctuations, in which case the concept of “reaction rate” also applies.
Epithelium
The norm in urinary sediment is the finding of single cells, usually this number is equal to three. The following types of biological substances are distinguished:
- flat urethral (genitourinary tract);
- transient, located in the kidneys, ureters and bladder;
- renal.
In the absence of elementary hygiene measures, a woman may experience an increased level of squamous epithelium. Most often, an increase in the number of cells indicates the presence of pathology. The occurrence of a kidney variety of epithelium may indicate a disease.
Slime
The normal content of mucus in healthy people is its complete absence. The appearance of an element means the presence of pathology in the organs of the urinary system.
Bacteria
In the urinary sediment of a healthy person, the norm is the absence of bacteria, the appearance of which is possible only during infectious and inflammatory processes in the reproductive system.
Salts in the analysis
The following types of biological substances are distinguished in urine sediment: oxalates, urates, trippelphosphates. The appearance of crystals in the analysis may depend on changes in the diet or on the acidity of the material taken, the amount of fluid used and much more. For example, a large amount of fresh tomatoes in food leads to the occurrence of oxalates in the urine. Frequent consumption of chocolate, wine (red) and meat leads to the appearance of urates. Some salt crystals precipitate only in an acidic environment, and there are elements that occur exclusively in alkaline. It follows that a change in acidity in the urinary environment is the starting point for the crystallization of salts. Prior to this, they were completely dissolved and were not identified in the analysis.
After reading this material, you can confidently answer the question of what is the reaction rate.