The intestines are one of the largest organs. Its length is about 4 meters. This organ is part of the digestive tract. The intestine occupies most of the abdominal cavity. It originates from the pylorus and ends with the anus. The small and large intestines are isolated . The first is involved in the digestion of nutrients. The second - in the formation of feces and their removal from the body. In most cases, the colon is exposed to medical manipulations. This is due to the fact that it is more prone to trauma and inflammatory processes.
Therefore, operations on the colon are performed more often. In addition to inflammatory diseases, there is a high risk of the formation of oncological processes and benign tumors in this organ. There are many diseases of the large intestine requiring surgical treatment. If the lesion has a small extent, an organ resection or removal of the formation itself (for example, a polyp) is performed. Surgery for colon cancer involves hemicolectomy. In such cases, half the organ is resected. Naturally, such interventions require rehabilitation measures and lifestyle changes.
Symptoms of colon pathologies
Colon diseases are common among both adults and children. Many of these ailments are related to surgical pathologies. The most common and harmless disease that occurs most often is considered appendicitis. It relates to acute inflammatory processes of a part of the colon. It is difficult to detect the disease at an early stage. Appendicitis can be masked by poisoning, exacerbation of gastritis or pyelonephritis (with an atypical location).
In addition to pain, an indisputable indication for surgery is bowel obstruction. It develops in various pathological conditions. Regardless of the cause, all diseases accompanied by obstruction require colon surgery. In addition to severe pain, this syndrome is accompanied by constipation and vomiting.
The main function of the large intestine is the removal of decay products from the body. 5 anatomical parts are distinguished. The first is the cecum. It is located in the right iliac region. It is from this anatomical structure that the appendix, the appendix, departs. The second part is the ascending colon, followed by the transverse and descending. They can be palpated in the lateral abdomen and at the level of the navel. The final section is the sigmoid colon, which passes into the next section of the digestive tract.
Damage can occur in any part of the body. Regardless of this, in case of damage, surgery is performed on the colon. Oncology is more common in the descending and sigmoid regions. A characteristic symptom of a tumor is obstruction of feces and intoxication of the body. Cancer of the right half of the large intestine differs in the clinic. The main symptom of the disease is anemic syndrome.
Indications for surgical treatment
In different age groups, indications for operations on the colon are similar. Nevertheless, certain pathologies predominate in children. Among them - megacolon, Hirschsprung's disease and cystic fibrosis, intussusception. Also, congenital atresia in any part of the organ and diverticulosis are referred to the causes of intestinal obstruction. Hirschsprung's disease is characterized by a violation of innervation. Cystic fibrosis is a rare genetic pathology accompanied by increased secretion of mucus. All of these ailments lead to disruption of the intestines. Due to the fact that stool can not move to the outlet, they stagnate and obstruction.
Indications for surgical intervention in adults are as follows:
- Appendicitis.
- Diverticulitis.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn's disease.
- Acute violation of mesenteric circulation.
- Benign formations.
- Bowel cancer.
All of these diseases are dangerous, as they lead to inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) and obstruction. Without surgical help, such violations are irreversible and lethal. Therefore, each of the pathologies is an absolute indication for operations on the colon.
Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the appendix, associated with hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissue. In the first hours, the disease resembles ordinary poisoning, after which the patient's condition worsens. The pain passes to the right half of the abdomen, the temperature and nausea increase. Only a surgeon can diagnose a pathology according to special symptoms and a blood test.
Intestinal diverticula are branches of the mucous membrane in which incompletely digested food or feces accumulate (depending on location). Due to the constant stagnation of decay products, inflammation develops, and sometimes an oncological process. To prevent this from happening, diverticula are removed.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are systemic pathologies that affect the entire digestive tract. They require prolonged therapeutic treatment and observation. Surgery is required if complications or drug inefficiencies develop. The volume of surgery depends on the prevalence of the affected area of the intestine. Sometimes it is limited to suturing the ulcer. In severe cases, a bowel resection is necessary.
Disruption of mesenteric circulation develops due to the ingress of a blood clot into large vessels. This is accompanied by necrosis of the intestinal tract. A similar state of danger is equated to a heart attack and stroke. It requires immediate colon removal surgery. If the resection of the affected area is not completed on time and blood circulation is not restored, bacterial shock and sepsis occurs.
Colon cancer: surgery, prognosis for life
Oncology studies not only cancers, but also benign tumors. Unfortunately, such pathologies often affect the colon. According to statistics, cancer of this organ is one of the first places. Only malignant processes of the mammary gland, skin, lungs and stomach give way to him. According to the histological structure, carcinoma of the large intestine is most often found. The lower the level of differentiation of cancer cells, the neoplasm is more malignant and more difficult to treat. All oncological processes are an indication for surgery. The prognosis for such pathologies depends on the prevalence of the tumor and the degree of differentiation.
Benign polyp is a colon polyp. Operations with this pathology are required. After all, most polyps can transform into carcinoma. If a benign tumor is removed on time, the prognosis for life is favorable. When cancer is detected, surgery is performed to remove the colon. In most cases, you have to resort to resection of half of the organ. Such an intervention refers to radical operations. It is called hemicolectomy. If the lesion is small, remove a smaller part of the intestine, including the tumor itself and 40 cm of healthy tissue. This is necessary to prevent recurrence of carcinoma.
If there are no metastatic tumors in other organs, radical surgery for colon cancer helps not only save the patient's life, but also significantly extend it. Launched carcinoma in most cases is considered a contraindication for surgical treatment. With a large oncological process and germination in neighboring organs, palliative removal of a colon tumor is performed. The operation helps to restore the digestive process and relieve the patient from torment. The prognosis for such interventions is unfavorable. Due to the presence of a residue of malignant cells in the body, the tumor continues to grow.
Varieties of surgical treatment
There are several types of operations on the large intestine. The choice of surgical treatment method depends on the nature of the pathology and the extent of the lesion. In addition, doctors pay attention to the general condition of the patient and the presence of concomitant ailments. Severe pathologies of the vascular system, heart, kidneys and other organs are a contraindication for massive surgical interventions.
If the disease is not cancer, the doctor does everything possible to save the gut. This can be done in the presence of small ulcerative defects and benign tumors. In such cases, suturing of the defect or polypectomy is performed. Such operations often do not require an anterior abdominal wall incision. They are carried out by the endoscopic method, often during an examination of the intestine. The presence of a purulent inflammatory process is an indication for surgical treatment. The most common of these operations is considered appendectomy.
Indications for radical surgical treatment are obligate polyps, acute violation of mesenteric circulation, common ulcers and non-metastatic colon adenocarcinoma. The operation consists in the removal of the affected area and the adjacent healthy tissues. Radical surgery includes bowel resection and hemicolectomy.
In the presence of metastases and a serious condition of the patient, palliative treatment is performed. The main indication is a colon tumor. The operation is non-radical in nature, as it does not allow to remove the entire carcinoma. It consists in resection of most of the malignant process and suturing of the intestine. Thus, it is possible to eliminate the block that caused the obstruction. The distal end of the intestine is sutured tightly, and a stoma is formed from the proximal part. An unnatural opening is led to the anterior abdominal wall. If after a few months the patient’s condition allows for massive abdominal surgery and the tumor does not progress, the colostomy is removed by lowering the stump and stitching with the rectum. This stage of surgery is carried out only in the absence of metastases.
Colon polyp removal
A polyp is a small outgrowth on the surface of the intestinal mucosa. In oncology, 2 varieties of these benign formations are distinguished. The first is optional precancers. Similar polyps rarely transform into adenocarcinoma. The likelihood of malignant degeneration increases if a person is exposed to adverse factors (smoking, malnutrition, radiation). If the risk of developing cancer is small, perform an endoscopic surgery to remove the colon polyp, which is carried out using a special camera and a coagulation loop. It is a beam of electric current. The coagulator not only quickly removes small mushroom-like polyps, but also stops bleeding at the site of damage.
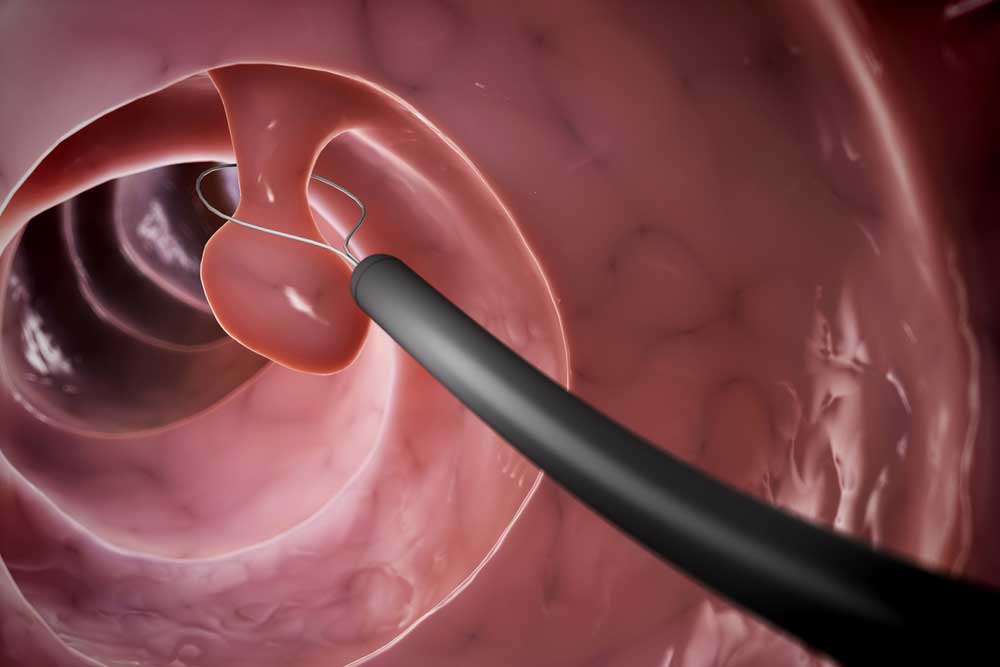
In some cases, benign formations are impressive in size and have a broad base. This may be an adenomatous or villous polyp of the colon. In this case, operations are performed both by the endoscopic method and by open surgery. Large polyps are removed in a fragmented manner. Using a special coagulator, a diametrical loop is created. It captures the neoplasm and splits off its fragments. In the presence of multiple polyposis, a bowel resection is recommended. Adenomatous and villous formations are referred to as obligate precancers, since the likelihood of their malignancy is high. All polyps should undergo morphological examination.
Preparation for colon removal
Intestinal resection and hemicolectomy are major surgical interventions that require special preparation. Such surgical treatment can be carried out only in the absence of cardiovascular diseases, as well as pathologies of the hematopoietic system and renal failure. In addition, the patient must understand the essence of the upcoming intervention and possible complications. The patient himself and his relatives should know that after surgery on the colon, rehabilitation and lifestyle changes, in particular nutrition, are required.
Before performing surgical treatment, a series of tests are performed. In addition to standard laboratory tests, ECG and colonoscopy, a consultation with a cardiologist and therapist are required. The patient must donate blood for HIV and parenteral viral hepatitis. On the eve of surgery, a complete bowel cleansing is performed. For this purpose, cleansing enemas or taking the drug "Fortrans" are performed. It is diluted in 3-4 liters of water and begin to drink the day before the operation.
Anesthesia is selected individually for each patient. During abdominal surgery, general anesthesia is required. Often used combined anesthesia. It consists of intravenous and endotracheal anesthesia. To monitor the state of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, the patient is connected to the apparatus. Access to the central vein is required to prevent complications. The patient's condition during the operation is monitored by an anesthesiologist and nursing staff. If necessary, hypotensive and other drugs are administered.
Bowel cancer surgery technique
Some foreign doctors practice laparoscopic bowel resection and hemicolectomy. This avoids a large scar on the stomach. However, such a technique is not welcome during large operations, as there is a high risk of bleeding in the abdominal cavity. In addition, small laparoscopic openings restrict access to the tumor. Thus, metastatic lymph nodes can be skipped.
Bowel resection begins with an incision on the anterior abdominal wall and dissection of all layers of underlying tissues. Then the surgeon mobilizes the affected area and estimates the extent of the lesion. If the tumor is small, it is resected with the capture of healthy tissue (20-40 cm). With colon cancer of the 2-3rd stage, hemicolectomy is most often performed. This operation is different from volume resection. By hemicolectomy is meant the removal of the left or right half of the large intestine. After the affected area is resected, an anastomosis is formed. This is the most critical part of surgical treatment. Anastomosis should be strong and, if possible, preserve the anatomy of the organ. After its formation, the tissue is sutured in layers.
Possible complications of surgical treatment
One of the serious oncological diseases requiring surgical treatment is colon cancer. After surgery, there is a risk of complications. Even despite the professionalism of doctors, it is not always possible to carry out the intended treatment for oncology. In some cases, metastases are detected that were not visible during the examination. In this case, it is necessary to expand the scope of treatment or completely cancel the operation. Possible consequences of surgery include:
- Bleeding.
- Microbial infection.
- Herniation.
The most dangerous complication is bleeding and the failure of the anastomosis, which develops as a result of infection of the wound. Each of these effects requires repeated surgery to find a source of bleeding. When wounds are infected, the anastomosis must be re-formed. Delayed complications include adhesions and the appearance of a hernia.
Condition after colon surgery
The patient should spend the first day after removal of part of the intestine in the intensive care unit. After the patient departs from anesthesia and begins to breathe on his own, he is transferred to the ward. Parenteral nutrition is carried out for 2-3 days. Then, if there are no signs of complication and the patient's condition allows, he is allowed to drink low-fat broth and water. Within 10-12 days, the condition of the patient should be monitored by doctors. , . 2 , " ". , 95 %. , . 5- . 90 %. , 1,5-2 . .
Subject to the regimen and all the doctor’s prescriptions, the digestion process is almost completely restored even after hemicolectomy. It is worth noting that the functions of the large intestine are violated. Therefore, the diet should restore losses. Food should be fractional - 6-7 times a day. Due to disruption of the digestive tract, the intestines cannot be overloaded. Food should be easily digestible, contain vegetable protein, lean meat, butter. To make up for losses, vitamins, minerals, enzymes and water are required.