Vietnam, located on the famous Indochina Peninsula, is widely known throughout the world not only for its sad pages of history, but also for its relatively inexpensive and extremely attractive resorts. Friendly smiling people, ancient history and extremely exotic cuisine - all this and much more can be found in this hot tropical country. Vietnam's unique geographical location affects all forms of its social and economic life. We will try to consider this effect in more detail in this article.
Geographical location of Vietnam (briefly)
As already mentioned above, the country is located on the Indochina Peninsula, and more precisely - on its southeastern tip. On the east side, Vietnam is washed by the South China Sea.
The economic and geographical position of Vietnam is quite favorable: on the western side, the country borders on such states as Cambodia, Laos and China (People's Republic of China). This allows the state to successfully trade with these countries. The longest joint border is with Laos (more than 1.5 thousand kilometers), a slightly less long border is with China (almost 1.3 thousand kilometers), and Cambodia (0.98 thousand kilometers) is in third place. The total area of the state is 329.6 thousand square kilometers.
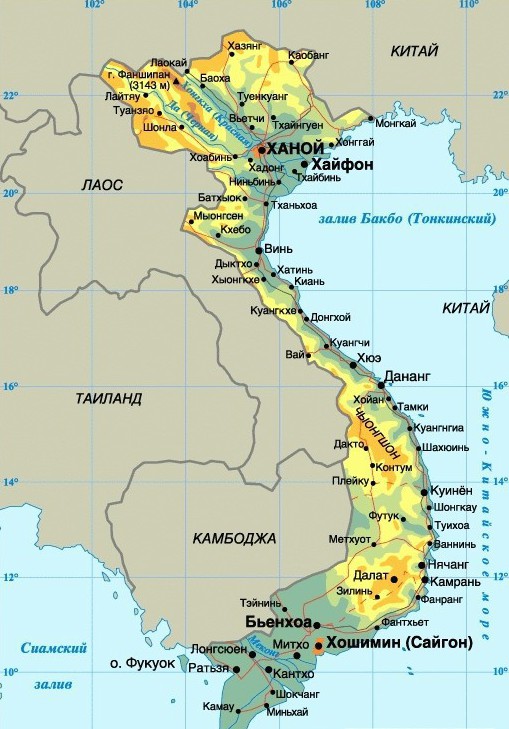
The geographical position of Vietnam is pronounced elongated meridian character. The state stretches along a narrow strip along the 105 meridian, repeating the eastern and southern parts of the bends of the western coast of the East China Sea, including the Vietnamese part of the Siamese and Tonkin bays. In the north, the country begins from the source of the Lo River - the left tributary of the Krasnaya River, and in the south ends with the Kamau Peninsula and the cape of the same name.
The second main feature of the geographical position of Vietnam is the record-long coastline of the sea compared to the area, which has a powerful effect on the country's climate.
Relief
In the very south of the country lies a huge plain irrigated by the waters of the Mekong (there is a river delta before it flows into the South China Sea). To the north lies the ridge of the Annam Mountains, in parallel with which, closer to the sea, the coastal lowland stretches. Further north is the high Yunnan Highlands, in the area of which you can find the highest point of Vietnam - Mount Fanshi-Pan (3.143 kilometers high). The Yunnan Highlands are cut by the channel of the second largest river, the Red (Hongha).
The state includes many islands, the largest of which is about. Phu Quoc, located in the Gulf of Thailand west of the Kau Peninsula and south of Cambodia.
Climate
The geographical position of Vietnam on the mainland determines its climate. Studying the weather features, it is worth mentioning the three climatic parts of the country - the North, South and Middle, which are very different. Such features of the geographical position of the country of Vietnam, such as a large elongation in the meridian direction and the alternation of hills and lowlands, have led to a huge variety of climatic conditions.
So, if the northern part of the country has a fairly pronounced winter period (winter is very mild), then in its southern part we can already talk about the rainy season in winter and the drought season in summer. In the mountainous region of Vietnam, the average temperature does not exceed +20 ° C. In general, its average annual temperature is +22 ... + 27 ° C.
Agriculture
Along with tourism, agriculture is one of the leading sectors of the Vietnamese economy. This is greatly facilitated by the favorable agro-geographical position of Vietnam. Relative proximity to the equator (the main part of the country is located between the 10th and 20th parallels); high humidity due to the proximity of the sea and two large rivers (Mekong River and Krasnaya River) and a large number of sunny days - all this allows the country's farmers to collect several crops a year.
Of course, first of all it concerns rice so adored by the local population, along with seafood being the basis of their diet. In all areas of the country you can see rice fields flooded with water, and in the mountainous areas they are laid out in beautiful rows - this is one of the attractions of the state.
Tourism
The geographical position of Vietnam and its climatic diversity make the country attractive to almost any tourist. Tourists who prefer cooler weather choose the northern and mountainous parts of the country; lovers of hotter conditions - southern and flat.
No matter how the weather is, the Vietnamese cuisine is unlikely to leave anyone indifferent. The number of national dishes includes more than five hundred diverse exotic dishes. A huge number of meat dishes (including those from the most unusual “varieties” of meat, for example, from a viper or young crocodile) are adjacent to the original culinary products of a very different kind, taste and smell. But the basis of the national cuisine of local peoples, of course, is rice in all forms. It is added almost everywhere and almost always.
Flora
Despite the fact that the country is quite densely populated, in the northern mountains of Vietnam you can still see almost untouched nature reserves of nature. A third of the territory is covered with impenetrable thickets of the jungle - all this under the generous tropical sun and in conditions of high humidity!
It is not surprising that the nature of Vietnam has gained enormous species diversity. Only tree species, there are more than a thousand. Of the most valuable species, one can cite an example of an iron tree, named after an amazing fortress similar to iron), cinnamon, mahogany, ebony and many others. The country's forests are characterized by pronounced altitudinal zonation. Subtropical species grow at heights of up to a thousand and a half thousand meters; an amazing variety of conifers is observed above two thousand.
Fauna
The fauna of Vietnam in wealth and diversity does not lag behind the flora. In the jungle of the country, there are about 1000 species of birds, about 300 reptiles, approximately 170 mammal species. The rivers, in which there are more than a thousand species of ichthyofauna (fish) alone, are not inferior to the jungle!
Of the most common inhabitants of the jungle can be called such as monkeys, parrots, wild pigeons, deer, wild boars, panthers, wolves, pheasants, bears. A careless traveler can also meet the owner of the jungle - a magnificent tiger, although the latter are wary of people and try to stay away from human paths. Some time ago, even rhinos lived in the jungle, but nowadays, unfortunately, they are practically exterminated.
In addition to rhinoceroses, about 80 species of mammals and birds, including sika deer, tapirs, peacocks, gibbons, and many others, are among the endangered species.