Humanity has always been attracted by secrets hidden from its gaze. From the vast expanses of the Universe to the deepest points of the oceans ... Modern technologies partially allow us to learn some of the secrets of the Earth, Water and Space. The more the curtain of secrets is opened, the more a person wants to know, because new knowledge raises questions. The largest, oldest and least studied Pacific Ocean is no exception. Its influence on the processes that occur on the planet is obvious: it is precisely this that provides the opportunity for a deeper and more thorough study. The average depth of the Pacific Ocean, the topography of the bottom, the direction of the currents, communication with the seas and other water bodies - everything is important for the optimal use by a person of his unlimited resources.
World Ocean
All biological species on Earth depend on water, it is the basis of life, so the importance of studying the hydrosphere in all its manifestations becomes a priority for humanity. In the process of generating this knowledge, much attention is paid to both fresh water sources and huge volumes of salty resources. The oceans are the main part of the hydrosphere, which occupies 94% of the earth's surface. The continents, islands and archipelagos share water spaces, which makes it possible to territorially designate them on the face of the planet. Since 1953, four oceans have been marked on the modern map of the world by the international hydrogeographic society : Atlantic, Indian, Arctic and Pacific. Each of them has corresponding coordinates and boundaries, which are conditional enough to move water flows. Relatively recently, a fifth was identified - the Southern Ocean. All of them differ significantly in occupied area, water volumes, depths and composition. More than 96% of the entire hydrosphere is salty ocean water, which moves in the vertical and horizontal directions and has its own global mechanism of metabolism, the creation and use of energy flows. In the life of modern man, the oceans plays a significant role: it forms the climatic conditions on the continents, provides an indispensable transport structure, gives people a lot of resources, including biological, and at the same time remains an ecosystem whose capabilities have not yet been fully explored.

Pacific Ocean
49.5% of the world's oceans and 53% of its water resources are occupied by the most ancient and mysterious part of it. The Pacific Ocean with the incoming seas has the greatest length of the water area: from north to south - 16 thousand km, from west to east - 19 thousand km. Most of it is located in the southern latitudes. The most significant are the digital expressions of quantitative characteristics: the volume of water mass is 710 million km 3 , the occupied area is almost 180 million km 3 . The average depth of the Pacific Ocean, according to various estimates, varies from 3900 to 4200 meters. The only continent that is not washed by its waters is Africa. More than 50 countries are located on its coast and islands, with all parts of the hydrosphere it has conditional borders and a constant exchange of flows. The number of cores located in the Pacific Ocean exceeds 10 thousand; they have different sizes and structure of formation. More than 30 seas are included in its water area (including inland), their area occupies 18% of the entire surface, the largest part is located on the west coast and washes Eurasia. The greatest depth of the Pacific Ocean, as well as the entire World, is in the Mariana Trench. Her research has been carried out for more than 100 years, and the more information about a deep-sea career comes in, the more interest it attracts from scientists around the world. The shallowest depths of the Pacific Ocean are observed in its coastal zones. They have been studied quite well, but, taking into account their constant use in human economic activity, the need for further scientific research is increasing.
Development history
The peoples inhabiting the Pacific coast on different continents knew a lot about its individual parts, but did not represent the full power and size of this body of water. The first European to see a small coastal bay was the Spaniard - the conquistador Vasco de Balboa, who for this overcame the high mountain ranges of the Isthmus of Panama. He took what he saw over the sea and called it Southern. That is why the discovery of the Pacific Ocean and the appropriation of its current name is the merit of Magellan, who was very lucky with the conditions in which he crossed his southern part. This name does not correspond at all to the true nature of this water giant, but it has taken root more than all the others that were offered as it was studied. Many expeditions followed in the footsteps of Magellan, the Pacific Ocean attracted new researchers with a lot of questions. The Dutch, English, Spaniards searched for ways of communication with the known lands and at the same time opened new ones. Everything was of interest to researchers: what is the greatest depth of the Pacific Ocean, the speed and direction of movement of water masses, salinity, flora and fauna of waters, etc. More accurate information was collected by scientists in the 19th-20th centuries, this is the period of the formation of oceanology as a science. But the first attempt to determine what is the depth of the Pacific Ocean was made by Magellan using hemp line. It was a failure - he could not get the bottom. A lot of time has passed since then, and today the results of measurements of the ocean depths can be seen on any map. Modern scientists use advanced technology and can with high probability indicate where the maximum depth of the Pacific Ocean is, where are the places with a lower level, and where are the shallows.
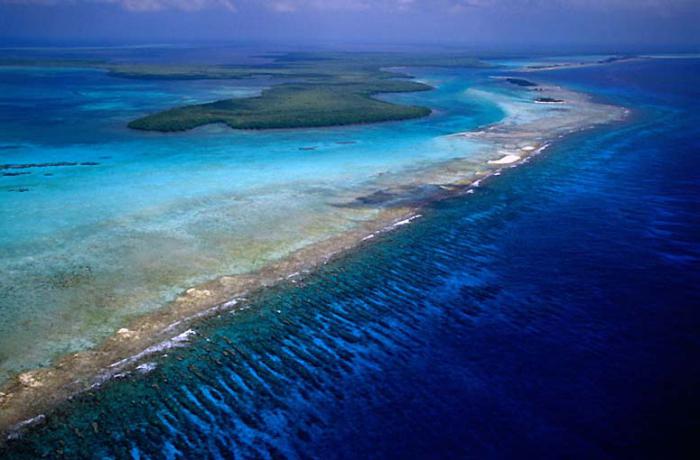

Bottom relief
More than 58% of the surface of the globe is occupied by the ocean bed. It has a diverse relief - these are large plains, high ridges and deep depressions. In percentage terms, the ocean bed can be divided as follows:
- Continental sandbank (depth from 0 to 200 meters) - 8%.
- Continental slopes (from 200 to 2500 meters) - 12%.
- Ocean bed (from 2500 to 6000 meters) - 77%.
- The maximum depths (from 6,000 to 11,000 meters) are 3%.
The ratio is quite approximate, measured 2/3 of the ocean floor, and the data of various research expeditions may vary due to the constant movement of tectonic plates. The accuracy of measuring instruments increases every year, information obtained earlier is adjusted. In any case, the greatest depth of the Pacific Ocean, its minimum value and average value depend on the topography of the ocean bed. The smallest depths, as a rule, are observed in the territory adjacent to the continents - this is the coastal part of the World Ocean. It can have a length of 0 to 500 meters, the average indicator varies within 68 meters.
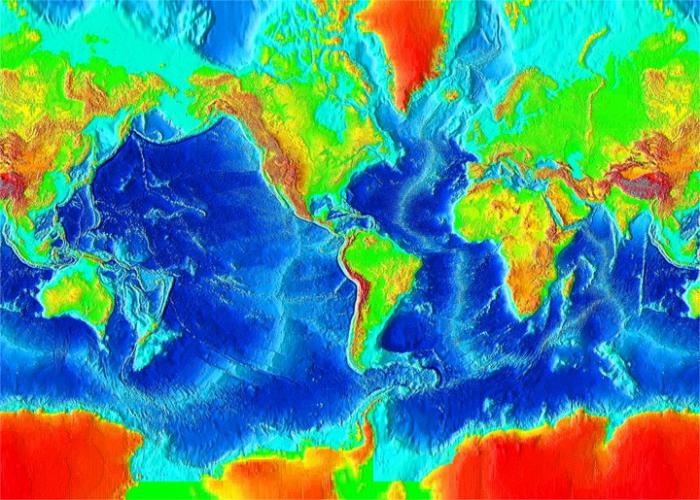
The continental bank is characterized by a slight slope, i.e., it is flat, with the exception of the coast, on which mountain ranges are located. In this case, the relief is quite diverse, troughs and cracks in the bottom can reach a depth of 400-500 meters. The minimum depth of the Pacific Ocean is less than 100 meters. The large reef and its lagoons with warm clear water provide a unique opportunity to see everything that happens at the bottom. The continental slopes also vary in angle of inclination and length - this depends on the location of the coastal region. Their typical structure has a smooth, gradually lowering relief or the presence of a deep canyon. They tried to explain this fact in two versions: tectonic and flooding of river valleys. The latter assumption is supported by soil samples from their bottom, which contains river pebbles and silt. These canyons are quite deep, due to their average depth of the Pacific Ocean is quite impressive. The bed is a more flat part of the relief with constant depth. Cracks, crevices and depressions at the bottom of the oceans are frequent, and the maximum value of their depths, as already mentioned, is observed in the Mariana Trench. The bottom relief of each locality is individual; it is fashionable to compare it with land landscapes.
Pacific relief features
The depths of the deeps in the Northern Hemisphere and a large part of the Southern (and this is more than 50% of the total ocean floor area) varies within 5000 meters. In the northwestern part of the ocean, a large number of depressions and cracks are located along the edge of the coastal zone, in the region of the continental slope. Almost all of them coincide with mountain ranges on land and have an oblong shape. This is characteristic of the coast of Chile, Mexico, and Peru, and the Aleutian Northern Depression, the Kuril and Kamchatka, also belong to this group. In the Southern Hemisphere, a hollow of 300 meters is located along the islands of Tonga and Kermadek. To find out how much the depth of the Pacific Ocean is on average, people used various measuring instruments, the development history of which is closely connected with research work on the water expanses of the planet.
Depth gauges

Lot is the most primitive means of measuring depth. This is a cable with a load at the end. This instrument is not suitable for measuring the sea and ocean depths, since the weight of the flat cable will exceed the mass of the cargo. Measurement results using the lot gave a distorted picture or did not bring results at all. An interesting fact: Peter 1 actually invented the Brook lot. His idea was that a load was attached to the cable, which popped up when it hit the bottom. This stopped the process of lowering the lot and made it possible to determine the depth. A more advanced depth gauge worked on the same principle. Its feature was the ability to capture part of the soil for further research. All these measuring devices have a significant drawback - the measurement time. To fix the value of a large depth, the cable must be lowered in stages for several hours, while the research vessel should stand in one place. Over the past 25 years, measurements have been carried out using an echo sounder, which operates on the principle of signal reflection. The operating time was reduced to a few seconds, while on the echogram you can view the types of bottom soils and detect sunken objects. To determine what the average depth of the Pacific Ocean, it is necessary to make a large number of measurements, which are then summed up, as a result, the delta is calculated.
History of measurements

The 19th century is the golden one for oceanography in general and the Pacific Ocean in particular. The first expeditions of Kruzenshtern and Lisyansky set as their goal not only the measurement of depths, but also the determination of temperatures, pressure, density and salinity of water. 1823-1826: taking part in the research work of O. E. Kotzebue, physicist E. Lenz applied the bathometer he created. The year 1820 was marked by the discovery of Antarctica, the expedition of sailors F.F. Bellingshausen and M.P. Lazarev explored the northern seas of the Pacific Ocean. At the end of the 20th century (1972-1976), the English ship Challenger conducted a comprehensive oceanological study, which provided most of the information used to date. Since 1873, the United States, with the help of the navy, measured the depths and fixed the relief of the bottom of the Pacific Ocean for laying a telephone cable. The 20th century was marked by a technological breakthrough of all mankind, which greatly affected the work of researchers of the Pacific Ocean, who asked a lot of questions. Swedish, British and Danish expeditions went around the world to explore the largest body of water on our planet. How much depth of the Pacific Ocean is in the maximum and minimum value? Where are these points located? What underwater or surface currents affect them? What caused them to form? The bottom was studied for a long time. From 1949 to 1957, the crew of the Vityaz research ship put a lot of relief elements on the map of the Pacific bottom and tracked its course. Other vessels continued their shift, which constantly cruised in the water to obtain the most accurate and timely information. In 1957, scientists from the Vityaz vessel determined the point at which the largest depth of the Pacific Ocean is observed - the Mariana Trench. Until today, its bowels are carefully studied not only by oceanologists, but also by biologists, for whom a lot of interesting things were also found.
Mariana Trench
The gutter stretched for 1,500 meters along the islands of the same name in the western part of the Pacific coast. It looks like a wedge and has various depths throughout the area. The history of occurrence is associated with the tectonic activity of this part of the Pacific Ocean. In this segment, the Pacific plate gradually goes under the Philippine plate , moving 2-3 cm a year. At this point, the depth of the Pacific Ocean is maximum, and the World also. Measurements are carried out for hundreds of years, and each time their values are adjusted. A 2011 study provides the most surprising result, which may not be final. The deepest point of the Mariana Trench is the Challenger Abyss: the bottom is 10,994 m below sea level. For her research, a bathyscaphe was used, equipped with cameras and devices for soil collection.
What is the depth of the Pacific Ocean?
There is no definite answer to this question: the bottom topography is so complex and not fully understood that each named figure can be corrected in the near future. The average depth of the Pacific Ocean is 4000 meters, the smallest - less than 100 meters, the famous "Challenger Abyss" is characterized by impressive numbers - almost 11,000 meters! Along the mainland there are a number of depressions that also strike with their depths, for example: the Vityaz 3 Depression (Tonga Trench, 10,882 meters); Argo (9165, Northern Novogebridsky Trench); Cape Johnson (Philippine Trench, 10,497), etc. The Pacific Ocean has the largest number of the deepest points in the oceans. Modern oceanologists expect a lot of interesting work and amazing discoveries.
Flora and fauna
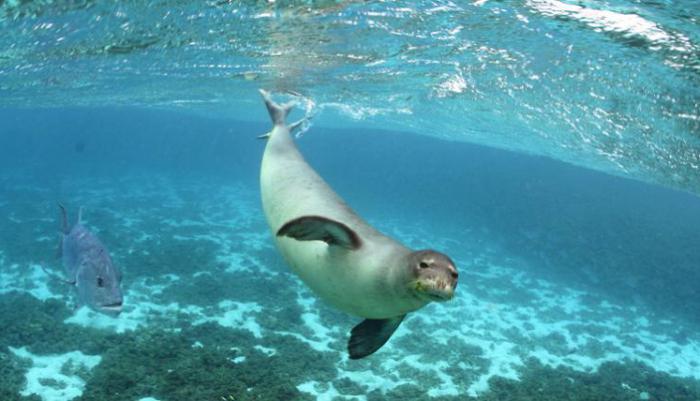

Noteworthy for researchers is the fact that even at a maximum depth of 11,000 meters, biological activity was found: tiny microorganisms survive without light, while being subjected to the monstrous pressure of many tons of water. The vast expanses of the Pacific Ocean are an ideal habitat for many species of animals and plants. What is confirmed by facts and specific figures. More than 50% of the biomass of the oceans lives in the Pacific, the diversity of species is due to the fact that huge bodies of water are found in all zones of the planet. Tropical and subtropical latitudes are more densely populated, but the northern borders are not empty either. A characteristic feature of the fauna of the Pacific Ocean is endemism. Here are the habitats of the most ancient animals of the planet, endangered species (sea lion, sea otter). Coral reefs are one of the wonders of nature, and the wealth of flora and fauna attracts not only a lot of tourists, but also a large number of researchers. The Pacific Ocean is the greatest and most powerful. The task of people is to study it and understand all the processes taking place in it, which will help reduce the degree of harm caused by humans to this unique ecosystem.